Addressing the Emerging Food Security Challenges in a Changing World
Global Trends Influencing Food Security

Climate Change and Its Impact on Agriculture
One of the most pressing issues facing food security today is climate change. As weather patterns become more erratic, crop yields are increasingly put at risk. Farmers must adapt to longer droughts, heavier rainfall, and unpredictable seasons.
These changes not only affect the amount of food produced but also the types of crops that can be grown in certain regions. This shift can lead to a reduction in biodiversity, making agricultural systems more vulnerable to pests and diseases.
To combat these challenges, innovative agricultural practices, such as climate-resilient crops and sustainable farming techniques, are becoming essential. Governments and organizations must also invest in research to support these adaptations.
Economic Factors Affecting Food Access
The global economy significantly influences food accessibility. Fluctuations in commodity prices can lead to increased food costs, disproportionately affecting low-income populations. Economic instability can result in food insecurity as families struggle to afford basic necessities.
Moreover, trade policies and international agreements also play a critical role in food availability. Tariffs, quotas, and subsidies can shift food prices and availability across different regions, complicating local food security efforts.
To address these economic challenges, policymakers need to focus on creating equitable trade practices and supporting local food systems. Investing in local farms can enhance food security by reducing dependency on global markets.
Technological Advancements in Food Production
Technology is emerging as a crucial factor in enhancing food security across the globe. Modern agricultural techniques, such as precision farming, can significantly increase efficiency and yield in food production. These advancements allow farmers to use resources more sustainably, reducing waste and boosting productivity.
Additionally, biotechnology plays a vital role in developing crops that can withstand harsh growing conditions. Innovations such as genetically modified organisms (GMOs) can offer solutions to food scarcity by enhancing resilience against pests and diseases.
However, the adoption of such technologies must be coupled with ethical considerations and public acceptance. Education and outreach are key to addressing concerns related to food safety and environmental impacts of these technologies.
Socio-Political Factors and Governance
Food security is not solely a technical issue; it is also heavily influenced by socio-political dynamics. Government policies regarding land use,, agricultural subsidies, and food distribution directly affect a community's access to food. Strong governance is essential for fostering a stable food environment that addresses the needs of vulnerable populations.
Moreover, conflicts and instability can severely disrupt food systems, leading to famine and displacement. In regions experiencing turmoil, humanitarian assistance becomes crucial to address immediate food needs and prevent long-term insecurity.
To improve food security, collaboration between governments, NGOs, and communities is vital. Strategies that empower local food systems and promote peace can create a resilient framework for food security in challenging environments.
Economic Factors Affecting Food Access
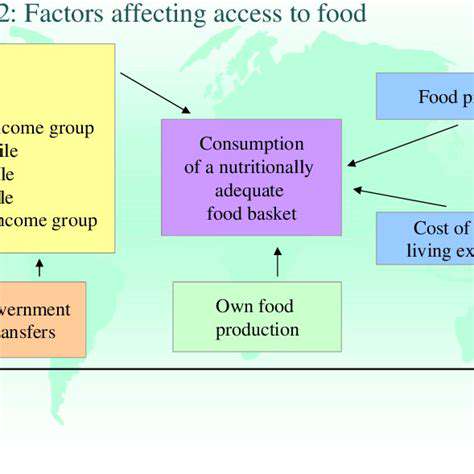
Impact of Inflation on Food Prices
Inflation significantly influences the cost of food production and distribution. As the prices of raw materials rise, farmers often pass these costs onto consumers. Higher food prices can lead to reduced access for lower-income families, exacerbating food insecurity. This dynamic creates a cycle where individuals may have to choose between essential goods and healthy food options.
Inflation can also affect purchasing power, making it challenging for families to afford a balanced diet. When food prices rise, it's not only the cost of staple items that increases, but also the prices of nutritious options such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. This shift further marginalizes those already struggling to meet their basic needs.
Understanding the relationship between inflation and food prices is crucial for policymakers. They need to develop strategies that mitigate the impact of rising costs on vulnerable populations. This may involve subsidies, food assistance programs, or initiatives to stabilize food supply chains.
Ultimately, addressing inflation’s effects on food prices is vital for ensuring that all communities have access to nutritious food. Efforts to improve economic conditions can lead to better health outcomes for the entire population.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions
The globalization of food supply chains has made markets more interconnected but also more vulnerable to disruptions. Natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and pandemics can severely impact food availability and transportation. When supply chains are disrupted, the consequences can lead to food shortages and increased prices.
