Breathe Easy: Exploring the Link Between Breathlessness and Anxiety
The Physiological Mechanism of Breathlessness
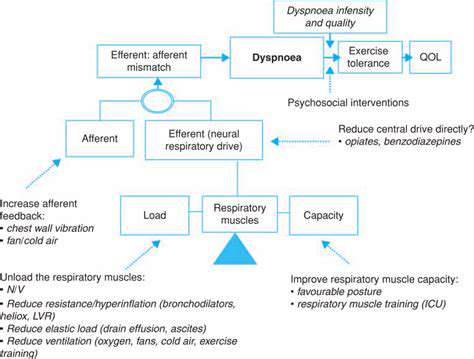
The Role of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system is crucial for the exchange of gases in our bodies. When we breathe, our lungs take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide, a process that is essential for our survival. Anxiety can disrupt this natural rhythm, leading to hyperventilation or shallow breathing. These changes can cause an individual to feel more breathless, which in turn can exacerbate anxiety levels. Understanding how the respiratory system functions can help individuals manage symptoms more effectively.
Gas exchange occurs primarily in the alveoli, tiny air sacs in the lungs. When anxiety sets in, the body's fight-or-flight response may trigger rapid breathing, resulting in decreased carbon dioxide levels in the blood. This state can lead to physical sensations that mimic panic attacks, including dizziness and increased heart rate. Recognizing these responses is a vital step in reclaiming one’s breathing pattern during anxious moments.
The Connection Between Anxiety and Perception of Breathlessness
Anxiety not only affects physical breathing patterns but also alters our perception of breathlessness. Individuals experiencing anxiety may become hyper-aware of their bodily sensations, magnifying the feeling of breathlessness. This heightened awareness can create a feedback loop where anxiety exacerbates the perception of breathlessness, leading to more anxiety. Such cycles can be challenging to break without conscious intervention.
Ultimately, understanding the psychological aspect of breathlessness empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their anxiety. By changing how one interprets breath-related sensations, the impact of anxiety on breathing can be significantly diminished.
Strategies for Managing Breathlessness and Anxiety
One effective method for managing anxiety-related breathlessness is through controlled breathing exercises. Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing encourage deeper, slower breaths that can calm the nervous system. Incorporating breathing exercises into daily routines can build resilience against anxiety triggers and improve overall lung function. Practicing these techniques regularly may lead to lasting effects on both mental and physical well-being.
Another beneficial strategy involves engaging in physical activities like yoga or tai chi. These practices not only promote better respiratory function but also integrate mindfulness, which helps lower anxiety levels. Participants often report an increased sense of well-being and decreased breathlessness after incorporating these activities into their lives.
Seeking support from mental health professionals can also provide invaluable tools for managing anxiety. Therapy sessions can help individuals to develop coping mechanisms and personalized strategies that address their unique experiences with breathlessness. Ultimately, a comprehensive approach that combines physical, psychological, and emotional support offers the best chance for relief from anxiety-related breathlessness.
Anxiety Disorders and Their Impact on Breathing
Understanding the Connection Between Anxiety and Breathlessness
Anxiety disorders often manifest with a variety of symptoms, one of the most common being breathlessness. This experience can range from feeling slightly short of breath to a more intense sensation of choking or inability to breathe. The physical sensations associated with anxiety can trigger a cycle of panic, leading individuals to hyperventilate or adopt improper breathing techniques.
The fight or flight response, a natural reaction to perceived danger, can stimulate rapid, shallow breathing. This physiological response can elevate heart rates and create a feeling of suffocation, further exacerbating anxiety symptoms. As individuals become more aware of their breathlessness, it can lead to increased anxiety about breathing itself, forming a vicious cycle.
Moreover, not all individuals experience breathlessness in the same manner. Some may report tightness in the chest, while others might feel an urge to take deep breaths or yawn frequently. Understanding these variations is crucial for both individuals suffering from anxiety and their healthcare providers, as it informs more effective strategies for intervention.
