The Essential Role of Anxiety Management in Daily Life
1. The Impact of Unmanaged Anxiety
Understanding the Physical Effects of Unmanaged Anxiety
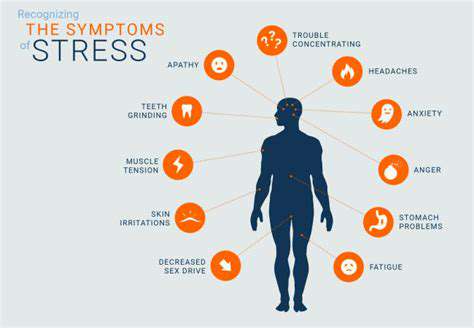
Anxiety isn't just a mental health concern; it has substantial physical repercussions as well. When anxiety levels aren't managed effectively, they can lead to chronic stress. This stress manifests through various physical symptoms such as headaches, muscle tension, and digestive issues. Over time, these chronic symptoms can significantly hinder daily activities and overall health.
Heart palpitations, which many experience during anxiety episodes, are indicative of the body's 'fight or flight' response being triggered. This response can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, putting strain on the cardiovascular system. Persistent anxiety can contribute to long-term heart problems if left unmanaged.
Furthermore, anxiety can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or poor-quality sleep. A lack of restful sleep can exacerbate anxiety, creating a vicious cycle that is difficult to break. Sleep deprivation affects cognitive functions, making it harder to focus, remember information, or perform daily tasks efficiently.
The immune system can also be compromised due to the prolonged effects of unmanaged anxiety. Stress hormones can weaken immune responses, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses and infections. Keeping anxiety in check is therefore crucial for maintaining not just mental, but also physical well-being.
In summary, unmanaged anxiety has profound effects on the body's physical health. Recognizing and addressing these physical symptoms through anxiety management practices is essential for leading a healthy, balanced life.
Psychological Repercussions of Unmanaged Anxiety
The psychological effects of unmanaged anxiety can be equally detrimental. Individuals may find themselves caught in a cycle of negative thinking and rumination. This can lead to feelings of hopelessness and despair, making it challenging to engage in normal day-to-day activities.
Social interactions are often adversely affected as well. People dealing with unmanaged anxiety may withdraw from social situations, fearing judgment or discomfort. This withdrawal can lead to loneliness and isolation, further exacerbating anxiety and creating a feedback loop that amplifies the problem.
Unmanaged anxiety can also trigger a decrease in self-esteem. Constant worry about potential failures or negative outcomes can make individuals doubt their capabilities. This lack of confidence can deter them from pursuing opportunities, leading to stagnation in both personal and professional growth.
Consequently, productivity and performance at work or school can suffer. Anxiety often results in difficulty concentrating, completing tasks, and meeting deadlines. This can create additional stress and anxiety, forming a cycle that can be hard to break and impacting one's overall quality of life.
In essence, the psychological repercussions of unmanaged anxiety extend beyond the individual. They can ripple out to affect relationships, career prospects, and overall happiness, underscoring the importance of effective anxiety management techniques.
Practical Strategies for Managing Anxiety
There are various practical strategies that individuals can adopt to manage their anxiety effectively. One of the most effective methods is practicing mindfulness and meditation. Mindfulness involves being present in the moment and can help break the cycle of negative thought patterns. Regular meditation can also promote relaxation and enhance emotional regulation.
Physical activity is another powerful tool in managing anxiety. Exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, the body's natural mood lifters. Even a simple walk can reduce anxiety symptoms and improve overall mental health. Finding a routine that incorporates regular physical activity can be incredibly beneficial for long-term anxiety management.
Building a robust support system is also crucial. Sharing feelings and experiences with friends, family, or support groups can alleviate feelings of isolation and provide emotional relief. Open conversations about anxiety can help in normalizing the struggles and finding community-based solutions.
Establishing healthy routines can further assist in managing anxiety. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, limiting caffeine and alcohol, and ensuring regular sleep patterns. These lifestyle modifications can contribute to better mental health and resilience against anxiety.
Lastly, seeking professional help is an essential step for many individuals. Therapy, whether through cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or other modalities, can provide tailored strategies for managing anxiety. Medications may also be an option for some, highlighting the importance of consulting a healthcare provider for personalized treatment plans.
2. Techniques for Effective Anxiety Management

1. Understanding Your Triggers
To effectively manage anxiety, it’s crucial to identify the specific triggers that cause feelings of unease. Recognizing these triggers can help individuals anticipate and prepare for anxiety-provoking situations.
Many people find it helpful to maintain a journal where they note down situations that elevate their anxiety levels. This practice allows for a clearer understanding of patterns over time.
2. Mindfulness and Meditation Practices
Mindfulness and meditation techniques can significantly reduce anxiety by promoting relaxation and a sense of presence. Engaging in these practices regularly can help reset the mind and alleviate the overwhelming thoughts that contribute to anxiety.
Even starting with just a few minutes each day can make a substantial difference. Over time, this can lead to a more grounded and less reactive mindset.
3. Breathing Exercises
Simple breathing exercises can be an effective immediate response to anxiety. Techniques such as deep belly breathing can help signal the body to relax and alleviate the physical symptoms of anxiety.
Practicing these exercises when feeling anxious can help regain control and calm the mind. Incorporating these into your daily routine can provide a valuable tool for managing stress.
4. Physical Activity and Its Benefits
Regular physical activity can have a profound impact on anxiety levels. Exercise not only distracts from anxious thoughts but also releases endorphins that elevate mood and enhance overall mental health.
Integrating even short bursts of physical activity, like walking or stretching, can be rejuvenating. It's essential to find activities that are enjoyable, making it easier to incorporate them into daily life.
