Recognizing Silent Anxiety: Signs and Symptoms
Outline
Silent anxiety leads to overlooked physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat and discomfort.
Chronic anxiety affects physical health, leading to issues like hypertension and fatigue.
Emotional toll includes isolation, frustration, and low self-esteem for those affected.
Therapy and support groups help me to express emotions linked to silent anxiety.
Exercise, deep breathing, and mindfulness are effective strategies for managing symptoms.
Cognitive symptoms include distractibility, negative thinking, and indecisiveness.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps manage negative thought patterns effectively.
Regular routines and social support are crucial for managing silent anxiety symptoms.
Recognizing silent anxiety is key for timely intervention and support.
Avoidance behavior can hinder personal and professional progress for affected individuals.
Seeking help is vital for recovery; resources like therapists and groups exist.
Mindfulness and a healthy lifestyle empower individuals to cope with silent anxiety.
Physical Symptoms of Silent Anxiety
Understanding the Body's Response to Anxiety
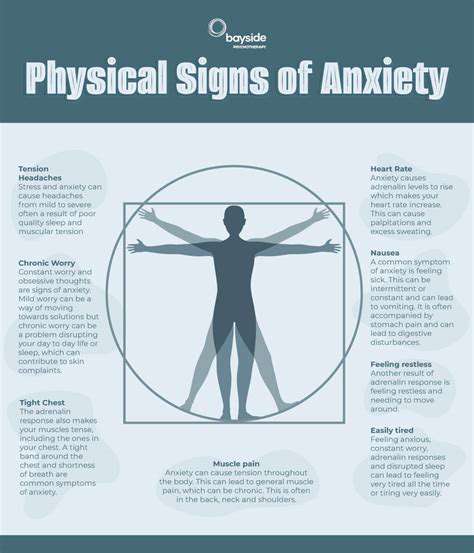
Silent anxiety often manifests through a range of physical symptoms, which can be easily overlooked. Individuals may not realize that their body is reacting to their mental state until symptoms become more pronounced. This can include a rapid heartbeat, muscle tension, or even gastrointestinal issues. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for recognizing the underlying anxiety that may not be vocalized.
When anxiety goes unspoken, it often builds up within the body, resulting in chronic discomfort or pain. Many people experiencing silent anxiety may feel persistent fatigue or a sense of restlessness that they cannot quite identify. These physical sensations can create a cycle of stress, where anxiety exacerbates feelings of unease, leading to further physical complaints.
Moreover, the body might produce stress hormones that trigger a fight-or-flight response, making individuals feel on edge. This physiological reaction can cause sweating, headaches, and even dizziness, symptoms that may seem unrelated to anxiety at first glance. Recognizing these connections is key to addressing both physical and mental health comprehensively.
It's essential to pay attention to how the body communicates stress signals. Keeping a journal, tracking symptoms, or consulting with health professionals can lead to better understanding and management of these conditions. By acknowledging these signs, individuals can begin to differentiate between typical bodily responses and those rooted in silent anxiety.
The Link Between Silent Anxiety and Physical Health
There is a significant connection between silent anxiety and various physical health issues. Chronic anxiety can lead to conditions such as hypertension and heart disease since it places continuous strain on the cardiovascular system. Being aware of this relationship is vital for individuals who may dismiss their anxiety as mere stress.
Furthermore, those with silent anxiety may neglect their physical health, choosing to focus on managing daily responsibilities instead. This neglect can lead to unhealthy habits, like poor nutrition or lack of physical activity, exacerbating physical symptoms of anxiety. It’s important to prioritize both mental and physical health to combat this cycle effectively.
Another dimension to consider is the impact of anxiety on the immune system. High levels of anxiety can suppress immune function, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses. Recognizing how silent anxiety might undermine overall well-being is crucial for fostering a healthier lifestyle and taking proactive measures to mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, understanding the physical implications of silent anxiety is integral to promoting better health outcomes. Regular health check-ups, stress management techniques, and supportive relationships can serve as protective factors against the adverse effects of anxiety on physical health.
Emotional Ramifications of Physical Symptoms
The emotional toll of experiencing physical symptoms related to silent anxiety can be profound. Individuals may feel isolated or misunderstood, as they struggle to convey the impact of their symptoms to others. This isolation can feed into their anxiety, leading to a vicious cycle of emotional and physical suffering.
Moreover, many individuals may experience heightened feelings of frustration or helplessness as they navigate their symptoms without acknowledgment from those around them. This can often result in low self-esteem or depressive feelings, making it even harder for individuals to reach out and seek help. The emotional intricacies related to silent anxiety often complicate recovery.
Seeking therapy or support groups can provide valuable avenues for emotional expression and understanding. Sharing experiences with others who have similar struggles allows individuals to feel seen and validated. By verbalizing their experiences, they can begin to disentangle the emotional from the physical manifestations of their anxiety.
