Understanding Body Shaking as a Symptom of Anxiety
Catalog
Mind-Body Connection affects anxiety-related physical symptoms.
Understanding physical manifestations empowers anxiety management.
Mindful breathing techniques reduce anxiety-induced shaking.
Exploring triggers enhances awareness and coping strategies.
Professional help is critical for managing anxiety symptoms.
Support systems mitigate feelings of isolation in anxiety.
Self-care promotes overall well-being and reduces anxiety.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy effectively addresses anxiety triggers.
The Connection Between Anxiety and Physical Symptoms
Understanding the Mind-Body Connection
The connection between the mind and body is pivotal in understanding how anxiety manifests physically. Traditionally, mental health was viewed separate from physical health, leading to inadequacies in treatment approaches. However, emerging research highlights that psychological states genuinely influence physiological reactions. This interplay suggests that unresolved emotional tension can trigger physical responses, creating a cycle that compounds anxiety.
When a person experiences anxiety, the brain signals the body to prepare for 'fight or flight,' resulting in an array of physical symptoms. This might include an accelerated heart rate, muscle tension, and even gastrointestinal disturbances. Such reactions are part of the body's natural defense mechanism but can become chronic if anxiety persists. Understanding this connection can empower individuals with anxiety to seek holistic treatments that consider both mental and physical well-being.
Mindfulness practices and body awareness strategies can be beneficial in easing symptoms. Techniques such as meditation or yoga help individuals reconnect with their physical sensations, fostering a sense of control over their anxiety. Recognizing that physical symptoms are not merely nuisances but manifestations of emotional struggles can lead to proactive management of anxiety, emphasizing the need for comprehensive treatment strategies.
The growing awareness of this mind-body connection is reshaping how mental health professionals approach anxiety treatment. By integrating psychological and physical therapies, practitioners can develop more effective treatment plans that cater to the unique needs of each patient. This encourages individuals to address both their emotional and physical symptoms, paving the way for improved health outcomes.
Common Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety manifests itself through a spectrum of physical symptoms, many of which may go unnoticed or be attributed to other causes. Common symptoms include muscle tension, headaches, and stomach issues, which can be particularly debilitating. For instance, muscle tension can lead to chronic pain, significantly impacting one's quality of life. Chronic headaches resulting from anxiety can take a toll on productivity and interpersonal relationships, compounding the emotional strain.
Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and diarrhea are also frequently reported by those experiencing anxiety. The gut-brain connection explains why psychological stress can lead to significant digestive discomfort. Oftentimes, anxiety exacerbates pre-existing conditions like irritable bowel syndrome, resulting in a vicious cycle of anxiety and physical symptoms. Such awareness can prompt people to seek medical evaluations to rule out underlying conditions.
Another common symptom is an increased heart rate or palpitations, which can mimic more serious cardiovascular issues. This can be particularly alarming for individuals unfamiliar with anxiety's physical effects. Recognizing that these symptoms stem from anxiety can be a crucial step in alleviating worry about potential heart problems, thus reducing the anxiety related to physical sensations.
Recognizing physical symptoms as part of anxiety can empower individuals to seek appropriate treatments. Addressing physical manifestations through therapy, medication, or lifestyle changes can bring significant relief. It is essential for both healthcare providers and patients to have open conversations about the physical effects of anxiety to create effective treatment plans that address all aspects of the condition.
The Role of Stress Management Techniques
Stress management techniques are essential for individuals struggling with anxiety, as they provide tools for regulating both mind and body. These techniques can help interrupt the cycle of anxiety and its physical manifestations. One effective approach is deep breathing exercises, which activate the body's relaxation response. By focusing on the breath, individuals can mitigate symptoms such as shortness of breath and racing heart rates associated with anxiety.
Similarly, progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) can be particularly beneficial in relieving muscle tension. This technique involves tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups, promoting awareness of the physical sensations related to anxiety. By systematically relaxing the body, individuals may find greater relief from discomfort and a noticeable reduction in anxiety levels.
