How Low Blood Sugar Can Trigger Anxiety Symptoms
The Mechanism Behind Low Blood Sugar and Anxiety
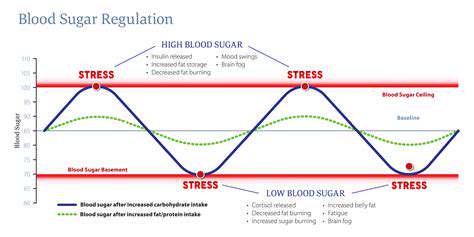
The Biological Responses to Low Blood Sugar
When blood sugar levels drop, the body activates a series of biological responses to counteract the low glucose levels. This includes the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can lead to symptoms commonly associated with anxiety, such as increased heart rate and a sense of urgency.
Additionally, the brain relies heavily on glucose as its primary energy source. When levels are insufficient, cognitive functions can be impaired, leading to feelings of confusion and distress.
These responses are part of the body’s survival mechanism, designed to prompt an immediate reaction to restore balance. However, in some people, these physiological changes may escalate anxiety symptoms.
The Connection Between Hypoglycemia and Anxiety Disorders
Research has shown a notable link between episodes of hypoglycemia and the development of anxiety disorders. Individuals who experience frequent low blood sugar may develop a heightened state of alertness and fear around food and eating times. This hyper-vigilance can lead to increased anxiety in daily life.
Moreover, the unpredictability of hypoglycemic episodes can create a continuous cycle of anxiety, where the fear of experiencing a drop in blood sugar instills a sense of dread. This can result in avoidance behaviors that can further impact one’s mental wellbeing.
Understanding this connection is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. It provides valuable insight into how physical health issues can manifest as psychological challenges.
Strategies to Manage Low Blood Sugar and Anxiety
Managing diet is crucial for individuals prone to low blood sugar. Consuming balanced meals that include complex carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats can help maintain steady glucose levels throughout the day. This can mitigate both physical and psychological symptoms associated with hypoglycemia.
Additionally, regular exercise can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall mood. Engaging in activities like walking, yoga, or biking promotes a balanced metabolic state, reducing the likelihood of anxiety spikes.
Moreover, techniques such as mindfulness and deep-breathing exercises can be beneficial. These practices help individuals learn to cope with anxiety symptoms as they arise, fostering a greater sense of control over one’s body and mind.
The Role of Professional Support and Intervention
For those experiencing significant anxiety linked to low blood sugar, it is important to seek professional help. Registered dietitians can provide tailored advice on meal planning to prevent hypoglycemic episodes. This professional guidance is essential for achieving long-term health improvements.
Additionally, mental health professionals can offer strategies to address anxiety management, which may include cognitive-behavioral therapy or other counseling techniques. These can assist individuals in reframing their relationship with food and anxiety.
Alongside lifestyle changes, medication may also be an option for some individuals, particularly if anxiety symptoms are severe. A comprehensive plan that addresses both dietary habits and mental health can lead to better outcomes for those affected by low blood sugar and anxiety.
Recognizing Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar

Common Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can present a variety of symptoms that may be alarming or distressing. Some common symptoms include sweating, shaking, and a fast heartbeat. These physical reactions are often the body’s immediate response to reduced glucose levels.
In addition to physical symptoms, individuals may also experience confusion or difficulty concentrating. This cognitive impairment can lead to feelings of panic or anxiety, further complicating the situation.
Moreover, emotional symptoms such as irritability or mood swings are common. These emotional swings can trigger a sense of anxiety, making it difficult for individuals to manage their responses.
People may also report feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness, which can create a sense of fear or impending doom. Such sensations can exacerbate anxiety symptoms, creating a vicious cycle.
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial. When individuals are aware of what low blood sugar feels like, they can take steps to address it before it escalates into more severe anxiety.
Psychological Impact of Low Blood Sugar
The psychological impact of low blood sugar can be profound and wide-ranging. Experiencing recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia can lead to heightened anxiety, particularly about future episodes. This condition can create a fear of food and regular eating habits, as individuals may worry that consuming too little might trigger another episode.
Furthermore, the stress of managing hypoglycemia can create a persistent state of hyper-vigilance. This heightened state of awareness can blur the lines between healthy caution and anxiety, causing individuals to feel overwhelmed.
Individuals might also develop anticipatory anxiety, where they worry excessively about when their next episode of low blood sugar will occur. This can significantly interfere with their daily lives and activities, leading to avoidance behaviors.
It's important to acknowledge that the psychological ramifications of low blood sugar can affect interpersonal relationships. Friends and family may not understand the severity of the situation, making it difficult for the individual to receive the support they need.
Ultimately, understanding the psychological impact of low blood sugar is vital for both patients and caregivers. This awareness can help in creating effective coping strategies to manage anxiety and improve overall well-being.
Managing Low Blood Sugar and Anxiety
Effective management of low blood sugar is key to reducing anxiety symptoms. Maintaining balanced meals and snacks throughout the day can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for anyone at risk of hypoglycemia.
Additionally, knowing which foods can quickly raise blood sugar can be beneficial. Simple carbohydrates, like glucose tablets or fruit juice, can provide a fast source of energy and alleviate symptoms rapidly.
Furthermore, stress-reduction techniques can be instrumental in managing anxiety. Mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can stabilize both mood and blood sugar levels.
Seeking professional help from a healthcare provider can also be important. A provider can offer personalized guidance on diet and lifestyle changes that can mitigate the effects of low blood sugar.
