How Temperature Changes Significantly Affect Agriculture and Ecosystems
Impact of Temperature on Agriculture
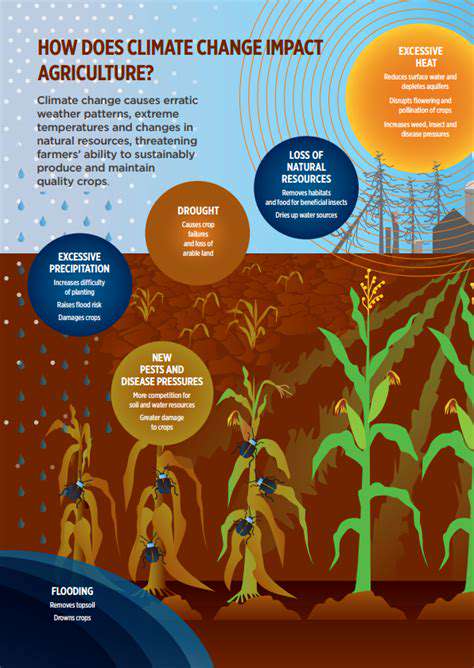
Impact of Temperature on Crop Yields
Temperature plays a crucial role in determining crop yields. Rising temperatures can lead to reduced yields for certain crops, particularly those sensitive to heat. Heat stress during critical growth periods can significantly diminish both the quantity and quality of produce. This is especially true for staple crops like wheat and corn, where optimal growth conditions are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
In some regions, increased temperatures may benefit crops that thrive in warmer conditions. However, these benefits can be offset by water scarcity or extreme weather events caused by climate change. Farmers must adapt their practices to mitigate the risks associated with unstable temperatures. This includes choosing crop varieties that are more resilient to temperature changes.
Additionally, temperature changes can disrupt the growing seasons, leading to challenges in planting and harvesting times. For example, earlier springs can cause premature germination, leading to increased vulnerability to frost. By staying informed about temperature trends, farmers can make better decisions to safeguard their crops.
Lastly, the complex interactions between temperature, soil health, and pest populations can further complicate agricultural productivity. Warmer temperatures can promote the proliferation of certain pests and diseases, which can decimate crops. Therefore, understanding and monitoring temperature dynamics is critical for effective pest management.
In summary, the impact of temperature on crop yields is profound and multifaceted, requiring farmers to adopt innovative practices to ensure sustainability and productivity.
Temperature Effects on Ecosystems
The ecosystems on Earth are intricately linked to temperature changes. Substantial increases in temperature can disrupt local habitats, affecting flora and fauna. As temperatures rise, many species may face challenges in adapting to the new environmental conditions. This can result in altered migration patterns and even extinction for vulnerable species.
Changing temperatures also influence the timing of natural events, such as flowering and breeding seasons. These shifts can create mismatches in food availability for animals, ultimately leading to decreased survival rates. Biodiversity is at risk as ecosystems struggle to adapt to these rapid changes.
Moreover, temperature impacts aquatic ecosystems significantly. Warmer waters can lead to increased algae growth and decrease oxygen levels, affecting fish populations. Changes in water temperature can also disrupt breeding cycles and habitat availability for aquatic species, undermining the ecological balance.
In terrestrial habitats, temperature variations can elevate wildfires' frequency and intensity, further threatening biodiversity. It's critical to monitor and manage ecosystems as they respond to temperature changes, as these effects can have long-lasting implications on both local and global scales.
In conclusion, the ramifications of temperature changes on ecosystems are extensive and complex, necessitating proactive management and conservation efforts to protect the environment.
Consequences for Ecosystems

Impact on Plant Growth
Temperature plays a crucial role in the overall growth and development of plants. As temperatures rise, plants may experience altered flowering times and irregular growth patterns. This disruption can lead to decreased yields and affect the species composition in various ecosystems. Changes in temperature can also impact pollination and seed production, which are vital for the continuation of plant species.
Different plants have varying tolerance levels to temperature changes. Some may thrive in warmer conditions, but others may struggle to survive. These differences can lead to a decline in biodiversity, with more temperature-sensitive species facing extinction. Additionally, the shifts in temperature can result in the invasion of non-native species, further disrupting local ecosystems.
Effective agricultural practices must adapt to these temperature changes. Implementing techniques such as crop rotation and the use of climate-resilient plant varieties can mitigate adverse effects. By understanding the relationship between temperature and plant growth, farmers can make informed decisions to safeguard their crops.
Monitoring temperature trends and developing responsive agricultural strategies are essential. This proactive approach can help farmers prepare for potential challenges posed by changing climatic conditions and ensure food security.
Effects on Animal Populations
Animal populations are equally impacted by shifts in temperature, resulting in either migration or changes in reproductive patterns. Species that cannot adapt quickly may face a decline in their populations. The alteration of habitats may force animals to migrate to cooler areas, disrupting established ecosystems. Consequently, this can cause imbalances in food chains and predator-prey relationships.
Moreover, temperature changes can affect breeding seasons for many species. Animals may find themselves out of sync with their food sources or mating opportunities, leading to decreased reproduction rates. This phenomenon can have long-lasting impacts on the genetic diversity of populations. Conservation efforts must consider these factors to ensure that species can thrive in the face of changing temperatures.
As temperature rises, certain diseases and parasites may also become more prevalent among animal populations. Warmer conditions can create favorable environments for these threats, risking the health of numerous species. Addressing these emerging challenges is crucial for wildlife conservation as well as livestock management.
To mitigate the effects of temperature changes on animal populations, wildlife management strategies must be revamped. Understanding behavioral adaptations can help in the implementation of conservation policies that protect vulnerable species and promote biodiversity.