Engaging in regular physical activity also plays a critical role in combating anxiety. Exercise has been shown to release endorphins, the body's natural mood lifters, while also improving sleep quality. Even simple activities such as walking or stretching can help alleviate physical symptoms of anxiety and improve overall well-being. Incorporating physical fitness into one's routine fosters resilience against stressors.
Seeking Professional Help
Seeking professional help is a critical step for individuals facing anxiety, especially when physical symptoms become overwhelming. Mental health experts, such as psychologists and psychiatrists, are trained to recognize the intricate connections between emotional and physical health. They can offer informed assessments, recommend therapeutic options, and provide ongoing support tailored to an individual's unique experiences.
Therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) are designed to address the root causes of anxiety while simultaneously providing coping mechanisms to manage physical symptoms. CBT helps individuals identify thought patterns that contribute to anxiety and teaches practical skills to counteract them. This dual approach is particularly effective, as it addresses both the mental and physical aspects of anxiety.
Medication can also be an integral part of managing anxiety and its symptoms. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, or even beta-blockers can alleviate physical symptoms of anxiety like heart palpitations and shaking. Working with a healthcare provider to find the right medication can offer significant relief, enabling individuals to engage more fully in life without the debilitating effects of anxiety.
Long-Term Strategies for Managing Anxiety
Developing long-term strategies for managing anxiety is essential for individuals seeking to improve their overall quality of life. Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a balanced diet, ensuring adequate sleep, and engaging in regular physical activity contribute significantly to both mental and physical well-being. These foundational habits create a stable baseline that can cushion against anxiety-driven episodes.
Incorporating mindfulness practices into daily routines can also enhance one’s ability to manage anxiety effectively. Mindfulness encourages individuals to remain present and aware, which can prevent spiraling into anxiety-driven thoughts. Regular meditation, journaling, or simply taking time to reflect can cultivate a greater sense of calm while also improving emotional regulation.
Establishing a reliable support system is another critical strategy. Building relationships with friends, family, or organized support groups ensures that individuals have access to encouragement and understanding during challenging times. Having someone to talk to can mitigate feelings of isolation and provide perspective on one’s experiences, which can be incredibly grounding.
Finally, setting realistic goals and celebrating small accomplishments promotes a sense of agency over one's life. It is important to recognize that managing anxiety is a journey rather than a destination. Acknowledging progress, no matter how minor, reinforces positive behaviors and encourages perseverance in the face of ongoing challenges. These long-term strategies can form a comprehensive approach to dealing with anxiety, fostering a balanced life.
Why Do We Shake? The Science Behind It
Understanding the Mechanisms of Shaking
Shaking, often termed as tremors, can be a physical manifestation of the body's response to various stimuli. When individuals experience anxiety, their body activates the fight-or-flight response, releasing adrenaline and other stress hormones. This biological reaction can lead to involuntary muscle contractions, resulting in shaking. The intensity and visibility of these tremors can vary significantly from person to person, influenced by both their psychological state and physiological makeup.
The shaking we observe during anxiety is heavily rooted in evolutionary biology. Our ancestors needed to react quickly to threats, and muscle shaking facilitated rapid physical responses. Today, even as the nature of threats has transformed, our bodies still react similarly. The involuntary muscle spasms can serve as a reminder of that primal instinct, though in modern contexts, they often present themselves in the absence of any immediate danger.
Additionally, it's important to consider other physiological mechanisms associated with shaking. During anxiety, our body may also experience an increase in heart rate, heightened blood pressure, and rapid breathing. These factors contribute to a general state of heightened arousal, which can exacerbate the shaking sensations felt, making it difficult for individuals to regain control during heightened moments of stress.