Moreover, these disruptions disproportionately affect developing countries that rely on imports for food. With limited local production capabilities, these nations are more susceptible to external shocks. Addressing the vulnerabilities in these supply chains is critical for improving food security globally.
Investments in local agriculture and sustainable practices can help reduce dependency on global markets. Strengthening local food systems can create resilience against future disruptions and ensure a steady supply of essential food products. Education and training for farmers in these regions can also enhance productivity.
In summary, understanding and mitigating the impacts of global supply chain disruptions is essential for food security. Collaborative efforts at international and local levels can help build a more sustainable and equitable food system.
Climate Change and Its Impact on Agriculture
Climate change poses significant challenges to agricultural productivity around the world. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt growing seasons and reduce yields. This can lead to increased hunger and malnutrition, particularly in regions that are already vulnerable.
Farmers are facing the reality of shifting weather patterns, including more frequent droughts and floods. Adaptation strategies such as developing drought-resistant crops and implementing conservation practices are becoming increasingly important. These strategies not only help in managing current challenges but also prepare for future impacts.
Furthermore, climate change affects the availability of natural resources like water, which is critical for agriculture. Water scarcity can lead to increased competition among various sectors, further impacting food production. Sustainable water management practices will be vital for ensuring long-term food security.
Addressing the intersections between climate change and food security requires a multi-faceted approach. Policymakers must prioritize environmental sustainability while supporting agricultural innovation to meet the challenges posed by climate change.
Socioeconomic Disparities in Food Accessibility
Socioeconomic status plays a critical role in determining food access. Individuals from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers that prevent them from obtaining nutritious food. These disparities are not solely economic; they also encompass factors such as education, employment, and transportation.
Food deserts, areas with limited access to affordable and nutritious food, are prevalent in many urban and rural communities. Residents of these areas may be forced to rely on convenience stores or fast food, both of which typically offer unhealthy options. This situation leads to a cycle of poor nutrition and related health problems.
Addressing these disparities requires comprehensive strategies beyond increasing food supply. Initiatives that focus on improving access through transportation services, increasing availability of healthy food outlets, and fostering community gardens can have a positive impact. Additionally, public awareness campaigns can educate communities about nutrition and healthy eating.
Ultimately, reducing socioeconomic disparities in food accessibility is key to achieving food security for all. Policymakers, community leaders, and organizations must collaborate to create equitable solutions that foster a healthier population.
The Role of Policy and Governance in Food Security
Effective policymaking is essential in addressing food security challenges. Governments can play a pivotal role in implementing regulations that ensure fair food distribution and access. By prioritizing food security in their agendas, policymakers can create frameworks that promote sustainable agricultural practices and enhance local food systems.
In addition to regulations, government-funded programs aimed at food assistance can help vulnerable populations access the nutrition they need. These programs may include food stamps, nutritional education, and support for local farmers' markets. Ensuring that these programs are adequately funded and accessible is critical for their success.
Collaboration between government, non-profits, and private sectors can also drive innovative solutions to food security issues. Public-private partnerships can mobilize resources and expertise to create more resilient food systems. Additionally, engaging with communities to understand their specific needs can lead to more effective policies.
In conclusion, strong governance and well-designed policies are indispensable in the fight against food insecurity. By prioritizing food security in national and local policy discussions, we can forge a path towards a more equitable and sustainable food future.
The Role of Technology and Innovation in Food Security
The Impact of Climate Change on Food Production
Climate change poses significant threats to food security worldwide. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can disrupt crop yields, leading to decreased food availability. Farmers may face challenges in selecting the right crops for their environments, which can further exacerbate food scarcity.
Additionally, extreme weather events such as floods, droughts, and hurricanes can destroy crops and disrupt supply chains. These disruptions can create volatility in food prices, making it harder for vulnerable populations to access essential nutrition.
Adaptation strategies, including the development of climate-resistant crops, are essential for mitigating these impacts. Research into varieties that can withstand drought or flooding is becoming increasingly important in ensuring stable food production.
Moreover, global cooperation is crucial in addressing the complexities of climate-induced food insecurity. Sharing knowledge and resources across borders can help nations adapt more effectively to changing environmental conditions.
Innovations in Agricultural Technology
The agriculture sector is undergoing a revolution thanks to technological advancements. Precision agriculture, which utilizes data analytics, GPS, and IoT devices, allows farmers to optimize their operations and increase yields. By assessing and responding to specific field conditions, farmers can ensure sustainable production practices.
