Signes d'anxiété chez les femmes : comprendre les symptômes
Transpiration
La transpiration excessive, ou hyperhidrose, est une manifestation physique courante de l'anxiété. Cela se produit souvent dans les paumes des mains, les aisselles et sur le front, mais peut également affecter d'autres zones du corps. La transpiration intense peut être inconfortable
Indicateurs émotionnels et comportementaux d'anxiété chez les femmes
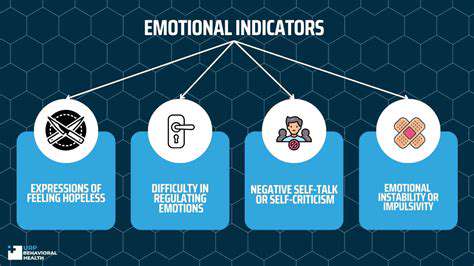
Comprendre les indicateurs émotionnels
Les indicateurs émotionnels sont essentiels pour reconnaître et répondre à l'anxiété
Stratégies d'adaptation et ajustements de style de vie pour les femmes
Pratiques de pleine conscience et de méditation
L'intégration de pratiques de pleine conscience et de méditation dans la routine quotidienne peut réduire significativement les symptômes d'anxiété chez les femmes. La pleine conscience implique...
Disclaimer: All articles on this site are original, please do not reprint
Read more about Signes d'anxiété chez les femmes : comprendre les symptômes
Reconnaître le Spasme Oculaire comme un Signe d'Anxiété : Perspectives pour une Meilleure Conscience
Comprendre le Spasme Oculaire et sa connexion avec l'AnxiétéMéthadescription : Découvrez le lien entre le spasme oculaire (myokymie) et l'anxiété, comprenant les déclencheurs courants, les stratégies de gestion efficaces et quand chercher de l'aide professionnelle. Apprenez à réduire les symptômes et à améliorer votre bien-être.--- Introduction au Spasme Oculaire et à l'AnxiétéLe spasme oculaire, également connu sous le nom de myokymie, est souvent une condition bénigne mais ennuyeuse qui peut être exacerbé par l'anxiété. Ce spasme musculaire involontaire affecte principalement la paupière et peut entraîner une distraction et un inconfort dans les activités quotidiennes. Reconnaître la connexionL'anxiété se manifeste souvent physiquement, et le spasme oculaire peut être un signe que votre corps est dans un état d'alerte accru. Comprendre comment le stress et l'anxiété sont liés aux sensations physiques permet aux individus d'identifier les déclencheurs et de prendre des mesures proactives. Identification des DéclencheursLes déclencheurs courants du spasme oculaire incluent la fatigue, une consommation excessive de caféine et un temps d'écran prolongé. Tenir un journal peut vous aider à suivre quand ces symptômes se produisent, façonnant ainsi un plan personnalisé pour une meilleure gestion. Stratégies de Gestion EfficacesAtténuez le spasme oculaire grâce à des techniques de relaxation comme la respiration profonde, la méditation et l'activité physique. Un mode de vie équilibré, comprenant une bonne hygiène de sommeil et une nutrition saine, joue également un rôle crucial dans la gestion des symptômes liés à l'anxiété. Quand Chercher de l'Aide ProfessionnelleUn spasme oculaire persistant peut nécessiter une évaluation professionnelle pour écarter les conditions sous-jacentes. Consulter des professionnels de santé peut offrir des perspectives adaptées aux besoins individuels, y compris des options thérapeutiques potentielles pour la gestion de l'anxiété. ConclusionEn comprenant les complexités du spasme oculaire et sa connexion avec l'anxiété, les individus peuvent mieux gérer leurs symptômes et améliorer leur qualité de vie. Prenez le contrôle en reconnaissant vos déclencheurs et en déployant des stratégies efficaces pour le soulagement.
Explorer les raisons pour lesquelles l'anxiété peut survenir sans raison apparente
Aperçu complet des troubles anxieux. Les troubles anxieux peuvent être complexes et multiples, façonnés par une combinaison de facteurs psychologiques, biologiques et environnementaux. Comprendre ces éléments est essentiel pour une gestion et un traitement efficaces.
Pourquoi l'anxiété peut être pire le matin et comment y faire face
Pourquoi l'anxiété peut être pire le matin et comment y faire face
Que faire lors d'une attaque de panique : un guide rapide
Que faire lors d'une attaque de panique : un guide rapide
Gérer l'anxiété des pieds moites : causes et remèdes
Gérer l'anxiété des pieds moites : causes et remèdes
Différents types d'attaques de panique : Ce qu'il faut savoir
Différents types d'attaques de panique : Ce qu'il faut savoir
Gérer les problèmes de sommeil dus à l'anxiété : conseils pratiques
Gérer les problèmes de sommeil dus à l'anxiété : conseils pratiques
Aborder l'anxiété chez les femmes : défis et solutions spécifiques
Aborder l'anxiété chez les femmes : défis et solutions spécifiques
Comment surmonter l'anxiété sociale : Techniques efficaces
Comment surmonter l'anxiété sociale : Techniques efficaces
Options de traitement efficaces pour les problèmes d'anxiété graves
Options de traitement efficaces pour les problèmes d'anxiété graves
Gérer les sensations étranges dans la tête liées à l'anxiété
Gérer les sensations étranges dans la tête liées à l'anxiété
Gérer les mains moites : Un symptôme d'anxiété courant
Gérer les mains moites : Un symptôme d'anxiété courant