Emotional Influence on Physical Symptoms
The connection between our emotions and our physical responses cannot be understated when discussing why we shake. Anxiety can alter our perception of threats, often inflating fears. This distorted perception not only heightens emotional distress but also prompts physical reactions like trembling. Consequently, the relationship between mind and body becomes a cyclical one, wherein heightened anxiety leads to shaking, which in turn, may lead to increased anxiety.
This emotional influence extends beyond immediate feelings of anxiety. Chronic anxiety sufferers may frequently experience shaking, which can create a feedback loop whereby the anticipation of shaking further exacerbates the anxiety. This cycle highlights the importance of understanding individual triggers and working towards management techniques that can help break the cycle.
People dealing with anxiety-induced shaking can benefit from various coping strategies, such as mindfulness techniques, cognitive behavioral therapy, and physical exercises. These practices can focus on grounding oneself in the present moment, thus providing emotional stability and reducing the impact of anxiety on physical symptoms like shaking.
Strategies for Managing Shaking During Anxiety
Understanding the root causes of shaking can empower individuals to develop effective management strategies. One commonly recommended approach is deep breathing exercises, which can activate the body's relaxation response. By focusing on long, controlled breaths, individuals can reduce their heart rate and lower adrenaline levels, thereby minimizing the stress-induced shaking.
Another beneficial technique is progressive muscle relaxation. This practice involves tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups, promoting an increased awareness of bodily sensations and helping to counteract the tension that manifests as shaking. Incorporating this practice into daily routines can enhance one's ability to cope with anxiety over time.
Finally, seeking professional help cannot be overstated. A mental health professional can provide tailored coping strategies and therapeutic approaches suited to each unique situation. Engaging in therapy not only helps individuals understand the underlying factors contributing to their anxiety but also equips them with tools to manage shaking and its effects on daily life. Recognizing that one is not alone in this struggle can also provide immense relief.
Identifying Triggers and Situational Contexts
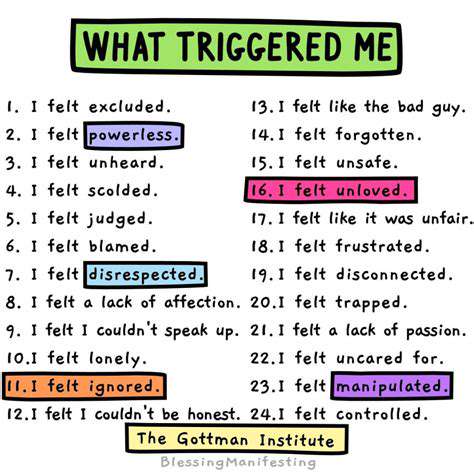
Understanding Triggers of Anxiety-Induced Body Shaking
Identifying the specific triggers that lead to anxiety-induced body shaking is essential for effective management. Common triggers include high-stress environments, public speaking, or significant life changes. By recognizing these triggers, individuals can begin to develop coping mechanisms that align with their personal experiences. Moreover, understanding the nature of these triggers can help in differentiating between situational anxiety and clinical anxiety disorders.
Environmental factors can also play a crucial role in triggering anxiety responses. For instance, crowded spaces may make some individuals feel overwhelmed, potentially leading to physical manifestations like shaking. Noticing patterns in one's environment can significantly enhance self-awareness and preparedness. Keeping a journal that documents these situations and subsequent reactions can be a powerful tool for understanding and managing anxiety.
Once triggers are identified, individuals can start working on desensitization techniques. By systematically and gradually exposing oneself to anxiety-inducing situations, they can learn to manage their physiological responses more effectively. It's beneficial to practice relaxation techniques in these scenarios to minimize shaking and restore a sense of control.
Situational Contexts and Their Impact on Body Shaking
Every individual's experience of anxiety is unique, influenced significantly by their situational contexts. For example, someone might find themselves shaking only in tense social situations, while another person might experience it during high-pressure work scenarios. The context in which anxiety occurs can affect both the intensity and the nature of the shaking. Hence, a comprehensive understanding of one's individual circumstances is necessary for effective management.
