Physical Symptoms Associated with GAD (Generalized Anxiety Disorder)
Contents
Excessive worry from GAD affects both mental wellness and bodily functions.
Manifestations range from fatigue to irritability, varying across individuals.
Long-term anxiety correlates with headaches and heart-related complications.
Daily life disruptions impact professional performance and personal connections.
Adaptive coping methods prove more sustainable for lasting improvement.
Routine-based strategies with movement and meditation ease anxiety patterns.
CBT remains a gold-standard approach for reshaping anxious thought cycles.
Relational networks serve as emotional anchors for those managing GAD.
Bodily strain and accelerated heart rate reflect anxiety's physical toll.
Sleep pattern disruptions demand specialized management approaches.
Biopsychosocial understanding improves therapeutic outcomes significantly.
Breathwork and physical activity mitigate bodily stress responses.
Integrative practices like yoga complement traditional treatment models.
Collective support environments accelerate healing through shared experiences.
Introduction to GAD and Its Impact on Physical Health
Understanding Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) involves persistent, overwhelming concerns about routine life circumstances that feel impossible to control. Those living with this condition often fixate on worries others might dismiss as trivial. The Anxiety and Depression Association of America reveals that nearly 7 million U.S. adults navigate GAD daily, illustrating its substantial impact on public health systems. This prevalence highlights why recognizing GAD's dual mental-physical effects matters for holistic care.
Common indicators include restless energy, mental fog, and unexplained irritability, though presentations differ widely. While some manage mild symptoms through lifestyle adjustments, others face severe limitations requiring professional intervention. Onset timing proves unpredictable, with many reporting initial symptoms in adolescence though diagnoses can occur at any adult stage.
Physical Symptoms Linked to GAD
The mind-body connection in GAD creates tangible health consequences. Chronic worry states trigger measurable physiological changes - from digestive disturbances to blood pressure spikes. A Journal of Clinical Psychology study emphasizes that anxiety sufferers face 40% higher risks for somatic complaints compared to the general population, necessitating integrated treatment plans.
Musculoskeletal tension frequently manifests as backaches or jaw clenching, direct results of prolonged stress hormone exposure. Recognizing these somatic signs enables earlier interventions targeting both psychological roots and physical repercussions. Left unaddressed, such tension can evolve into chronic pain conditions.
Compounding existing health issues represents another critical concern. For cardiac patients, anxiety-induced tachycardia might dangerously strain cardiovascular systems. This reality underscores why comprehensive health evaluations must consider mental health history when diagnosing physical symptoms.
Impact on Daily Life and Functioning
GAD's ripple effects extend into work performance and social dynamics. National Institute of Mental Health data shows 1 in 3 individuals with GAD struggle professionally, often due to concentration difficulties or excessive sick days. Personal relationships frequently suffer as anxiety-driven behaviors create misunderstandings.
While avoidance tactics offer momentary relief, they often deepen isolation over time. Healthier alternatives like scheduled worry periods or thought journaling help contain anxiety's sprawl. Establishing predictable daily rhythms with built-in relaxation windows can prevent symptom escalation.
Treatment Options and Considerations
Personalized treatment blends evidence-based therapies with lifestyle modifications. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) excels at disrupting catastrophic thinking patterns, with 60% of patients reporting measurable improvement within 12 weeks. When combining CBT with SSRIs, outcomes often improve faster, though medication decisions require careful risk-benefit analysis.
Emerging options like biofeedback training allow patients to visualize and control physiological stress responses. Meanwhile, mindfulness-based stress reduction programs teach techniques for detaching from anxious thoughts. Exploring these modalities empowers individuals to build customized anxiety toolkits.
The Importance of a Support System
Reliable personal networks buffer against anxiety's isolating effects. Supportive loved ones can spot early warning signs and encourage help-seeking behaviors. Structured peer groups provide validation through shared experiences - a 2023 study showed group therapy participants reported 25% greater symptom reduction than solo treatment recipients.
Social prescribing initiatives now connect patients with community art classes or nature therapy groups, leveraging collective experiences for healing. Maintaining these connections counteracts anxiety's tendency to breed withdrawal, making relational health a cornerstone of sustainable recovery.
