Coping Strategies for Social Anxiety Attacks
Catalog
Pinpointing social anxiety triggers forms the foundation of successful management strategies.
Enhanced self-awareness illuminates emotional patterns in anxiety-provoking scenarios.
Cognitive restructuring through therapy demonstrates measurable symptom reduction.
Community connections offer validation and practical coping insights.
Systematic exposure builds resilience through incremental challenges.
Daily stress-reduction habits create cumulative mental health benefits.
Controlled breathing patterns directly influence physiological stress responses.
Consistent mindfulness routines rewire automatic anxiety reactions.
Holistic lifestyle adjustments amplify breathwork effectiveness.
Progress documentation enables personalized strategy refinement.
Expert-guided exposure accelerates therapeutic outcomes.
Professional intervention becomes crucial when anxiety impedes functionality.
Persistent strategy application cultivates social self-assurance.
Targeted affirmations reshape neural pathways related to self-perception.
Effective declarations use vivid present-tense phrasing.
Progress metrics validate affirmation efficacy over time.
Initial affirmation resistance diminishes through regular practice.
Shared affirmation practices strengthen communal support systems.
Recognizing Triggers and Developing Awareness
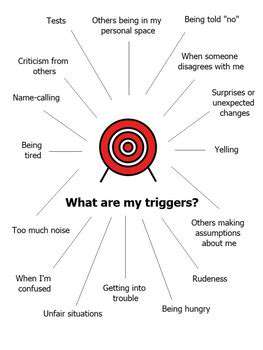
Understanding Social Anxiety Triggers
While some find casual conversations effortless, those with social anxiety often experience visceral reactions to routine interactions. Public speaking engagements and unfamiliar social environments frequently trigger disproportionate distress, creating physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat and cognitive distortions about social judgment. Recognizing these unique response patterns enables targeted intervention strategies.
Recent data from the National Institute of Mental Health reveals that 7% of adults experience clinically significant social anxiety annually. This prevalence underscores the importance of personalized trigger identification rather than relying on generic solutions.
Developing Self-Awareness Techniques
- Grounding exercises using sensory awareness techniques
- Emotion tracking through time-stamped journal entries
- Simulated social scenarios with progressive difficulty levels
Cultivating moment-to-moment awareness helps disrupt automatic anxiety cycles. Sensory-focused mindfulness practices create cognitive distance from distressing thoughts, while structured self-reflection identifies subtle trigger patterns often overlooked. Many find that combining these approaches yields deeper insights than isolated techniques.
The Role of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
This evidence-based approach transforms how individuals interpret social cues. Through systematic tracking of thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, patients learn to challenge catastrophic predictions. A typical session might involve analyzing a recent anxiety episode to identify distorted thinking patterns and develop balanced alternatives.
Clinical trials show CBT produces lasting improvements for 60-80% of adherent participants. The modality's strength lies in its adaptability - therapists can tailor exercises to address specific workplace, academic, or personal social challenges.
Utilizing Support Networks
Human connection serves as both buffer and mirror for social anxiety struggles. Disclosing vulnerabilities within trusted relationships often reduces their emotional intensity, while peer support groups provide real-world coping models. Digital platforms now offer 24/7 access to specialized communities, though in-person groups remain valuable for practicing interpersonal skills.
Emerging research highlights the particular effectiveness of skill-building groups that combine support with structured exercises. These hybrid models help translate emotional validation into concrete behavioral changes.
Gradual Exposure to Anxiety-Inducing Situations
The exposure process resembles muscle training - consistent, incremental challenges build emotional resilience. A person fearing restaurant interactions might progress from visualizing meals to ordering takeout, then dining during off-peak hours. Each successful experience becomes a reference point for future challenges.
Neuroscience research confirms that repeated positive exposures strengthen prefrontal regulation of amygdala responses. This biological change makes previously overwhelming situations feel manageable through practiced coping strategies.
Maintaining Regular Stress-Relief Practices
Consistent self-care routines act as anxiety circuit-breakers. While yoga and nature immersion help many, some discover unexpected benefits through creative outlets like pottery or drumming. Rhythmic physical activities particularly effective for discharging nervous energy, while creative pursuits engage different neural networks than verbal processing.
Emerging studies emphasize circadian rhythm alignment - maintaining consistent sleep/wake cycles enhances emotional regulation capacity. When combined with nutritional support for neurotransmitter production, these biological foundations amplify other therapeutic efforts.
Breathing Techniques and Mindfulness Practices
Understanding the Physiology of Breathing
Breath patterns directly communicate with the body's survival mechanisms. Shallow chest breathing triggers fight-or-flight responses, while diaphragmatic breaths stimulate parasympathetic nervous system activation. This biological lever explains why controlled breathing remains one of the most accessible anxiety management tools.
University of Michigan research demonstrates that six weeks of breath training can reduce anxiety sensitivity by 40%. Participants reported decreased catastrophic thinking about physical anxiety symptoms after mastering basic techniques.
Practical Breathing Techniques for Anxiety Management
The physiological sigh - two quick inhales followed by a prolonged exhale - offers rapid relief during acute anxiety. This pattern, recently popularized by Stanford neuroscientists, quickly balances oxygen and carbon dioxide levels to counteract hyperventilation.