Cultural background can also shape how individuals experience and exhibit anxiety symptoms. In certain cultures, expressing emotions might be discouraged, leading to a more pronounced physical manifestation like shaking. It’s important for individuals to reflect on how their cultural narratives influence their understanding of anxiety. Recognizing this connection can pave the way for more compassionate self-education and help.
Additionally, social support systems play a pivotal role in shaping situational contexts associated with anxiety. A strong support network can mitigate feelings of isolation and increase feelings of safety, reducing the likelihood of experiencing shaking during social interactions. Conversely, environments that lack understanding or supportive figures can exacerbate feelings of anxiety, leading to heightened physical symptoms.
Strategies to Manage Body Shaking in Anxiety-Provoking Scenarios
Implementing effective strategies to manage body shaking when faced with anxiety-inducing situations can significantly improve quality of life. One of the most beneficial techniques is practicing mindfulness. Through mindfulness exercises, individuals can become more attuned to their bodies and emotional states, helping to ground themselves during overwhelming moments. This grounding effect often reduces physical manifestations like shaking.
Deep breathing exercises can also serve as a quick and effective way to counter anxiety. By inhaling deeply and exhaling slowly, individuals can activate the body's relaxation response, helping to calm both mind and body. This technique is particularly useful in high-pressure situations where shaking is likely to occur.
In addition to these techniques, seeking professional help, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can provide invaluable tools for managing anxiety. A trained therapist can assist in developing personalized strategies and provide support for navigating challenging emotional landscapes. Group therapy can also offer a sense of community and shared experience, fostering resilience and connection among those dealing with similar issues.
Strategies to Manage Body Shaking

Understanding the Causes of Body Shaking
Body shaking can be a physical manifestation of anxiety, often triggered by stress or overwhelming situations. Identifying the underlying causes is crucial for effective management. Some individuals may experience shaking as a response to panic attacks, while others might notice it in everyday stressors. By pinpointing these causes, one can better prepare and adapt their coping mechanisms. This understanding also allows individuals to separate their physical responses from the anxiety itself, thereby reducing fear and panic associated with these symptoms.
Additionally, physiological factors such as caffeine consumption or withdrawal can induce shaking. Individuals should carefully monitor their intake of stimulants, which can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Being aware of triggers greatly aids in developing a proactive management strategy. Furthermore, hormonal changes or medical conditions might also contribute to bodily trembling. It is always advisable to consult healthcare professionals if shaking persists, ensuring comprehensive care and support.
Emotional factors play a significant role in body shaking as well. Heightened feelings of fear, nervousness, or apprehension typically elevate anxiety levels, leading to physical responses like shaking. It's essential to cultivate emotional awareness to recognize when anxiety levels are peaking. This can prepare individuals for what’s to come and provide them with options to address their anxiety before it escalates into shaking.
Moreover, past trauma or experiences can trigger anxiety responses, leading to bodily shaking. An understanding of personal history can offer insight into occurrences of anxiety and shakiness. When individuals learn how their past influences their present reactions, they can develop more informed strategies for handling stress. Ultimately, recognizing the myriad of causes will empower individuals in managing their body shaking symptoms more effectively.
Effective Breathing Techniques
One of the most powerful tools for managing anxiety and minimizing body shaking is through effective breathing techniques. When faced with anxiety, breathing becomes shallow, which can heighten feelings of panic. Practicing deep, controlled breathing can counteract this response. Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing encourage individuals to inhale deeply through the nose and exhale slowly through the mouth. This practice not only calms the nervous system but also reduces the physical sensations associated with anxiety-related shaking.
Another beneficial approach is the use of the 4-7-8 breathing technique. In this method, individuals breathe in for a count of four, hold for seven, and exhale for eight. This systematic approach to breath regulation not only stabilizes the heart rate but also increases the body's ability to manage stress effectively. Incorporating this practice into daily routines can help individuals stay grounded, especially in high-anxiety situations. Over time, mastering these techniques can lead to a tangible reduction in body shaking.