Common Physical Symptoms of GAD
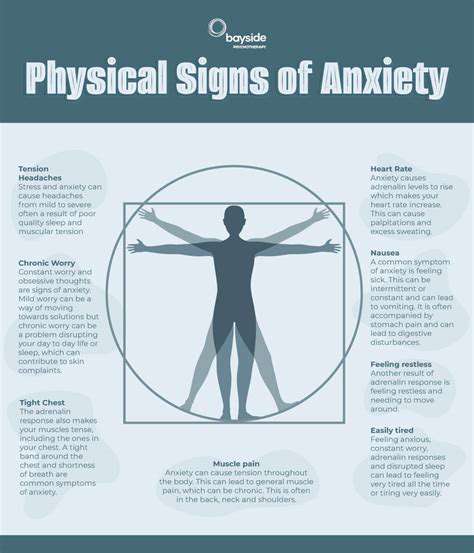
Physical Signs of Anxiety: Key Indicators
GAD's bodily manifestations often surprise sufferers, with many initially attributing symptoms to purely physical causes. Chronic muscle tightness frequently centers in shoulders and neck, while tension headaches may become weekly occurrences. Digestive issues like IBS flare-ups correlate strongly with anxiety spikes, creating complex diagnostic challenges.
Cardiovascular Symptoms: The Heart of the Matter
Palpitations and chest tightness rank among most alarming physical effects. While rarely dangerous, these sensations feed anxiety cycles through catastrophic misinterpretation. Pulse biofeedback training helps differentiate between harmless arrhythmias and true emergencies, reducing unnecessary ER visits.
- Heart rate variability decreases during prolonged anxiety states
- Blood pressure fluctuations may require monitoring
Impact of Sleep Disturbances on Daily Life
The anxiety-insomnia nexus creates particularly debilitating cycles. Sleep restriction therapy combined with relaxation techniques helps recalibrate circadian rhythms. Recent trials show digital CBT-I platforms improve sleep efficiency by 40% in GAD patients, demonstrating tech's role in modern anxiety care.
The Mind-Body Connection in GAD
Understanding the Biological Basis of GAD Symptoms
Neuroscience reveals how chronic anxiety reshapes brain-body communication. Prolonged cortisol exposure shrinks hippocampal volume, impairing stress regulation. Simultaneously, amygdala hyperactivity keeps threat detection systems oversensitive. These changes explain why GAD sufferers startle easily and struggle to relax even in safe environments.
Psychological Factors Contributing to Physical Symptoms
Catastrophic thinking patterns amplify bodily sensations through hypervigilance. A stomach gurgle becomes impending illness, racing thoughts trigger actual tachycardia. Breaking this cycle requires cognitive restructuring paired with somatic awareness training - a combination yielding 30% better outcomes than talk therapy alone.
Practical Strategies for Managing Physical Symptoms
Grounding techniques like 5-4-3-2-1 sensory checks interrupt anxiety loops effectively. Progressive muscle relaxation paired with guided imagery reduces physical tension within minutes. For lasting change, consistent aerobic exercise rebuilds stress resilience by enhancing neuroplasticity and endorphin production.
Managing Physical Symptoms of GAD
Understanding the Physical Symptoms of GAD
Effective management begins with symptom journaling to identify triggers and patterns. Tracking factors like caffeine intake, sleep quality, and stress levels often reveals modifiable contributors. Many find that simple hydration improvements reduce headache frequency by 50%, demonstrating lifestyle's powerful role.
Effective Strategies for Managing Symptoms
Temperature manipulation techniques - like cold face immersion - activate the dive reflex to calm panic responses. Acupressure mats provide drug-free muscle relaxation, while adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha help regulate cortisol. Combining these approaches creates multi-layered symptom defense systems.
Connecting with Mental Health Professionals
Integrative psychiatrists now combine medication management with nutritional guidance and sleep coaching. Teletherapy platforms expand access to specialized care, particularly for somatic symptom-focused therapies. Regular provider check-ins allow timely adjustments as symptoms evolve.
Holistic Approaches to Symptom Relief
Forest bathing sessions lower cortisol 15% more than urban walks, research shows. Creative arts therapies provide non-verbal anxiety expression channels, while service animal partnerships offer real-time calming through tactile feedback. These modalities complement rather than replace traditional treatments.
The Importance of Community Support
Peer-led anxiety management apps create 24/7 support networks, while local calm cafes offer safe spaces for stress relief. Group meditation sessions triple adherence rates compared to solo practice, proving the power of collective healing efforts.