Therapeutic approaches that focus on breath control, such as diaphragmatic breathing and mindfulness practices, can be beneficial. These techniques are designed to reduce the physiological symptoms of anxiety, helping individuals regain a sense of control over their breathing patterns and overall mental state.
The Role of Therapy and Medication in Managing Symptoms
Effective management of breathlessness related to anxiety often requires a multifaceted approach, combining therapy and medication. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective, as it helps individuals identify and challenge the negative thought patterns that contribute to their anxiety, including fears related to breathing.
Medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and benzodiazepines, can also play a role in alleviating anxiety symptoms. While these medications may help reduce the intensity of anxiety, they should ideally be used in conjunction with therapy to address the root causes of anxiety and breathlessness.
Patients are encouraged to communicate openly with their healthcare providers about their symptoms, including breathlessness. This dialogue can lead to more personalized treatment plans, ensuring that both psychological and physiological aspects of anxiety are addressed.
Support groups and peer networks can provide additional avenues for relief, as individuals share their experiences with anxiety and breathlessness. These communities foster a sense of belonging and understanding, which can be vital in reducing feelings of isolation often associated with anxiety disorders.
Breaking the Cycle: Strategies for Managing Breathlessness and Anxiety
Understanding the Connection Between Breathlessness and Anxiety
Breathlessness can often manifest as a physical symptom in individuals experiencing anxiety. This sensation, medically known as dyspnea, can create a feedback loop where the fear of not getting enough air exacerbates feelings of panic and stress.
Anxiety triggers the fight-or-flight response, which can lead to rapid breathing or hyperventilation. This, in turn, can cause sensations of breathlessness, making the person feel like they are not breathing adequately, even in the absence of physical issues.
Additionally, people with pre-existing respiratory conditions may be more likely to experience increased anxiety levels when they feel breathless, leading to a complex interplay between their mental and physical health.
Recognizing this link is crucial for both clinicians and patients to develop holistic treatment approaches that address both the psychological and physical aspects of the symptoms.
Practical Techniques to Alleviate Breathlessness
Several breathing techniques can help alleviate symptoms of breathlessness associated with anxiety. One popular technique is diaphragmatic breathing, which encourages deep, full breaths to increase oxygen intake while promoting a sense of calm.
Progressive muscle relaxation is another method that can be effective. This technique involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups to help reduce overall tension and anxiety, which can subsequently improve breathing patterns.
Mindfulness and meditation practices also play a vital role. By helping individuals focus on their breath and the present moment, these practices can reduce the fear associated with breathlessness, allowing for a more effective management of anxiety symptoms.
Using visualization techniques during breathing exercises can enhance their effectiveness, enabling individuals to imagine calming environments while focusing on their breath, promoting relaxation and a decrease in breath-related anxiety.
Seeking Professional Help: When to Consult a Therapist
While self-management strategies can be effective, there are times when professional help is necessary. If breathlessness and anxiety interfere with daily life or well-being, consulting a healthcare professional is essential.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a common therapeutic approach for those struggling with anxiety disorders, including symptoms like breathlessness. CBT helps individuals identify negative thought patterns and develop effective coping strategies.
Therapists may also incorporate techniques such as exposure therapy, where the individual gradually faces their anxiety-inducing situations related to breathlessness, which can help desensitize them to these experiences.
Furthermore, it may be beneficial to work with a respiratory therapist who can provide specialized guidance on breathing techniques, ensuring that individuals not only understand but also practice these methods effectively.
Building a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment is vital for anyone dealing with anxiety and breathlessness. Family and friends can play a significant role in helping individuals feel safe and understood, reducing anxiety triggers in their surroundings.
Open communication about anxiety symptoms can foster empathy and understanding, allowing loved ones to offer support without judgment. This can lead to assistance in finding strategies that help manage breathlessness effectively.
Joining support groups or therapy groups can provide individuals with a sense of community and shared experiences, mitigating feelings of isolation that often accompany anxiety-related disorders.
Lastly, incorporating regular physical activity, when possible, can improve overall physical health and resilience against anxiety, further supporting an atmosphere conducive to mental well-being and effective breath management.