Mindful breathing exercises, where a person focuses entirely on their breath, can also help drown out racing thoughts that often accompany anxiety. By encouraging a focus on the present, these techniques reduce the likelihood of overwhelming emotions leading to physical reactions like shaking. Engaging in such practices during moments of uncertainty can foster a sense of control and empowerment.
In addition, using guided meditation or apps focused on breathing exercises can provide additional support. These resources offer structured programs to help individuals practice regularly and can provide reminders to take breaks and breathe. Building a habit around mindful breathing can become a manageable routine. Ultimately, these breathing techniques play a critical role in alleviating symptoms of anxiety, including body shaking.
Mindfulness and Grounding Techniques
When anxiety leads to body shaking, practicing mindfulness and grounding techniques can effectively anchor individuals in the present moment. Mindfulness encourages awareness of one’s thoughts, feelings, and physical sensations without judgment. This practice can help in recognizing the onset of anxiety and the accompanying physical symptoms. Mastering mindfulness can significantly reduce the power of anxious thoughts over time.
Grounding techniques, such as the 5-4-3-2-1 method, can also be beneficial. This technique involves identifying five things one can see, four things one can feel, three things one can hear, two things one can smell, and one thing one can taste. This sensory engagement effectively pulls the focus away from anxiety and stabilizes body responses. By developing an appreciation for the present, individuals can create a safe environment that minimizes the likelihood of shaking.
Another effective practice is progressive muscle relaxation, which helps to systematically tense and then relax muscle groups throughout the body. This process not only elevates physical awareness but also encourages a deeper connection between mental and physical states. As individuals learn to differentiate between tension and relaxation, it becomes easier to manage symptoms of anxiety and shaking.
Additionally, participating in yoga or tai chi can integrate mindfulness and movement into a calming practice. These activities promote physical awareness and enhance emotional regulation, which can significantly alleviate feelings of anxiety. Engaging in regular practices of mindfulness and grounding can lead to long-term benefits, not only reducing body shaking but also improving overall mental health.
Building a Support System
Having a strong support system is vital for managing body shaking and anxiety. Friends, family, or support groups can provide a sense of belonging and understanding, essential when dealing with anxiety. Expressing concerns about body shaking in a safe space encourages open dialogue and validation of feelings. Supportive relationships contribute greatly to feeling less isolated in coping with symptoms. Listening to others’ experiences can also offer new perspectives on managing similar issues.
Seeking professional help, such as a therapist or psychologist, can be an important step to understanding and addressing body shaking. Professionals can offer personalized strategies tailored to individual needs that can effectively reduce anxiety symptoms. They can also facilitate conversations around coping techniques that have worked for others, offering insights that may resonate with the individual. The support of a professional can be life-changing, especially in those moments when anxiety seems insurmountable.
Joining anxiety support groups—either online or in-person—can provide a sense of community. These groups often share resources, coping strategies, and emotional support that individuals can utilize. Engaging with those who understand the struggles of anxiety can create a powerful network where individuals can share experiences without fear of judgment. This collective approach strengthens resilience and fosters a sense of courage in facing body shaking.
Additionally, cultivating self-compassion is essential in this journey. Individuals should practice being kind to themselves rather than self-critical when facing anxiety and shaking. This kindness helps to build resilience over time and encourages a healthier relationship with one’s emotions. Establishing self-supportive practices alongside a broader support system can yield phenomenal results in managing body shaking as a symptom of anxiety.
Seeking Help and Treatment
Understanding the Importance of Seeking Help
Recognizing the symptoms of anxiety is crucial in seeking help. Body shaking often manifests as a physical response to overwhelming stress or fear. When individuals notice this symptom, it may be indicative of an anxiety disorder that requires professional attention. Delaying help can lead to worsening symptoms, so timely intervention is essential for effective management.
