The Connection Between Stress and Physical Health Issues
The Biological Response to Stress
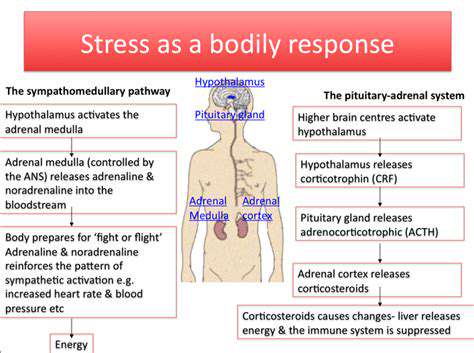
The Impact of Chronic Stress on the Body
Chronic stress can lead to significant disruptions in various physiological processes. When the body is under constant stress, it may experience increased levels of the hormone cortisol, which is linked to numerous health issues.
Over time, elevated cortisol levels can result in serious conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease. Understanding the connection between prolonged stress and these health risks is essential for promoting overall well-being.
The Link Between Stress and Immune Function
Stress not only affects mental health but also has profound implications on the immune system. Research indicates that stress can weaken immune response, leaving the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Moreover, individuals experiencing prolonged stress may take longer to recover from illness. This highlights the importance of stress management as a component of maintaining good physical health.
Coping Mechanisms and Their Effects on Health
Effective coping strategies can mitigate the negative effects of stress on physical health. Practices such as mindfulness, regular exercise, and social support are crucial in managing stress levels.
Implementing these strategies not only helps alleviate stress but also enhances resilience against physical health problems. By prioritizing healthy coping mechanisms, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life.
Chronic stress has been linked to numerous physical health issues, including: Cardiovascular Problems: Prolonged stress can increase heart rate and blood pressure, raising the risk of hypertension and heart disease. Weakened Immune Function: Stress can impair your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Digestive Issues: The gut-brain connection means that stress can exacerbate conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and can lead to digestive disorders. Musculoskeletal Issues: Stress often results in muscle tension, leading to chronic pain, headaches, and sleep disturbances. Metabolic Changes: Chronic stress can affect how your body processes food, potentially leading to weight gain or loss and increased risk of diabetes.

Cardiovascular Problems
Chronic stress is a major contributor to cardiovascular problems, encompassing a range of issues affecting the heart and blood vessels.
When an individual experiences prolonged stress, their body releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure.
This physiological response, known as the “fight or flight” mechanism, may seem beneficial in the short term but can be detrimental over time.
The continued elevation of blood pressure lays the groundwork for conditions like hypertension, putting strain on the heart.
Moreover, individuals under chronic stress often engage in unhealthy behaviors, such as poor diet and lack of exercise, further exacerbating their cardiovascular health risks.
Weakened Immune Function
The immune system is crucial for combating infections and protecting the body from disease.
Unfortunately, chronic stress has a profound negative impact on immune function, making the body significantly more vulnerable to various illnesses.
Stress hormones can directly interfere with the production of immune cells, diminishing the body's ability to fend off pathogens.
Studies have shown that individuals experiencing high stress levels tend to get sick more frequently, as their bodies are in a constant state of disarray.
As a result, managing stress is essential not only for mental well-being but also for maintaining physical health.
Digestive Issues
The gut-brain connection is an important physiological aspect that explains how stress can affect digestive health.
When under stress, the body may respond in various ways, including heightened gut sensitivity and changes in gut motility.
This can exacerbates existing conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), leading to symptoms such as bloating, cramps, and irregular bowel movements.
Chronic stress can also trigger episodes of gastritis, acid reflux, and other digestive disorders due to the overproduction of stomach acids.
Therefore, it is vital to engage in stress-relief techniques to protect not just mental health but also digestive function.
Musculoskeletal Issues
Stress often manifests physically, with many individuals experiencing muscle tension as a direct response.
Increased muscle tension can lead to a variety of musculoskeletal problems, such as chronic pain, headaches, and even sleep disturbances.
This persistent discomfort can impair daily functioning and significantly hinder one’s quality of life.
Moreover, individuals might develop a habit of poor posture as they carry tension in their bodies, contributing to further complications.
Addressing stress through relaxation techniques and physical therapy can greatly alleviate these musculoskeletal issues.
Metabolic Changes
Chronic stress can significantly alter metabolic processes in the body, leading to serious health concerns.
When stress is present, the body may release insulin improperly, which can influence how food is metabolized.
This disruption can result in unwanted weight gain or loss, depending on the individual's coping mechanisms and lifestyle choices.
Stress may also lead to cravings for sugary and high-fat foods, which can contribute to obesity and other metabolic syndromes.
Understanding the connection between stress and metabolism is essential in adopting healthier lifestyle practices that prioritize overall health.
Strategies for Managing Stress

Understanding the Impact of Stress on the Body
Chronic stress can lead to a variety of physical health issues, affecting different systems in the body.
When we experience stress, our body releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare us for a "fight or flight" response.
Over time, these hormones can contribute to problems like high blood pressure and heart disease if stress is not managed appropriately.
Furthermore, stress can weaken the immune system, making us more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Recognizing the signs of stress is crucial to preventing serious health repercussions.
Effective Techniques for Reducing Stress
Implementing relaxation techniques can significantly help in managing stress levels.
Practices such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga are proven methods to promote relaxation and mental clarity.
Physical activity also plays a vital role; regular exercise releases endorphins, which improve mood and help to alleviate stress.
Additionally, spending time in nature or engaging in hobbies can be an excellent distraction from daily stressors.
Prioritizing self-care and finding enjoyable activities is essential for maintaining good mental and physical health.
Seeking Professional Help for Stress Management
For some individuals, stress can become overwhelming, leading to anxiety or depression.
In such cases, seeking professional help is vital to navigate these feelings effectively.
Counseling or therapy can provide support, coping strategies, and tools to combat stress-related health issues.
Support groups and community resources can also offer a sense of connection and understanding.
Don't hesitate to reach out for help; acknowledging the need for support is a sign of strength.