Exploring Stellate Ganglion Block as an Anxiety Treatment
The Link Between the Sympathetic Nervous System and Anxiety
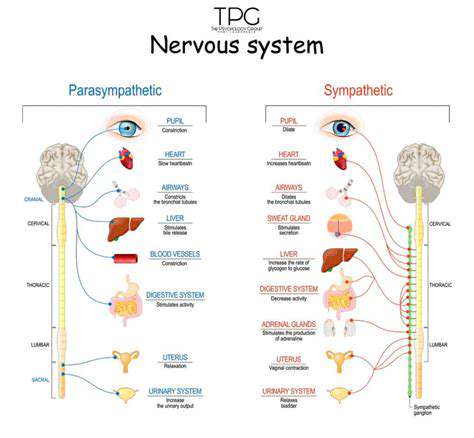
The Sympathetic Nervous System's Role in Stress Response
When faced with stress, our bodies rely on the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) to initiate what's commonly called the fight-or-flight response. This sophisticated neural network spans throughout the body, triggering the release of key hormones including adrenaline and noradrenaline. These biochemical messengers accelerate heart rate, quicken breathing, and elevate blood pressure - all designed to prepare muscles for rapid action when danger appears. This physiological cascade represents an evolutionary adaptation crucial for human survival in hazardous situations.
The SNS demonstrates remarkable adaptability, continuously assessing environmental threats and modulating its response accordingly. What many don't realize is that this system responds not just to physical dangers, but also to psychological stressors like emotional turmoil or anxiety-provoking thoughts. When this activation becomes persistent without adequate recovery periods, it can establish a harmful cycle of chronic stress that undermines overall health.
Cardiovascular Consequences of Chronic Activation
Persistent SNS activity creates substantial strain on heart health. The continuous elevation of blood pressure and heart rate forces the cardiovascular system to operate under excessive workload conditions. Over time, this contributes to the development of serious conditions including high blood pressure and atherosclerosis. Stress hormones also impair endothelial function, promoting inflammatory processes that accelerate arterial plaque formation.
While cortisol serves important regulatory functions in acute stress situations, its prolonged elevation due to chronic SNS activation produces damaging effects. This hormonal imbalance further compounds cardiovascular risks by disrupting metabolic processes and promoting vascular inflammation.
Implementing lifestyle modifications like consistent aerobic exercise and mindfulness practices can help counteract these negative cardiovascular impacts while enhancing overall resilience.
Mental Health Implications
The SNS profoundly influences psychological well-being through its effects on brain chemistry. Sustained overactivation disrupts neurotransmitter balance, particularly affecting serotonin and dopamine systems crucial for mood regulation. This neurochemical imbalance manifests as increased anxiety, depressive symptoms, and cognitive difficulties including impaired concentration and memory retrieval.
Sleep architecture becomes significantly disrupted under chronic SNS activation, preventing the restorative deep sleep phases essential for emotional processing and cognitive maintenance. This creates a vicious cycle where sleep deprivation exacerbates stress sensitivity, which in turn further degrades sleep quality.
Emerging research indicates prolonged stress may actually remodel brain structures involved in emotional regulation and memory formation. These neurological changes underscore the critical importance of developing effective stress management strategies for preserving both mental acuity and emotional health.
How Stellate Ganglion Block Could Treat Anxiety

Mechanism of Action
The stellate ganglion block (SGB) represents an innovative intervention targeting a critical neural junction at the cervical-thoracic transition. This precise procedure involves administering anesthetic agents directly to the stellate ganglion, effectively disrupting pathological sympathetic signaling. By modulating this key autonomic relay station, SGB can produce profound effects on pain perception and emotional regulation pathways.
As a major integration center for sympathetic outflow, the stellate ganglion influences diverse physiological processes from pupil dilation to cardiac function. The exact neurobiological mechanisms through which SGB exerts its therapeutic effects continue to be elucidated through ongoing clinical research.
Clinical Applications for Pain Management
SGB demonstrates particular efficacy for certain refractory pain conditions including cluster headaches and complex regional pain syndrome. These debilitating disorders often prove resistant to conventional therapies, leaving patients desperate for relief. The procedure's targeted approach allows for selective interruption of maladaptive pain signaling while preserving normal sensory function.
Performing SGB requires specialized expertise, typically utilizing fluoroscopic or ultrasound guidance to ensure accurate needle placement. This imaging-assisted technique maximizes therapeutic benefit while minimizing potential complications.
Therapeutic Potential and Limitations
While outcomes vary between individuals, many patients experience meaningful symptom reduction across various pain syndromes including neuropathic facial pain and certain headache disorders. Response duration ranges from temporary relief to lasting benefit, highlighting the importance of individualized treatment planning. Some protocols incorporate series of blocks to achieve cumulative therapeutic effects.
Safety Considerations
As with any interventional procedure, SGB carries inherent risks including potential nerve injury, vascular complications, or infection. A comprehensive pre-procedural evaluation remains essential for identifying patients who stand to benefit most while having acceptable risk profiles. Practitioners must carefully weigh potential benefits against possible adverse outcomes for each clinical scenario.
Patient Preparation and Post-Procedure Care
Thorough patient education forms the foundation for successful SGB outcomes. Individuals should disclose complete medical histories, including any bleeding disorders or medication use that might affect procedural safety. Appropriate pre-procedural preparation significantly enhances both safety and potential efficacy.
Common transient side effects like voice hoarseness or eyelid drooping typically resolve spontaneously within hours to days. Close post-procedural monitoring helps identify any rare but serious complications requiring prompt intervention.
Alternative Therapeutic Options
SGB generally represents a tertiary intervention after more conservative measures prove inadequate. Patients should engage in detailed discussions with pain specialists to understand all available options including pharmacotherapy, physical rehabilitation, and psychological interventions. Multimodal approaches often yield superior outcomes compared to any single treatment modality.