How Stress Levels Affect Overall Health and Well being
The Physiological Impact of Stress
The Body's Stress Response
When an individual experiences stress, the body undergoes a physiological reaction known as the "fight or flight" response. This reaction is triggered by the release of stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones prepare the body to either confront or flee from a perceived threat, leading to increased heart rate, heightened alertness, and energy surge.
While this response can be beneficial in short-term scenarios, chronic stress can lead to negative health consequences. Prolonged exposure to stress hormones can disrupt various bodily functions, including immune response and digestion, leading to chronic health issues such as autoimmune diseases or gastrointestinal disorders.
Understanding this response is crucial because it helps individuals recognize the importance of stress management techniques—such as mindfulness, meditation, and physical activity—in mitigating these physiological effects and promoting overall well-being.
The Mental and Emotional Consequences
Beyond the physiological effects, stress significantly impacts mental health and emotional stability. High stress levels can lead to anxiety disorders, depression, and cognitive impairments. Individuals under constant stress may find it challenging to concentrate, make decisions, or manage day-to-day responsibilities effectively.
Additionally, emotional responses to stress can manifest as irritability, mood swings, or withdrawal from social interactions. These emotional struggles often create a cycle where stress exacerbates mental health issues, leading to further stress and diminished coping mechanisms.
It is essential to recognize these signs of mental and emotional strain. By implementing stress management strategies and seeking support, individuals can break this cycle and nurture a healthier mindset.
Long-term Health Risks Associated with Stress
Chronic stress has been linked to numerous long-term health risks, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and obesity. The persistent state of stress leads to heightened inflammation and blood pressure, which contribute to the development of these conditions over time.
Moreover, stress can influence lifestyle choices, prompting unhealthy behaviors such as poor eating habits, smoking, or excessive alcohol consumption. These behaviors further increase the risk of developing chronic diseases and create a detrimental impact on overall health.
To combat these long-term risks, proactive measures such as adopting a balanced lifestyle, engaging in regular physical exercise, and building strong social support networks can be effective in managing stress levels and promoting long-term health and well-being.
The Mental and Emotional Effects of Stress
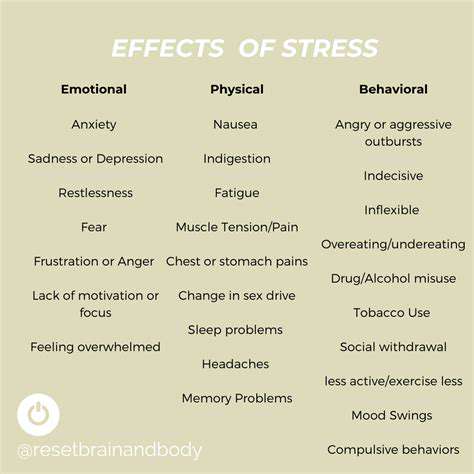
The Psychology of Stress
Stress is a natural response to challenges and demands in life. It triggers the body's fight-or-flight response, releasing hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. When stress becomes chronic, it can lead to significant psychological issues such as anxiety and depression.
These mental health conditions can further complicate daily functioning and relationships. Individuals may find themselves withdrawing from social interactions or losing interest in activities they once enjoyed. It's crucial to recognize these symptoms early to seek appropriate help and intervention.
Additionally, stress can impact cognitive functions such as memory and focus. People under constant stress may struggle with decision-making and experience diminished productivity. Understanding the psychology behind stress is essential in developing strategies for effective coping.
The Physical Consequences of Stress
While stress primarily affects mental health, its physical repercussions can be profound. Chronic stress can lead to a variety of health problems, including cardiovascular diseases, obesity, and gastrointestinal disorders. The body's prolonged exposure to stress hormones can significantly disrupt normal bodily functions.
Moreover, stress is known to weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. This means that a person under significant stress may find it harder to recover from illnesses. Taking steps to manage stress effectively can help mitigate these negative physical outcomes.
