Top Breathing Exercises for Anxiety Available on YouTube
Understanding the Box Breathing Technique
Box breathing, sometimes called square breathing, is a straightforward yet remarkably effective method for regulating your breath and soothing your nervous system. The process includes inhaling, holding your breath, exhaling, and holding once more, each for an equal length of time. This steady rhythm fosters a feeling of control and steadiness, counteracting anxiety's physical effects. Slowing your breathing can lower your heart rate and blood pressure, encouraging relaxation. Many consider it a cornerstone practice for handling anxiety and panic episodes.
Therapists frequently employ this approach because it delivers quick relief. The structured pattern of box breathing focuses the mind, creating distance from anxious thoughts and helping you regain balance during stressful moments. For those looking to manage anxiety, this technique proves invaluable.
How to Practice Box Breathing
To begin box breathing, settle into a comfortable seated or lying position. Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose, noticing your stomach rise as your lungs fill. Hold for four seconds. Exhale fully through your mouth, feeling your stomach fall as air leaves your lungs. Hold again for four seconds. Repeat this sequence for several minutes, keeping each phase equal in duration. Maintaining this ratio is essential for optimal results.
Benefits of Box Breathing for Anxiety
Box breathing provides numerous advantages for anxiety management. It calms the sympathetic nervous system, which triggers stress responses. By slowing your breath, you reduce stress hormones like cortisol, alleviating anxiety and panic. This controlled breathing also sharpens focus, clearing mental clutter tied to anxiety. Regular practice builds resilience against anxiety triggers and cultivates everyday calm.
This method is especially helpful for symptoms like racing thoughts, rapid heartbeat, and breathlessness. Concentrating on your breath's rhythm grounds you in the present, easing anxious mental chatter.
Integrating Box Breathing into Your Daily Routine
Incorporating box breathing into daily life enhances its anxiety-relieving effects. Start with brief sessions, gradually extending them as you grow more at ease. Use it during stressful moments or as part of morning/evening rituals. Choose a quiet space to focus without distractions. Consistency is crucial—the more you practice, the more effective it becomes. It complements other anxiety-management strategies well.
Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana): A Traditional Technique for Inner Peace
Benefits of Alternate Nostril Breathing
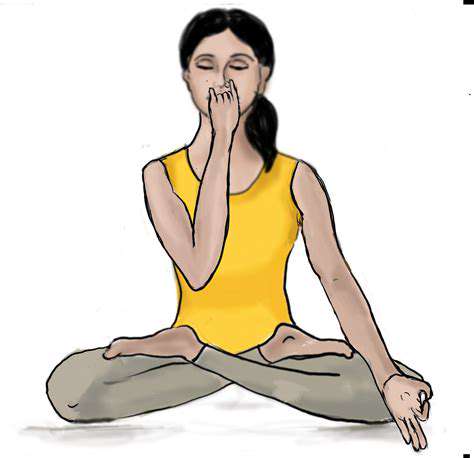
Alternate nostril breathing, or Nadi Shodhana Pranayama, is a time-honored yogic practice with profound benefits for body and mind. Rooted in Ayurveda, this technique harmonizes the body's energies, fostering tranquility and mental clarity. It regulates the nervous system, eases stress and anxiety, and deepens self-awareness.
The alternating breath flow through each nostril cultivates mindfulness, quieting racing thoughts and enhancing focus. It also boosts concentration and memory, making it ideal for cognitive enhancement.
The Technique of Alternate Nostril Breathing
Nadi Shodhana follows a precise breath sequence. Sit comfortably with a straight spine, eyes softly closed. Rest your right hand on your right knee and left hand on your left knee. Gently close your right nostril with your right thumb. Inhale deeply through your left nostril. Close the left nostril with your ring and pinky fingers, then exhale through the right nostril. Repeat, inhaling left and exhaling right, maintaining a smooth rhythm. Regular practice yields deep relaxation and well-being. This exercise is remarkably potent.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While safe for most, alternate nostril breathing requires mindfulness. Adjust the practice to your needs and limitations. Those with high blood pressure or respiratory issues should consult a doctor first. Discontinue if discomfort arises. Begin with short sessions, increasing duration gradually. Stay gentle and attentive throughout. Always heed your body's signals.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation with Breathing: A Holistic Approach

Understanding Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) reduces stress by systematically tensing and relaxing muscle groups. This method identifies and releases tension linked to mental stress. Focusing on tension and relaxation sensations helps manage physical stress responses. This awareness is key for developing coping strategies.
PMR targets individual muscle groups, calming mind and body. Many describe it as mindfulness, as it emphasizes present-moment awareness.
Preparing for Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Choose a quiet, comfortable space free from interruptions. Sit or lie down comfortably, wearing loose clothing. A serene environment maximizes relaxation benefits.
Tensing and Relaxing Muscle Groups
PMR's core involves tensing specific muscles briefly, then releasing, noting the shift from tension to relaxation. This builds mind-body connection. This tension-release cycle is central to relaxation. It heightens bodily awareness.
The Role of Breathing in PMR
Deep, controlled breathing complements PMR by calming the nervous system and deepening relaxation. Breath focus enhances the technique's effectiveness.
Benefits of Progressive Muscle Relaxation
PMR lowers stress and anxiety, improves sleep, and sharpens focus. Regular practice reduces muscle tension and fosters mental peace. It also decreases blood pressure and heart rate.
Practical Application and Practice
Start with short PMR sessions, gradually lengthening them. Consistency helps manage stress responses. Use it during anxious moments or as daily practice. Daily PMR cultivates lasting calm and well-being.
Finding Resources and Support
Guided PMR resources include books, websites, and apps. For personalized advice, consult a healthcare provider or therapist, especially with health concerns. Professional input can customize the practice.