Biotechnology is also transforming the landscape of food production. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) can be engineered to resist pests, reduce the need for chemical fertilizers, and improve nutritional content. These innovations can contribute significantly to enhancing food security by increasing the resilience of food systems.
Furthermore, vertical farming and aquaponics are emerging as innovative solutions that can produce food in urban environments. These methods require less land and water, thus making food production more sustainable and accessible to city dwellers.
Collaboration between tech companies and agricultural stakeholders is vital in creating solutions tailored to the challenges of food security. Investing in research and development in agricultural tech can lead to breakthroughs that will sustain future food systems.
The Importance of Sustainable Practices
Implementing sustainable agricultural practices is fundamental in securing food for future generations. Techniques such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and organic farming can enhance soil health and restore ecosystems, ultimately leading to more resilient food production.
Additionally, reducing waste across the food supply chain is critical. An estimated one-third of the food produced globally is wasted, which not only affects food availability but also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Addressing this issue through better logistics and consumer education can have a significant impact on food security.
Promoting local food systems can also increase sustainability. By supporting local farmers and food producers, communities can reduce dependency on lengthy supply chains while enhancing access to fresh and nutritious food.
Ultimately, fostering a culture of sustainability within both agriculture and consumption can create a more secure food future. It is essential to educate stakeholders at all levels about the benefits and practices of sustainable agriculture to ensure long-term success.
Global Policy and Governance Challenges
Food security is not just a local or national issue; it requires global collaboration and effective governance. Policies that promote fair trade, equitable access to resources, and investment in agriculture are essential for overcoming the challenges of food insecurity.
International organizations play a crucial role in coordinating efforts to combat food insecurity. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and other entities work to establish standards and practices that member countries can adopt to improve their food systems.
However, political instability and conflict can severely hinder food security efforts. Areas affected by war and unrest often experience disrupted agriculture and distribution systems, leading to famine and malnutrition. Addressing the underlying causes of conflict is essential for ensuring food security in these regions.
In addition, integrating food security into national policies and development plans can help ensure a comprehensive approach to tackling food-related issues. Governments must prioritize food security in their agendas to achieve meaningful and lasting change.
The Role of Community Engagement and Education
Engaging local communities in discussions about food security fosters resilience and empowerment. Education about nutrition, agricultural practices, and food sourcing can enhance community capacity to address food insecurity effectively.
Community gardens and cooperative farming initiatives can provide not only access to fresh produce but also a sense of ownership and agency. These local efforts can connect people to their food sources and foster a greater appreciation for agriculture.
Moreover, involving youth in agricultural education and innovation can yield long-term benefits. By teaching younger generations about sustainable practices and food systems, we can cultivate a culture of responsibility and innovation in agriculture.
Finally, community engagement can drive legislative support for food security initiatives. When communities voice their needs and priorities, policymakers are more likely to consider those issues in their approaches to food security challenges.
Building Resilient Food Systems

Understanding the Impact of Climate Change on Food Security
The impacts of climate change are becoming increasingly evident, affecting agricultural productivity and food availability globally. Changing weather patterns have led to unpredictable growing seasons, which further complicate food production efforts. Farmers face challenges such as droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures, which can drastically diminish crop yields. These environmental factors threaten food security and increase the risk of hunger in vulnerable communities. Addressing these challenges requires a thorough understanding of the local climate and adaptive agricultural practices.
Climate change also affects food supply chains by disrupting transportation and logistics. This can lead to delays in getting food to markets and increased prices for consumers. As temperatures rise and severe weather events become more frequent, regions that rely heavily on certain crops might find themselves without adequate supplies. It is essential for policymakers to consider these impacts when planning food security strategies. Adapting to climate change is not just about protecting crops but also ensuring the stability of entire food systems.
Moreover, climate change disproportionately affects marginalized communities who often lack the resources to adapt. These populations may not have access to technologies or financial support that could help them manage agricultural risks. Building resilience in these communities is crucial for their survival and food security. Involving local populations in the planning of adaptive measures can lead to more effective and sustained outcomes. Collaboration among various stakeholders, including governments and NGOs, is needed to provide resources and knowledge-sharing platforms.
In conclusion, addressing climate change's effects on food security requires a multifaceted approach. Research into climate-resilient crops, investment in sustainable agricultural practices, and education for farmers is key. By prioritizing these areas, we can build a food system that can withstand the pressures of a changing climate. It is essential to act quickly and decisively to mitigate food security risks exacerbated by climate change.