Fostering emotional awareness is paramount. Mindfulness techniques, journaling, and creative outlets can play significant roles in helping individuals manage their emotional responses. Identifying triggers and exploring emotional reactions can provide a roadmap toward healing and understanding oneself better.
Practical Strategies for Addressing Physical Symptoms
There are several practical strategies that individuals can utilize to address the physical symptoms of silent anxiety effectively. Regular physical activity is one of the most powerful tools, as exercise can help reduce stress hormones and promote the release of endorphins, known as 'feel-good' hormones. Incorporating movement into one’s daily routine can alleviate many physical symptoms associated with anxiety.
Moreover, deep breathing exercises and mindfulness practices can help calm the body's response to anxiety. These techniques encourage relaxation, allowing individuals to regain control over their physical sensations. Activities such as yoga or tai chi also combine movement with mindful breathing, which can be particularly beneficial for those dealing with silent anxiety.
Nutrition plays a critical role too; maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is paramount for overall health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and probiotics can directly impact mood and anxiety levels. Individuals should be mindful of their dietary choices as an integral part of managing silent anxiety symptoms.
Lastly, seeking professional guidance from healthcare providers or mental health professionals can provide tailored support and intervention strategies. Incorporating therapy, medication, or alternative treatments can offer a comprehensive approach to managing both the mental and physical health aspects of silent anxiety.
Emotional and Behavioral Indicators

Understanding Emotional Indicators of Anxiety
Recognizing emotional indicators is paramount in identifying silent anxiety. Individuals suffering from anxiety may experience overwhelming feelings of fear or dread, often without a clear cause. These emotions can manifest as persistent worry that impacts daily functioning and hampers peace of mind. Emotions associated with anxiety can fluctuate, sometimes becoming intense, which further complicates emotional regulation.
Another emotional indicator is the sense of being easily overwhelmed by everyday tasks or situations. Those facing silent anxiety may find that their emotional responses are heightened, making common social interactions feel daunting. This heightened sensitivity can lead to avoidance behaviors, where the individual seeks to minimize exposure to stressful situations instead of facing them. It's important to acknowledge these feelings since they can significantly impact one's self-esteem and overall mental health.
Shame and guilt often accompany silent anxiety, leading individuals to feel inadequate or abnormal for experiencing discomfort. This stigma can prevent many from seeking help, reinforcing the silence surrounding their struggles. Addressing these emotions openly can foster a more supportive environment for discussion and healing.
Furthermore, irritability can be a significant emotional sign of underlying anxiety. Those suffering from silent anxiety might find themselves snapping at loved ones or feeling easily annoyed by minor inconveniences. Understanding these emotional eruptions as part of a larger anxiety experience can encourage individuals to approach their feelings with compassion.
Exploring Behavioral Signs of Anxiety
Behavioral indicators of anxiety often intertwine with emotional symptoms, creating a complex web that can be challenging to navigate. One common behavior exhibited is avoidance, where individuals may shy away from social gatherings or situations that trigger anxiety. This avoidance can become a pattern, leading to isolation and further exacerbating feelings of loneliness and fear.
Another significant behavioral sign is a change in sleep patterns. Those dealing with silent anxiety may struggle with insomnia, unable to quiet their racing thoughts and fall asleep. Conversely, other individuals might find themselves sleeping excessively as a way to escape their anxiety. This inconsistency in sleep can lead to fatigue, which negatively impacts overall well-being and daily functioning.
Physical restlessness can also serve as a behavioral indicator of anxiety. Individuals may fidget, tap their feet, or engage in other repetitive actions as a way of managing their anxious feelings. Such nervous habits can be distracting and may go unnoticed by the person engaging in them, making it essential for friends and family to be vigilant and supportive.
Furthermore, a decrease in productivity can signal the presence of silent anxiety. Anxiety can sap motivation, leading to feelings of procrastination or disengagement from responsibilities. Recognizing these behaviors as symptoms rather than personal failings is crucial in creating an environment that encourages help-seeking and healing.
Cognitive Signs of Silent Anxiety
Understanding the Cognitive Symptoms of Silent Anxiety
Cognitive symptoms play a crucial role in understanding silent anxiety as they can often manifest without overt signs. Individuals grappling with silent anxiety may experience distractibility, which hampers their ability to focus on tasks at hand. This inability to concentrate can stem from persistent worry or fear, creating an overwhelming mental barrier that is hard to overcome. As a person struggles to engage with their environment, this cognitive impairment can significantly affect productivity and overall well-being.
Moreover, negative thinking patterns are common manifestations of silent anxiety. Individuals may find themselves caught in a cycle of pessimistic thoughts, forecasting negative outcomes in various aspects of life. This incessant rumination leads them to dwell on what might go wrong, thereby amplifying their feelings of unease and fear. Such toxic thought patterns can lead to a diminished sense of self-worth and an increased likelihood of social withdrawal, as the individual fears judgement and rejection.