Alternate nostril breathing (nadi shodhana) provides another option, particularly effective before anticipated stressors. This yogic technique synchronizes brain hemispheres while requiring focused attention that displaces anxious thoughts.
Merging Mindfulness with Breathing Techniques
Mindful breathing transforms a biological function into a meditation anchor. Noticing the coolness of inhalation versus warmth of exhalation creates sensory focus points. When anxious thoughts arise, practitioners learn to acknowledge them like passing clouds rather than engaging their content.
Harvard neuroimaging studies reveal that eight weeks of this practice thickens prefrontal cortex regions involved in emotional regulation. These structural changes correlate with reduced social anxiety symptoms and improved stress recovery times.
Creating a Routine for Consistent Practice
Habit-stacking proves effective for maintaining practice consistency. Pairing breathwork with existing routines - like morning coffee preparation or evening tooth-brushing - leverages established neural pathways. Many find that brief sessions (3-5 minutes) done multiple times daily yield better results than single extended practices.
Behavioral economists suggest using temptation bundling - combining breath practice with enjoyable activities like listening to favorite music. This approach increases adherence by linking effort with immediate rewards.
Combining Breathing Techniques with Lifestyle Modifications
Respiratory health optimization amplifies breathwork benefits. Addressing allergies, improving posture, and practicing vocal exercises all enhance breathing efficiency. Surprisingly, singing lessons help many anxiety sufferers through combined breath control and social exposure elements.
Nutritional adjustments also play a role - magnesium-rich foods support diaphragm function while reducing caffeine intake prevents respiratory muscle tension. These synergistic approaches create compounding benefits over time.
Gradual Exposure to Social Situations
Understanding the Basics of Gradual Exposure
Exposure therapy success relies on the inhibitory learning model - creating new, non-threatening associations with feared situations. Rather than eliminating anxiety, the goal becomes developing confidence in one's ability to function despite discomfort. This paradigm shift proves liberating for many chronic anxiety sufferers.
A 2023 meta-analysis in JAMA Psychiatry confirms that graduated exposure maintains superior long-term outcomes compared to medication-only approaches. The key differentiator appears to be the development of self-efficacy alongside symptom reduction.
Implementing a Structured Exposure Plan
Effective exposure hierarchies balance challenge and achievability. A sample progression might include:1. Texting a friend to arrange coffee2. Brief phone call with family member3. Attending small gathering with two close friends4. Participating in work meeting with prepared comments5. Volunteering to present at team meeting
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Techniques
Digital tools now enhance traditional journaling methods. Apps like Worry Watch allow users to track anxiety predictions versus actual outcomes, visually demonstrating decreasing catastrophe likelihood. Wearable devices provide physiological data (heart rate variability, skin conductance) to complement subjective experience reports.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Specialized therapists employ exposure variants like interoceptive exposure (simulating physical anxiety symptoms) to address fear of fear itself. Virtual reality platforms now enable controlled practice environments for complex social scenarios like job interviews or public performances.
Seeking Support and Professional Help

Recognizing the Need for Support
Persistent avoidance behaviors - declining invitations, excessive preparation for interactions, or relying on safety behaviors - signal the need for professional intervention. When anxiety consistently dictates life choices, expert guidance becomes crucial for breaking destructive patterns.
Types of Professional Help Available
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) for values-based action
- Psychodynamic approaches addressing underlying self-concept issues
- Biofeedback-assisted relaxation training
Implementing the Support in Daily Life
Therapy homework assignments bridge clinical insights with real-world application. A common exercise involves creating anxiety budgets - allocating specific worry periods to prevent constant rumination. Others practice social experiments to test feared predictions through behavioral testing.
Building Self-Confidence Through Positive Affirmations
Understanding Positive Affirmations
Neuroscientific research reveals that affirmations activate the ventromedial prefrontal cortex, associated with positive self-valuation. Regular practice strengthens these neural pathways, gradually overwriting entrenched negative self-narratives.
How to Create Effective Affirmations
Impactful affirmations combine aspirational content with current capability acknowledgments. Examples include:- I'm learning to handle social feedback with curiosity- My presence contributes value to group interactions- I choose to focus on connection over perfection
Incorporating Affirmations into Daily Life
Technology integration boosts consistency - setting affirmation reminders on smart devices or using wallpaper affirmations on digital screens. Pairing affirmations with routine actions (e.g., affirmations while brushing teeth) enhances habit formation through existing behavioral triggers.
Measuring the Impact of Affirmations
Pre-post measures using standardized scales (e.g., Social Phobia Inventory) provide objective progress tracking. Subjective units of distress (SUD) ratings during social interactions offer immediate feedback on affirmation effectiveness.
Overcoming Challenges with Affirmations
When affirmations feel inauthentic, adding yet softens resistance (I don't feel confident in meetings yet). Gradual scaling from neutral to positive statements helps bypass inner criticism - beginning with I'm willing to consider my strengths progresses to I confidently share my ideas.
Encouraging Others to Use Affirmations
Group affirmation practices create reciprocal reinforcement. Workplace initiatives like strength spotlights where colleagues share observed affirmations foster supportive environments. Family practices might involve shared affirmation whiteboards or daily check-ins.