Finally, maintaining open communication about symptoms with friends and family can foster understanding and support. Creating a support network can be a powerful tool in managing both the physical and psychological aspects of low blood sugar.
Preventive Measures and Management Strategies
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main source of energy for the body's cells. It’s essential for various bodily functions, including brain activity. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for mental and physical well-being.
Normal blood sugar levels range from 70 to 130 mg/dL when fasting. Levels below 70 mg/dL are considered low, or hypoglycemia. This condition can lead to various symptoms, including anxiety, irritability, and confusion.
Low blood sugar can occur due to several factors, including prolonged fasting, excessive physical activity, or poorly managed diabetes. Understanding these factors is essential to prevent hypoglycemia and its psychological effects.
Individuals often experience a rapid drop in blood sugar levels, leading to immediate physical symptoms. This fluctuation can dramatically affect mood and lead to feelings of anxiety or panic, making it important to monitor levels actively.
Educational resources are available to help individuals learn how to keep their blood sugar levels stable. Consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized strategies to manage blood sugar effectively.
Link Between Low Blood Sugar and Anxiety
The connection between low blood sugar and anxiety is complex. When glucose levels fall, the body initiates a stress response, which can stimulate the release of hormones such as adrenaline. This can manifest as anxiety symptoms.
People may not realize that their anxiety symptoms can be caused by physiological conditions like hypoglycemia. This lack of awareness can exacerbate the problem, leading to a cycle of anxiety and unstable blood sugar levels.
Individuals might experience physical symptoms, such as trembling, sweating, or a racing heart, which can mimic anxiety attacks. Recognizing this distinction is essential for effective management.
Moreover, the brain relies heavily on glucose, and when levels drop, cognitive functions can become impaired. This impairment can lead to further anxiety, creating a feedback loop that can be difficult to break.
Research continues to explore this relationship, highlighting the importance of considering both physical and psychological factors when addressing anxiety, particularly in those with a history of diabetes or hypoglycemia.
Preventive Measures for Low Blood Sugar
One of the most effective ways to prevent low blood sugar is to eat regular, balanced meals that include a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. This can help maintain stable glucose levels throughout the day.
Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is crucial, especially for individuals at risk, such as those with diabetes. Keeping a log of food intake and corresponding glucose levels can help identify patterns and prevent drops.
Engaging in regular physical activity can help regulate blood sugar levels but should be balanced with proper nutrition to avoid hypoglycemia. It's essential to understand how exercise impacts individual glucose responses.
Staying hydrated and avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol can also be beneficial, as these can affect blood sugar fluctuations. Incorporating hydration into daily routines can help support overall health.
For those prone to severe drops, keeping snacks on hand, especially those rich in complex carbohydrates and protein, can provide a quick energy boost and stabilize blood sugar when needed.
Management Strategies for Anxiety Related to Low Blood Sugar
When low blood sugar triggers anxiety, it’s important to address both conditions simultaneously. Identifying stressors and implementing relaxation techniques can help minimize anxiety symptoms.
Practicing mindfulness and deep-breathing exercises can be effective in calming the mind when anxious feelings arise. Grounding techniques can also help individuals feel more present and reduce the influx of anxious thoughts.
Developing a support system, whether through friends, family, or support groups, can provide emotional assistance. Talking openly about experiences with low blood sugar and anxiety can help reduce feelings of isolation.
Educational interventions, such as workshops on managing blood sugar and anxiety, can equip individuals with practical skills to handle both issues. Knowledge empowers individuals to make informed choices regarding their health.
Lastly, it may be beneficial for individuals experiencing severe anxiety due to low blood sugar to consult mental health professionals. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can provide tools to manage symptoms effectively.
When to Seek Professional Help
It's essential to recognize when low blood sugar is a concern. Persistent symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as confusion, irritability, or recurrent anxiety, warrant a discussion with a healthcare professional.
Indicator symptoms may include frequent episodes of low blood sugar, difficulty concentrating, or increased feelings of anxiety without clear triggers. These signs can indicate a need for further assessment and intervention.
Working with a healthcare provider to establish a personalized management plan can significantly improve quality of life. This plan may include a combination of dietary adjustments, medications, and psychological support.
A healthcare provider can also help determine the necessity of continuous glucose monitoring systems for individuals at high risk of severe hypoglycemia. These devices can alert users to falling blood sugar levels in real time.
Remember, seeking help is a strength, not a weakness. Addressing both low blood sugar and anxiety symptoms can lead to better overall health and a more balanced life.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Understanding the Relationship Between Blood Sugar Levels and Anxiety
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can significantly impact the body and mind. When blood sugar levels drop, the brain is deprived of its primary energy source, leading to various cognitive and emotional symptoms. Anxiety is one common reaction, as the body enters a state of stress in response to the lack of glucose, which is crucial for brain function.
Individuals may experience increased heart rate, sweating, and feelings of panic when their blood sugar drops. This physiological response can mimic or exacerbate existing anxiety disorders, creating a vicious cycle where anxiety leads to poor eating habits, further contributing to low blood sugar episodes.
Strategies for Managing Low Blood Sugar and Anxiety
To manage both low blood sugar and its anxiety-related symptoms, it is essential to maintain stable glucose levels throughout the day. This can be achieved through a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Regular meal timing and incorporating snacks can also help prevent significant drops in blood sugar.
Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, or physical activity can alleviate anxiety symptoms when they arise. Recognizing the signs of low blood sugar early and addressing them swiftly with a quick source of glucose, like fruit juice or glucose tablets, can also help in managing the situation effectively.