Exploring Restless Leg Syndrome and Its Connection to Anxiety
What Exactly Is Restless Legs Syndrome?
Restless legs syndrome (RLS) represents a neurological condition where individuals experience unusual sensations in their legs coupled with an overwhelming need to move them. Patients frequently describe these sensations as tingling, creeping, or even painful pulling feelings that intensify during evening hours. This condition can wreak havoc on sleep quality and dramatically reduce daytime productivity. While researchers haven't pinpointed a single cause, they believe it stems from complex interactions between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers.
Symptom severity varies dramatically between individuals - some report mild annoyance while others face debilitating discomfort. Medical consultation becomes essential for proper diagnosis and creating an individualized treatment approach. Early detection and intervention often lead to better symptom control and improved life quality.
Iron's Critical Role in Neurological Health
Numerous studies highlight iron deficiency as a major contributor to RLS development and progression. This essential mineral plays vital roles in oxygen transport and proper nerve function throughout the body. When iron levels drop below optimal ranges, neurological processes may become disrupted, potentially triggering or worsening RLS symptoms.
Clinical research consistently demonstrates connections between low iron stores and increased RLS occurrence. For patients diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia, iron supplementation frequently provides noticeable symptom relief.
Sleep Disruption Consequences
The nocturnal nature of RLS symptoms creates significant sleep challenges. The irresistible urge to move legs often strikes precisely when the body attempts to relax into sleep, creating a frustrating cycle of wakefulness.
Chronic sleep deprivation from RLS commonly leads to daytime exhaustion, emotional instability, and reduced mental sharpness. Addressing sleep disturbances must form a core component of any comprehensive treatment strategy for affected individuals.
Multiple Contributing Elements
Beyond iron imbalance, several other factors may influence RLS presentation. Certain medications, hormonal changes during pregnancy, and various neurological conditions have all shown associations with symptom development.
Genetic factors appear particularly influential. Those with immediate family members experiencing RLS face substantially higher risk of developing the condition themselves. Recognizing these potential contributors enables more targeted prevention and treatment approaches.
Diagnostic Process Essentials
Accurate RLS diagnosis requires thorough medical evaluation including detailed symptom history and physical assessment. Physicians must carefully differentiate RLS from other conditions with similar presentations.
Blood work examining iron levels and other relevant biomarkers often forms a critical component of the diagnostic process. Patients should prepare to describe symptom patterns, intensity fluctuations, and timing characteristics in detail.
Comprehensive Management Approaches
Effective RLS treatment strategies must be tailored to individual symptom profiles and underlying causes. Basic lifestyle adjustments like establishing regular exercise routines and consistent sleep-wake cycles often provide foundational support.
When needed, prescription medications targeting symptom reduction and sleep improvement can be highly effective. Many patients benefit most from combined approaches incorporating lifestyle modifications, pharmacotherapy, and sometimes complementary alternative treatments.
When RLS and Anxiety Symptoms Intersect
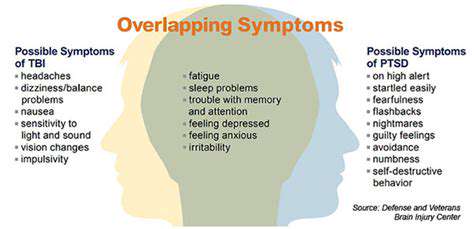
Identifying RLS Characteristics
Restless Legs Syndrome manifests through distinct physical sensations in the lower limbs accompanied by compelling movement urges. Patients describe these sensations diversely - from mild tingling to severe burning pain. These symptoms characteristically intensify during evening hours, frequently disrupting normal sleep architecture. Early recognition facilitates timely medical intervention and potential symptom mitigation.
The hallmark of RLS involves an almost uncontrollable need for leg movement, particularly during rest periods. This compulsion often prevents sleep onset and maintenance, with temporary relief only achieved through movement. The cyclical nature of these symptoms creates significant nighttime challenges.
Anxiety's Multifaceted Presentation
Anxiety disorders present complex combinations of emotional and physical symptoms that sometimes resemble other medical conditions. Persistent worry, irrational fears, and nervous tension represent hallmark emotional components. The physical manifestations complicate diagnosis by mimicking various organic disorders.
Common physical anxiety symptoms include cardiovascular changes, respiratory alterations, sweating episodes, and muscular tension. Cognitive effects like concentration difficulties and irritability frequently accompany these physical changes, creating comprehensive life disruption.
Shared Symptom Territories
RLS and anxiety demonstrate surprising symptom overlap, particularly regarding sleep disturbances. Both conditions can create similar patterns of sleep onset difficulty and maintenance insomnia, making differential diagnosis challenging.
Furthermore, the chronic discomfort and sleep deprivation caused by RLS often generates secondary anxiety. This creates a self-perpetuating cycle where each condition exacerbates the other, necessitating comprehensive treatment approaches.
Differentiating Key Features
Despite overlaps, crucial distinctions exist between these conditions. RLS primarily involves specific physical sensations and movement urges in the legs, while anxiety centers on cognitive-emotional distress with broader physical manifestations. Careful symptom analysis helps distinguish between these conditions.
Professional medical evaluation remains essential for accurate differentiation and appropriate treatment planning. Healthcare providers consider symptom patterns, timing, and response to various interventions when making diagnostic determinations.
Integrated Management Strategies
Addressing co-occurring RLS and anxiety requires holistic approaches targeting both physical and psychological components. Lifestyle modifications including physical activity optimization, nutritional adjustments, and stress reduction techniques benefit both conditions. Establishing consistent sleep routines proves particularly valuable for managing both disorders simultaneously.
Psychological interventions like cognitive behavioral therapy effectively address anxiety components while potentially improving RLS-related distress. Judicious medication use under medical supervision may be warranted for some patients to achieve optimal symptom control.
When to Seek Professional Guidance
The combined burden of RLS and anxiety symptoms can become overwhelming without proper support. Consulting qualified healthcare professionals ensures accurate diagnosis and development of evidence-based treatment plans. Early intervention typically yields better long-term outcomes.
Patients should feel empowered to discuss all symptoms openly with their providers. Comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment approaches can significantly improve quality of life for those experiencing these challenging conditions.