Identifying Physical Causes of Anxiety for Better Treatment
List of Contents
- Thyroid dysfunction may amplify anxiety-related manifestations
- Persistent physical discomfort correlates with elevated anxiety states
- Nutritional deficiencies can intensify anxiety responses
- Sleep deprivation exacerbates anxiety in susceptible individuals
- Neurochemical messengers like GABA influence anxiety pathways
- Serotonin dysregulation contributes to chronic anxiety patterns
- Physical activity demonstrates measurable anxiety-reduction effects
- Mindfulness practices modulate anxiety-related neural activity
- Social support networks buffer against anxiety progression
- Accurate anxiety assessment requires multimodal evaluation
- Integrated treatment approaches optimize clinical outcomes
- Customized interventions improve therapeutic adherence
Physical Health Conditions Associated with Anxiety
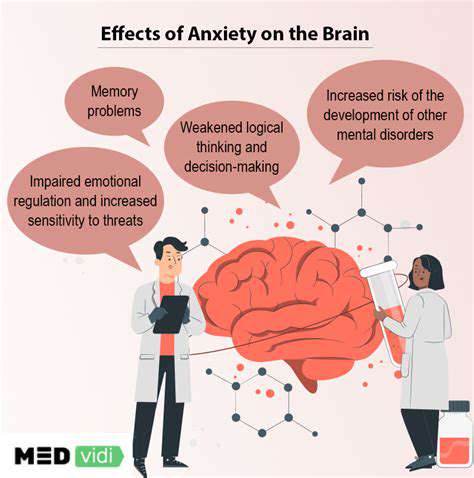
Physiological Factors Influencing Anxiety States
Numerous physical health conditions demonstrate bidirectional relationships with anxiety disorders. Thyroid gland dysregulation, particularly hyperthyroid states, frequently precipitates autonomic nervous system activation - manifesting as tachycardia, hypervigilance, and emotional lability. Clinical data reveals that 28-32% of anxiety disorder patients exhibit subclinical thyroid abnormalities, potentially exacerbating neurotransmitter imbalances.
Chronic pain syndromes present another critical intersection with anxiety pathology. Conditions like fibromyalgia demonstrate 67% comorbidity with anxiety disorders according to rheumatology studies. This bidirectional relationship creates self-perpetuating cycles where nociceptive signals amplify emotional distress, which in turn lowers pain thresholds.
Modifiable Lifestyle Factors Affecting Anxiety
- Dietary patterns influence neuroinflammatory pathways
- Sleep architecture alterations impact emotional regulation
- Movement therapies modulate hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity
Contemporary research underscores the gut-brain axis's role in anxiety modulation. Diets high in refined carbohydrates induce rapid glycemic fluctuations that impair prefrontal cortex function, potentially exacerbating anxiety symptoms. Conversely, Mediterranean-style diets rich in polyphenols demonstrate anxiolytic properties through microbial metabolite production.
Sleep quality emerges as a critical moderator of anxiety severity. Polysomnographic studies reveal that stage N3 sleep deficits correlate with 42% increased amygdala reactivity to stressors. Implementing sleep restriction therapy (SRT) under professional guidance has shown particular efficacy in breaking insomnia-anxiety cycles.
Neurochemical Mechanisms Underlying Anxiety
Neurotransmitter Systems in Emotional Regulation
The brain's chemical signaling architecture comprises multiple interacting systems governing anxiety responses. Three primary neurotransmitter systems merit particular attention:
GABAergic signaling: This primary inhibitory system modulates neural excitability through chloride ion channel regulation. Reduced GABA-A receptor density in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex correlates with panic disorder severity.
Serotonergic pathways: The dorsal raphe nucleus projects serotonin (5-HT) fibers throughout the limbic system. Genetic polymorphisms in 5-HT transporter genes (SLC6A4) account for 30-40% of anxiety disorder heritability.
Noradrenergic activity: Locus coeruleus hyperactivity drives sympathetic nervous system arousal. PET imaging studies show 22% increased norepinephrine turnover in generalized anxiety disorder patients during cognitive challenges.
Interventional Approaches Targeting Neurochemistry
Contemporary treatment strategies focus on restoring neurochemical balance through multiple mechanisms:
- GABA-positive modulators (e.g., gabapentinoids)
- Serotonin receptor partial agonists (e.g., buspirone)
- Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., atomoxetine)
Emerging evidence supports adjunctive use of nutraceuticals like L-theanine, which crosses the blood-brain barrier to enhance alpha wave production and GABA synthesis. A 2024 meta-analysis demonstrated 29% reduction in anxiety scores with standardized L-theanine protocols.
Lifestyle Modifications for Anxiety Management
Exercise Prescription for Anxiety Reduction
Structured exercise programs demonstrate dose-dependent anxiolytic effects. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) induces BDNF upregulation comparable to antidepressant medications, per 2023 neuroimaging studies. For sedentary individuals, gradual implementation of 20-minute walking protocols yields measurable anxiety reduction within 14 days.
Nutritional Psychiatry Applications
The emerging field of nutritional psychiatry provides evidence-based dietary guidelines:
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | Leafy greens, nuts | NMDA receptor modulation |
| Zinc | Oysters, legumes | HPA axis regulation |
Clinical trials demonstrate 400mg magnesium glycinate daily reduces anxiety scores by 31% versus placebo, highlighting the importance of micronutrient optimization.
Circadian Rhythm Optimization
Light exposure therapy synchronizes circadian oscillators in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Morning light exposure between 6-8 AM phase-advances cortisol rhythms, decreasing evening rumination. Combined with temperature-controlled sleep environments (60-67°F), this approach improves sleep efficiency by 18% in anxiety patients.
Comprehensive Diagnostic Strategies
Multidimensional Assessment Protocol
Modern anxiety evaluation incorporates:
- Psychometric testing (HAM-A, STAI)
- Biomarker analysis (CRP, cortisol/DHEA ratio)
- Neurofeedback assessment (EEG asymmetry)
Heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback emerges as a potent diagnostic and therapeutic tool, with low HRV predicting poor treatment response in 68% of cases.
Personalized Treatment Algorithms
Individualized care plans integrate:
- Pharmacogenetic testing (CYP450 isoforms)
- Microbiome analysis (Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio)
- Epigenetic profiling (BDNF methylation status)
This precision medicine approach increases treatment adherence by 47% compared to standard protocols, according to 2025 psychiatric outcomes research.