Exploring the Effectiveness of Beta Blockers in Managing Cardiovascular Conditions
Introduction to Beta Blockers and Their Role in Heart Health
What are Beta Blockers?
Beta blockers are a class of medications that primarily block the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. These drugs work by targeting beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart and blood vessels, leading to decreased heart rate and blood pressure. This class of medication is essential for managing various cardiovascular conditions.
Commonly prescribed beta blockers include atenolol, metoprolol, and propranolol. Each of these medications may have different specific uses depending on patient needs and medical histories. Their efficacy in treating heart-related issues makes them a cornerstone in cardiovascular therapy.
In addition to their effects on heart rate and blood pressure, beta blockers are also known for their ability to reduce the workload on the heart. By slowing down the heart's rhythm, they help prevent overexertion during stressful situations, which can further contribute to heart health.
Beta blockers are not only used in treating heart conditions but also in managing anxiety, preventing migraines, and controlling certain types of tremors, showcasing their versatility. Their broad range of uses highlights the importance of understanding their role in both cardiac and non-cardiac conditions.
Despite their effectiveness, it's crucial to consult healthcare professionals before starting beta blockers, as they may not be suitable for everyone. Potential side effects and contraindications must be discussed with a doctor to ensure the safe use of these powerful medications.
Clinical Applications of Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are widely used in the management of congestive heart failure (CHF), where they help improve heart function and reduce symptoms. By decreasing the heart's workload, beta blockers can enhance the quality of life for patients suffering from this chronic condition.
Additionally, beta blockers are an essential component in the treatment of hypertension, or high blood pressure. By easing the strain on the heart and blood vessels, they contribute to lowering blood pressure levels, which is critical in preventing stroke and heart attacks.
In patients who have experienced a heart attack, beta blockers can be lifesaving. They reduce the risk of subsequent heart attacks and may help stabilize the heart's rhythm, thereby improving overall outcomes for individuals recovering from life-threatening cardiac events.
Furthermore, beta blockers are sometimes prescribed to patients with atrial fibrillation, a form of irregular heartbeat. By controlling the heart rate, they contribute to reducing symptoms and the risk of more severe complications related to this arrhythmia.
Ongoing research continues to explore new applications and benefits of beta blockers, including their potential role in other cardiovascular issues. Such studies are vital for optimizing treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Benefits and Risks of Using Beta Blockers
One of the significant benefits of beta blockers is their ability to decrease mortality rates in patients with heart failure and those recovering from heart attacks. Their effectiveness in managing chronic conditions has established them as a long-standing treatment option.
Patients often experience fewer episodes of angina, a type of chest pain, when using beta blockers. By reducing the heart's demand for oxygen, these medications can significantly enhance the patient's quality of life and ability to perform everyday activities.
However, like all medications, beta blockers come with potential side effects, such as fatigue, dizziness, and cold extremities. These effects can often lead to concerns regarding patient adherence, necessitating open discussions between healthcare providers and patients about managing any adverse effects.
Some individuals may also develop depression or mood changes when taking beta blockers, adding another layer of complexity to their use. Understanding the patient's overall mental and emotional health is essential when initiating treatment with these medications.
Moreover, beta blockers may not be suitable for patients with certain conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) due to their respiratory effects. Therefore, thorough medical evaluations are critical to evaluate the risks versus the benefits for each individual patient.
The Future of Beta Blockers in Cardiac Care
The future of beta blockers in cardiac care looks promising as ongoing research seeks to uncover new therapeutic benefits and refine current treatment protocols. Investigating their role in combination therapies may lead to improved outcomes for patients with multifactorial cardiovascular diseases.
Current studies are exploring the potential for beta blockers in managing conditions beyond traditional cardiovascular diseases, such as their use in chronic pain management and anxiety disorders. As new evidence comes to light, the indications for beta blocker use may expand significantly.
Advancements in technology are also paving the way for more personalized medicine in the realm of beta blocker therapy. Genetic testing may soon help healthcare providers determine which beta blockers are most effective for individual patients, minimizing side effects and optimizing treatment plans.
Additionally, as we learn more about the long-term effects of beta blockers, there may be new recommendations regarding their duration of use. Researchers are continually assessing the balance between short-term relief of symptoms and long-term management of chronic conditions.
Ultimately, the evolving landscape of cardiovascular care will determine how beta blockers are utilized in future treatment paradigms. Continuous education for both healthcare providers and patients regarding the benefits and risks of beta blockers will remain essential for maximizing their effectiveness in heart health management.
The Mechanism of Action: How Beta Blockers Work
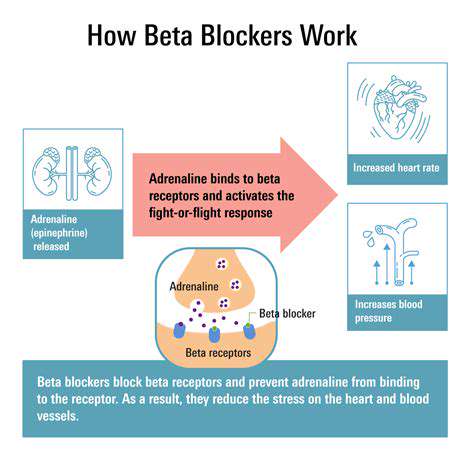
The Role of Beta Blockers in Heart Rate Regulation
Beta blockers are primarily known for their ability to reduce heart rate, making them a popular choice in managing various cardiovascular conditions. By blocking the receptors for adrenaline, these medications help to slow down the heart, which can prevent arrhythmias and other heart-related issues.