Another prevalent cognitive sign is an overwhelming sense of being on edge or feeling an impending sense of doom. People with silent anxiety may often experience a heightened state of alertness, constantly scanning their surroundings for potential threats. This hypervigilance can result in fatigue, as their brain is perpetually in a state of readiness, draining mental energy and exacerbating feelings of anxiety. In situations of perceived danger or stress, this state of mind can feel like an insurmountable hurdle to navigate.
Additionally, indecisiveness is a significant cognitive symptom that can hinder effective problem-solving and everyday functioning. Those with silent anxiety may struggle to make even trivial decisions, fearing the consequences of their choices. This paralysis by analysis can leave them feeling frustrated and lost, leading to an escalation of their anxiety. As they grapple with uncertainty, the cumulative impact of indecisiveness often fuels their anxiety further, creating a vicious cycle that is difficult to break.
Strategies for Managing Cognitive Symptoms of Silent Anxiety
Understanding the cognitive signs of silent anxiety is essential, but equally important is finding effective strategies for management. One effective approach is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which encourages individuals to identify and challenge their negative thought patterns. By reframing these thoughts and adopting a more balanced perspective, individuals can alleviate some of the burdens that contribute to their silent anxiety. Engaging in CBT can empower individuals to regain control over their thought processes and enhance their overall mental resilience.
Mindfulness practices also play a significant role in managing cognitive symptoms associated with silent anxiety. Techniques such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises enable individuals to anchor their thoughts in the present, reducing the tendency to ruminate on past worries or future fears. By fostering a state of heightened awareness and acceptance towards their feelings, they can create space to cultivate calmness within themselves, promoting a sense of tranquility amid anxious thoughts.
Additionally, establishing a regular routine can serve as a powerful strategy for those dealing with silent anxiety. By creating structure in their daily lives, individuals are better equipped to combat feelings of chaos and uncertainty. Predictability allows for the implementation of positive habits that can enhance mental clarity and provide a sense of accomplishment, thus combatting the cognitive signs of anxiety. This balanced approach can mitigate feelings of overwhelm, leading to improved decision-making and reduced stress.
Finally, seeking social support is an invaluable strategy in addressing the cognitive symptoms of silent anxiety. Having a trusted confidant, whether a friend, family member, or mental health professional, can provide a much-needed sounding board for anxious thoughts. Sharing experiences and feelings fosters a sense of connection and understanding, often alleviating feelings of isolation. This communal aspect of mental well-being can play a significant role in diminishing cognitive symptoms and promoting a healthier mindset for individuals coping with silent anxiety.
Recognizing the Silent Struggle

Understanding Silent Anxiety
Silent anxiety often manifests in subtle ways, making it difficult for both the individual and their loved ones to recognize. This type of anxiety can lead to a multitude of emotional and physical symptoms that may go unnoticed. People suffering from silent anxiety may experience internal turmoil while maintaining a calm exterior, often feeling isolated in their struggles.
Recognizing the indicators of silent anxiety is crucial for timely intervention. Common signs include pervasive feelings of dread, restlessness, and an overwhelming sense of worry, all of which can hinder daily functioning. Acknowledging these subtle cues can pave the way for effective coping strategies and support systems.
The Impact of Silent Anxiety on Daily Life
For individuals grappling with silent anxiety, the effects can permeate every aspect of life, from personal relationships to professional responsibilities. These individuals often appear composed on the surface, yet may be overwhelmed with internal stressors that impact their performance. This disconnect leads to further stress, as they may fear being misunderstood or judged by others.
Moreover, the burden of silent anxiety can result in avoidance behavior, where individuals steer clear of social situations or responsibilities that exacerbate their anxiety levels. The consequences of this avoidance can lead to significant personal and professional setbacks, further entrenching the cycle of anxiety. Understanding this impact is essential for fostering a supportive environment.
Importance of Seeking Help
Recognizing the need for help can be a significant hurdle for those experiencing silent anxiety. Many individuals worry that seeking support may reveal their vulnerabilities or lead to stigma, causing them to suffer in silence. However, reaching out for assistance is a vital step towards recovery and emotional well-being.
Various resources, such as therapists, support groups, and hotlines, are available to assist those affected by silent anxiety. Taking the initiative to find help not only promotes personal healing but also establishes a network of understanding and connection. Ultimately, this journey toward wellness fosters resilience and empowers individuals to reclaim their lives.
Coping Strategies for Silent Anxiety
Implementing effective coping strategies is crucial for managing silent anxiety and its impact on day-to-day living. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises, can help in grounding oneself and alleviating stress. These techniques allow individuals to better navigate their feelings and cultivate inner peace amidst chaos.
In addition to mindfulness, maintaining a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise and proper nutrition can greatly enhance mental well-being. Physical activity has been shown to reduce anxiety and improve mood, while a balanced diet nourishes both body and mind. Incorporating these habits can empower individuals to face their silent struggles with greater confidence.