The first step in addressing body shaking related to anxiety is acknowledging its occurrence. Many individuals may feel embarrassed or ashamed for experiencing such a symptom. However, it is important to know that anxiety disorders are common and affect numerous people. Opening up about one’s experiences is a significant step toward recovery.
In many cases, individuals may not fully understand the resources available to them. Psychologists, therapists, and support groups can provide a safe space for discussing these symptoms and their impacts. Professionals in the field can guide individuals through their anxiety and help them develop coping strategies that can reduce or eliminate body shaking during stressful situations.
Support from loved ones can also play a critical role in the healing process. Conversations with trusted friends or family members can alleviate feelings of isolation that often accompany anxiety. This supportive network is invaluable when seeking professional help, as it can provide encouragement and motivation throughout the treatment journey.
Types of Treatment Approaches
When seeking treatment for anxiety-related body shaking, several therapeutic approaches are available. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective methods, focusing on identifying and changing negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety. CBT equips individuals with tools to confront their fears and reduce the physiological symptoms associated with anxiety.
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques have also gained popularity as treatment options. Practices such as deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help individuals regain control over their physical responses to anxiety. Regular practice of these techniques can lead to long-term reductions in anxiety symptoms, including body shaking.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage anxiety. Anti-anxiety medications, antidepressants, or beta-blockers can be utilized depending on the severity of symptoms and the individual's unique situation. It's important to have an open dialogue with a healthcare provider about potential side effects and the expected duration of use.
Supportive therapies, such as group therapy or support groups, can also be beneficial. Sharing experiences with others who face similar challenges can provide a sense of community and understanding, ultimately making it easier to confront anxiety and its physical manifestations like body shaking.
Self-Care Strategies for Managing Symptoms
In addition to formal treatment options, self-care plays an essential role in managing anxiety and its symptoms. Regular exercise is one effective strategy, as physical activity can significantly reduce anxiety levels by releasing endorphins, which enhance mood and alleviate stress. Incorporating activities like jogging, yoga, or dancing into one's routine can serve as powerful tools against anxiety-induced body shaking.
Maintaining a balanced diet can also have a positive impact on mental health. Consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals can nourish the brain and stabilize mood. Staying hydrated and limiting caffeine and sugar intake can further contribute to overall well-being and lessen anxiety symptoms.
Establishing consistent sleep patterns is crucial for managing anxiety effectively. Quality sleep supports emotional regulation and cognitive function. Individuals should aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night to improve their ability to cope with stressful situations and mitigate body shaking during anxiety episodes.
Finally, engaging in creative outlets such as art, music, or writing can also help alleviate anxiety. These activities enable individuals to express their feelings and explore the underlying factors contributing to their anxiety. Such expressions can provide clarity and relief, contributing to a balanced mental state.
Building a Support Network
Creating a robust support network is vital in managing anxiety symptoms. Connections with empathetic friends and family members can serve as a buffer, offering comfort during difficult times. By expressing needs and feelings to a trusted individual, anxiety sufferers can feel less isolated and more grounded.
Joining local or online support groups can also provide additional reinforcement. These groups often consist of people who share similar challenges and can offer insight or strategies that have worked for them. Building relationships within these communities can foster a sense of belonging and shared purpose, mitigating feelings of anxiety.
Moreover, educational resources can enhance understanding and awareness of anxiety disorders. Books, podcasts, and workshops focused on mental health can empower individuals with knowledge, helping them navigate their experiences and enabling them to better support themselves and others.
Finally, professional mental health services may also include family therapy, where family members participate in the therapeutic process. This approach can build understanding and compassion, equipping families to support their loved ones more effectively. Involving loved ones in the treatment process ensures a holistic approach to tackling anxiety and its physical manifestations, such as body shaking.