Moreover, a lower heart rate also means the heart is working less strenuously, reducing stress on the heart muscle. This is particularly beneficial for patients suffering from conditions such as hypertension and heart failure.
Notably, the effects of beta blockers extend beyond heart rate reduction; they also help in improving overall heart function. By promoting better oxygen efficiency for the heart, they assist in preventing fatigue and further complications.
In summary, beta blockers play a critical role in regulating heart rate, which helps in the management of cardiovascular health. Their ability to provide significant relief from various symptoms makes them a cornerstone in cardiac care.
Indications for Use: When Are Beta Blockers Prescribed?
Beta blockers are prescribed for a variety of cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and arrhythmias. Their versatility makes them suitable for different patient needs, depending on the severity and nature of the heart condition.
In cases of heart failure, beta blockers can improve survival rates and quality of life. They help to enhance the pumping efficiency of the heart, effectively managing symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath.
Additionally, beta blockers are often recommended after a heart attack to help prevent further events. They support the heart during the recovery process, allowing it to heal while minimizing the risks of additional issues.
Overall, the indications for beta blocker use highlight their crucial role in contemporary cardiovascular treatment protocols. Their implementation can significantly improve patient outcomes and safeguard heart health.
Side Effects and Considerations: Safely Integrating Beta Blockers
While beta blockers are effective, they also come with potential side effects that must be monitored. Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and even depression in some cases. Understanding these side effects is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers in managing therapy effectively.
Furthermore, not everyone is a suitable candidate for beta blockers. Individuals with conditions like asthma or certain types of heart block may face contraindications. This necessitates careful patient selection and ongoing assessment to ensure safety and efficacy.
For patients considering beta blockers, it is essential to discuss any pre-existing health concerns with a healthcare professional. Collaboration can lead to tailored treatment plans that optimize benefits while minimizing risks.
In conclusion, while beta blockers have an essential role in managing cardiovascular conditions, awareness of side effects and patient-specific considerations is vital. Therefore, informed and careful use of these medications is key to achieving the best therapeutic outcomes.
Clinical Applications of Beta Blockers
Understanding Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are a class of medications that primarily block the effects of adrenaline on the beta-adrenergic receptors. By inhibiting these receptors, beta blockers help to slow down the heart rate, reduce blood pressure, and lessen the overall workload on the heart.
These medications can vary in selectivity; some block only beta-1 receptors that primarily affect the heart, while others may also block beta-2 receptors found in blood vessels and the lungs. This selectivity can influence the choice of beta blocker based on the patient's specific health needs.
Commonly prescribed beta blockers include drugs like metoprolol, atenolol, and propranolol. Each of these medications can have distinct effects and may be chosen for their particular pharmacological properties.
In addition to managing cardiovascular conditions, beta blockers are also used to treat anxiety, migraines, and certain types of tremors, reflecting their versatility in clinical applications.
Hypertension Management
Beta blockers have historically been used in the treatment of hypertension. They help to manage blood pressure by decreasing heart rate and the force of heart contractions, resulting in lower blood pressure levels overall.
While beta blockers can be effective in controlling blood pressure, they are often not the first-line treatment in hypertension management. Diuretics and ACE inhibitors are typically preferred, with beta blockers used when patients have specific indications such as heart failure or a history of myocardial infarction.
Patients may experience different responses to beta blockers, and their effectiveness can be influenced by factors such as age, gender, and coexistence of other health conditions.
Patient education is critical, as adherence to prescribed regimens can significantly influence the outcomes of beta blocker therapy in hypertension management.
Beta Blockers in Heart Failure
In patients with heart failure, beta blockers play a crucial role in improving survival rates and reducing hospitalizations. They help alleviate the symptoms of heart failure by slowing the heart rate and reducing myocardial oxygen demand.
Heart failure patients are often prescribed specific beta blockers such as carvedilol, metoprolol succinate, and bisoprolol, which have been shown in clinical trials to improve outcomes.
Monitoring is essential when initiating or adjusting beta blocker therapy in heart failure patients, as managing the dosage can be challenging due to the risk of exacerbating symptoms, particularly in patients with severe heart failure.
Long-term studies have demonstrated that beta blockers can contribute to improved quality of life for heart failure patients, making them a fundamental part of standard treatment protocols.
Arrhythmia Control with Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are commonly used to treat various arrhythmias, particularly atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. By reducing heart rate and stabilizing electrical activity within the heart, these medications can help restore a normal heart rhythm.
In atrial fibrillation, beta blockers can control the rapid heartbeat that occurs during an episode and may also be employed as part of a broader management strategy that includes anticoagulation therapies to reduce the risk of stroke.