5. Seeking Professional Help
Sometimes, self-management techniques may not be enough, and seeking professional help can be crucial. Therapists and counselors can provide tailored strategies and support, helping individuals navigate their anxiety more effectively.
Don’t hesitate to reach out for help; it is a sign of strength rather than weakness. Professional guidance can open avenues for understanding and coping that might not be apparent when tackling anxiety on your own.
3. The Role of Support Systems
Understanding Support Systems
Support systems encompass the people and resources that provide emotional, practical, and sometimes financial assistance. These can include family members, friends, colleagues, and professional services such as therapists or support groups.
Having a robust support system plays a crucial role in managing anxiety. It gives individuals a reliable network they can turn to during stressful times, helping to alleviate feelings of isolation that often accompany anxiety disorders.
Support systems can take many forms, from informal check-ins with friends to participating in organized therapy groups. Each type of support provides unique benefits tailored to individual needs, enhancing coping mechanisms.
Research shows that emotional support can lead to lower levels of stress and anxiety, making it an essential component in managing mental health. Supportive relationships can also foster resilience, allowing individuals to handle life's challenges more effectively.
Ultimately, understanding the various facets of support systems can empower individuals struggling with anxiety to seek help and forge connections that enhance their emotional well-being.
Building a Strong Support Network
Creating a strong support network requires intentionality and effort. Begin by identifying people in your life who are understanding, empathetic, and can provide comfort during tough times.
Consider expanding your support network beyond immediate family and friends. Joining community groups, attending workshops, or seeking online forums can connect you with others who face similar challenges.
It’s also important to communicate your needs clearly to your support network. This transparency helps others understand how best they can assist you, whether it is through listening, providing advice, or just being there when you need help.
Regularly nurturing these relationships contributes to their strength. Schedule time to interact, whether through casual meet-ups or more structured activities, to maintain the bonds that provide support and encouragement.
Remember that it's a two-way street; offer support back to those in your network. Such mutual support strengthens relationships and reinforces the feeling of connection.
Leveraging Professional Support
In addition to informal support networks, professional help is a key element in anxiety management. Therapists, psychologists, and counselors can provide expert guidance tailored to individual situations.
Psychotherapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), has been proven effective in treating anxiety disorders. These professionals can teach coping strategies and address negative thought patterns that fuel anxiety.
Medication is another option for some individuals, particularly when anxiety symptoms are severe. Consulting with a psychiatrist can help determine if medication is appropriate and what type would be the best fit.
Participating in structured support groups led by trained facilitators can also provide valuable insights and encouragement from those experiencing similar struggles. Such environments foster open discussion and sharing of coping strategies.
Recognizing the benefits of professional support can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards managing their anxiety effectively, leading to a healthier, more balanced life.
The Impact of Community Support
Community support systems play an essential role in holistic anxiety management. Communities can provide a sense of belonging that helps offset feelings of loneliness and despair often associated with anxiety.
Local organizations, clubs, or even online social platforms can offer connections to others who share common interests and experiences. Engaging in these communities can promote emotional well-being and lessen anxiety symptoms.
Volunteering or participating in community service can provide a dual benefit: helping others while simultaneously gaining a sense of purpose and fulfillment, which are crucial for mental health.
Awareness campaigns in communities also help reduce stigma around mental health issues and facilitate open discussions, making it easier for individuals to seek the help they need.
Ultimately, tapping into community-based resources can enhance personal support systems, enriching an individual's overall experience in managing anxiety in daily life.
4. Seeking Professional Help

Understanding When to Seek Professional Help
Recognizing the signs of severe anxiety can be challenging for many individuals. When anxiety begins to interfere with daily functioning, it is crucial to seek professional assistance.
Common indicators include persistent worry, avoidance behaviors, and physical symptoms like increased heart rate. Consulting a professional can provide clarity and pathways to effective coping strategies.
Types of Professional Help Available
There are various forms of professional help available for anxiety management, including therapy, medication, and support groups. Therapists can provide tailored strategies to navigate anxiety more effectively.
Medications, prescribed by doctors, can also play a crucial role in reducing symptoms, allowing individuals to focus more on coping mechanisms. Support groups provide a sense of community and shared experiences, which can be immensely comforting.
Benefits of Early Intervention
Seeking help early can significantly improve outcomes for those experiencing anxiety. Individuals who address their anxiety promptly tend to develop healthier coping mechanisms and experience less disruption in their lives.
Moreover, early intervention can prevent the escalation of symptoms, leading to a faster and more manageable recovery process. By prioritizing mental health, individuals can enhance their overall quality of life.
5. The Long-term Benefits of Managing Anxiety
Enhanced Mental Health and Well-being
Managing anxiety effectively can lead to significant improvements in overall mental health. By developing coping strategies and emotional regulation techniques, individuals can experience reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression.
With consistent practice in anxiety management, people often report a greater sense of calm and more resilience in the face of everyday stressors.
Improved Physical Health
The link between mental health and physical well-being is well-documented. Reducing anxiety not only alleviates mental strain but also positively impacts physical health, leading to lower blood pressure and improved heart health.
Moreover, individuals who manage their anxiety are more likely to engage in healthy behaviors, such as regular exercise and balanced nutrition, contributing to a healthier lifestyle.
Stronger Relationships and Social Connections
Effective anxiety management can enhance interpersonal relationships by fostering better communication and reducing avoidance behavior. This can lead to stronger connections with family, friends, and colleagues.
As individuals become more confident in managing their anxiety, they are often more willing to engage in social activities and form meaningful relationships, which are crucial for a supportive social network.