Innovative Solutions for Sustainable Agriculture
To combat food insecurity, innovative agricultural practices must be adopted. Techniques such as permaculture, hydroponics, and vertical farming have gained popularity as sustainable methods to produce food efficiently. These methods can increase yield in limited spaces, especially in urban environments. By leveraging technology, we can enhance crop production while minimizing environmental impacts. The integration of modern technologies, such as drones and precision agriculture, can provide real-time data for better decision-making in farming.
Additionally, encouraging organic farming practices can promote soil health and biodiversity. Organic farming reduces reliance on harmful pesticides and fertilizers, ensuring that the food produced is healthier for both consumers and the environment. It also fosters a more sustainable agricultural practice that can endure over time. Governments can support organic farming through subsidies and education campaigns. Raising awareness about the benefits of choosing organic products is also crucial.
Community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs encourage local food production and distribution, connecting consumers directly with farmers. This model empowers farmers financially while providing fresh produce to the community. Participation in CSA can also foster community relationships and promote local economies. Educating consumers about the advantages of supporting local agriculture can enhance this model's effectiveness. A robust CSA can inspire collective efforts toward improving food security.
Innovative solutions must also address food waste, which is a significant barrier to food security. Developing strategies to redirect surplus food to those in need can reduce waste while meeting the nutritional needs of underserved populations. Initiatives such as food recovery networks and composting programs can start to mitigate this issue effectively. By focusing on reducing food waste, we can maximize the use of available resources and contribute to a more sustainable food system.
Strengthening Food Policies and Governance
Effective food policies are vital in ensuring food security for all. Governments must adopt comprehensive policies that support sustainable agricultural practices and equitable food distribution. Addressing issues like land rights, access to resources, and investment in agricultural research is crucial in policy formulation. These policies should prioritize the needs of marginalized communities and promote equitable access to nutritious food. Collaboration between governments, NGOs, and the private sector can strengthen these policies.
Governments also need to establish resilient governance structures that can respond effectively to food crises. This requires the ability to gather data and analyze trends in food production and consumption. Building a responsive food policy framework helps mitigate the impacts of emergencies caused by conflicts or natural disasters. Communities must be involved in policy dialogues, ensuring that their voices are heard. Empowering local organizations can enhance the effectiveness of food security policies.
Moreover, international cooperation is essential in addressing food security challenges that transcend national borders. Global challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic and climate change require collaborative strategies and sharing of best practices. Organizations like the United Nations and regional bodies should lead initiatives that support food security for vulnerable populations. Raising awareness about global food security issues can galvanize public support for international efforts. Collaborative research and development can also facilitate knowledge sharing between countries.
In conclusion, effective governance and policies form the backbone of resilient food systems. Policymakers must stay adaptable and responsive to changing conditions in the agricultural sector. By investing in robust food policies and promoting strong governance structures, we can enhance food security and build a more sustainable future for all.
Promoting Global Collaboration and Community Engagement
Global collaboration is paramount in addressing food security challenges that affect various regions differently. Countries can share resources, knowledge, and technologies to improve food production and distribution processes. Partnerships between governments, NGOs, and the private sector can lead to innovative solutions that benefit all stakeholders. Creating global alliances can amplify efforts to combat hunger and malnutrition worldwide. These collaborations can also draw attention to vulnerable populations and their unique challenges.
Community engagement plays a critical role in promoting food security at the local level. Involving communities in decision-making processes fosters ownership and commitment to food security initiatives. Programs that educate local populations about nutrition and food production practices empower them to make informed choices. These initiatives can improve food sovereignty, allowing communities to take charge of their food systems. Active participation ensures that solutions are tailored to the specific cultural and environmental contexts of the community.
Furthermore, local food systems can bolster community resilience against crises. Encouraging the establishment of community gardens and local markets provides access to fresh produce while strengthening social ties. These initiatives enable communities to work together to increase food production and distribution. Educating communities about the importance of local food systems can create a culture of sustainability. Healthy communities are often more resilient to food insecurity challenges.
Education and awareness campaigns can further enhance global collaboration efforts. Citizens need to understand the scope of global food security issues and their own roles in addressing them. By raising awareness about food systems' interconnectedness, individuals can be motivated to contribute to larger solutions. Public campaigns can inspire people to support local farmers and advocate for justice in food policymaking. This grassroots involvement is vital for creating systemic change.