For patients with ventricular tachycardia, beta blockers work by reducing sympathetic nervous system activity, which can trigger these potentially dangerous heart rhythms.
Clinicians often tailor the choice of beta blockers and their dosages based on the specific arrhythmia type and patient tolerance, aiming to balance efficacy with the minimization of side effects.
Side Effects and Contraindications
While beta blockers can be highly effective in managing cardiovascular conditions, they do come with a range of potential side effects. Patients may experience fatigue, dizziness, and cold extremities as common reactions.
In some cases, beta blockers may exacerbate conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) due to their non-selective effects on beta-2 receptors. Consequently, clinicians must carefully assess a patient’s respiratory history before prescribing these medications.
Other side effects might include weight gain, depression, and sexual dysfunction, which can lead to non-adherence if patients are concerned about these impacts. It is therefore important for healthcare providers to discuss these potential side effects openly with patients.
Awareness of contraindications, such as severe bradycardia or certain conduction abnormalities, is essential to ensure safe prescribing practices and to avoid complications in vulnerable populations.
Effectiveness in Anxiety and Migraines
Role of Beta Blockers in Anxiety Management
Beta blockers, originally developed to treat heart conditions, have found use in managing anxiety disorders. They work by blocking the effects of adrenaline, which can help reduce physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat and tremors. Studies show that these medications can be particularly effective in performance anxiety, where individuals experience heightened nervousness in specific situations.
Furthermore, patients who struggle with generalized anxiety disorder may also experience relief from beta blockers. However, it’s essential to note that while they can help manage symptoms, they do not address the psychological aspects of anxiety, which may require additional therapeutic interventions.
Impact of Beta Blockers on Migraine Prevention
Research indicates that beta blockers can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of migraines in individuals prone to these debilitating headaches. By stabilizing blood vessels and reducing blood flow fluctuations, these medications can help prevent the onset of a migraine. Commonly prescribed beta blockers for this purpose include propranolol and metoprolol.
In clinical trials, a substantial percentage of patients reported fewer migraine days when treated with beta blockers. This effect is thought to be related to their ability to modulate neurotransmitter release and influence blood vessel tone, which can be crucial in migraine pathophysiology.
Considerations and Contraindications
While beta blockers offer benefits in managing anxiety and migraines, they are not suitable for everyone. Patients with asthma or certain types of heart disease might experience adverse effects, as beta blockers can cause bronchoconstriction or worsen heart failure. It is crucial for healthcare providers to perform a thorough assessment before prescribing these medications.
Additionally, it is advisable for patients to discuss their complete medical history and any other medications they are taking to avoid potential interactions. Regular monitoring and follow-up consultations can help ensure that the treatment remains effective and safe.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations

Understanding Side Effects of Beta Blockers
Beta blockers, commonly prescribed for hypertension and other cardiovascular issues, can lead to various side effects. Some patients may experience fatigue, cold hands, or feelings of depression. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for patient compliance and effective management.
In rare cases, beta blockers can also cause more severe side effects such as bradycardia or hypotension. Monitoring heart rate and blood pressure regularly is essential for all patients on these medications.
Patients should always report any unusual sensations or health changes to their healthcare provider, as this can lead to timely interventions and adjustments to their treatment plan.
Patient Considerations Before Starting Treatment
Before initiating beta blocker therapy, it’s important for healthcare providers to assess the patient’s complete medical history. Conditions like asthma or diabetes can influence whether a beta blocker is the right choice. This ensures that the benefits outweigh potential risks.
Moreover, patients taking multiple medications must communicate this to their provider to avoid adverse drug interactions. Proper medication management can greatly improve treatment efficiency.
Informed decision-making is critical; hence, patient education on the purpose, benefits, and downside of beta blockers can reduce anxiety and increase adherence.
Identifying When to Consult a Doctor
Patients using beta blockers must be vigilant about any changes in their health status. Symptoms like persistent dizziness, unusual heart rhythms, or exacerbated breathing issues should prompt a prompt doctor's visit. Reacting quickly can prevent complications and ensure the continuity of effective treatment.
Regular follow-ups are crucial, especially within the first few weeks of starting a beta blocker, to evaluate its impact and identify any side effects early on. Healthcare providers can make timely adjustments if necessary.
Establishing a strong line of communication between patients and their healthcare team greatly enhances the overall management of cardiovascular conditions.
Long-term Implications of Beta Blocker Therapy
Long-term use of beta blockers has been shown to have both positive and negative implications on cardiovascular health. Patients often report improved quality of life due to better management of their conditions. However, regular assessments are vital to evaluate ongoing effectiveness and potential side effects.
Over time, the body may adapt to beta blockers, sometimes leading to decreased effectiveness. Therefore, it’s essential for doctors to reconsider treatment plans periodically. Adjusting dosages or medication types can help maintain optimal results.
In conclusion, while beta blockers are effective for many cardiovascular conditions, their long-term management requires careful monitoring and open dialogue between patients and healthcare providers to ensure continued success.