In addition, stress can manifest through physical symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, and muscle tension. Recognizing these signs is vital in understanding how stress impacts overall health and well-being. Engaging in relaxation techniques and physical activity can significantly reduce these symptoms.
Coping Strategies for Managing Stress
Managing stress is essential for maintaining both mental and physical health. One effective strategy is practicing mindfulness or meditation, which allows individuals to focus on the present moment and reduce overwhelming feelings. Incorporating regular exercise into one's routine is another beneficial way to alleviate stress.
Social support plays a critical role in stress management. Connecting with friends and family can provide emotional support and help individuals process their feelings. Sharing experiences and seeking advice can be incredibly beneficial for coping with stress.
Additionally, developing time management skills can alleviate feelings of being overwhelmed. Setting realistic goals and prioritizing tasks helps create a sense of control. Implementing these strategies can lead to a healthier approach to handling stress in everyday life.
Practical Strategies for Stress Management

Understanding the Impact of Stress on Physical Health
Stress has a profound impact on physical health, often manifesting in various ailments. Chronic stress can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease and diabetes. The body's response to stress involves the release of hormones such as cortisol, which, when elevated for extended periods, can disrupt numerous bodily functions.
Furthermore, stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. Over time, persistent stress contributes to conditions such as obesity and gastrointestinal problems. The link between the mind and body underscores the necessity of addressing stress in order to maintain overall health.
It’s essential to recognize the signs of stress early. These may include headaches, fatigue, and changes in appetite or sleeping patterns. By addressing these symptoms promptly, individuals can prevent further health deterioration.
Adopting a proactive approach to stress management is crucial for long-term well-being. This can involve lifestyle changes, seeking social support, or utilizing relaxation techniques. The influence of stress on physical health is undeniable and should not be overlooked.
Ultimately, understanding how stress affects physical health can empower individuals to make more informed choices about their lifestyle. Implementing effective stress management strategies can lead to improved physical health outcomes.
Emotional and Mental Health Consequences of Stress
In addition to physical health, stress greatly impacts emotional and mental well-being. Individuals under stress often experience heightened anxiety and depression levels. These mental health conditions can interfere with daily activities and diminish overall quality of life.
Stress can also affect cognitive functioning, including memory, decision-making, and concentration. This impairment can hinder productivity and lead to frustration in both personal and professional situations. Recognizing these mental health impacts is crucial for addressing stress effectively.
Moreover, prolonged stress can foster negative emotional coping mechanisms such as substance abuse or social withdrawal. These patterns exacerbate the initial stress, creating a vicious cycle that is difficult to break. Establishing healthy coping strategies can enhance resilience and promote emotional healing.
Support networks play a critical role in mitigating stress-related emotional challenges. Engaging with friends, family, or mental health professionals can alleviate feelings of isolation and improve coping skills. The importance of seeking help when needed cannot be overstated, especially in times of heightened stress.
Ultimately, understanding the emotional and mental health consequences of stress can encourage individuals to prioritize their mental well-being. Addressing these issues can lead to a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Effective Techniques for Stress Relief
Managing stress effectively requires a combination of strategies tailored to individual needs. Mindfulness and meditation are powerful tools for promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety. These practices encourage individuals to focus on the present and cultivate a sense of peace amid chaos.
Physical activity is another critical stress relief technique. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Engaging in regular physical activity can greatly enhance overall well-being and combat stress. It does not have to be strenuous; even moderate exercises like walking or yoga can make a significant difference.
Time management skills also play a vital role in stress reduction. By organizing tasks and setting priorities, individuals can avoid feeling overwhelmed. Developing a schedule or using productivity tools can help create a balanced routine and manage obligations effectively.
Additionally, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as a balanced diet and proper sleep, can improve resilience against stress. Nourishing the body and ensuring adequate rest enables individuals to better cope with stressful situations. This holistic approach to health fosters a stronger base for managing stress.
In conclusion, incorporating various stress relief techniques into daily life can lead to improved mental, emotional, and physical health. Finding the right combination of strategies is essential for effective stress management.