Związek między niedoczynnością tarczycy a poziomem lęku
Rola hormonów tarczycy w regulacji nastroju
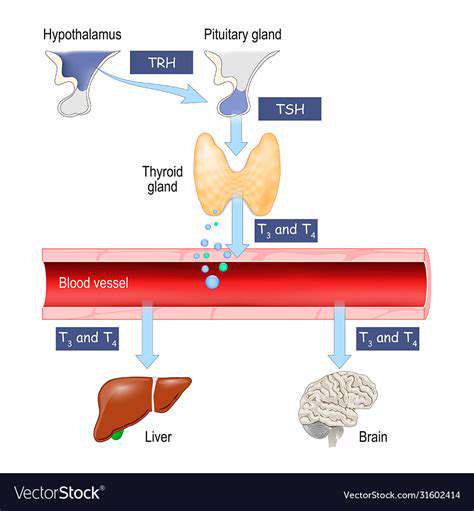
Produkcja i regulacja hormonów tarczycy
Tarczyca, narząd w kształcie motyla zlokalizowany w szyi, odgrywa kluczową rolę w
Potencjalne Nakładanie się Objawów i Wyzwania Diagnostyczne
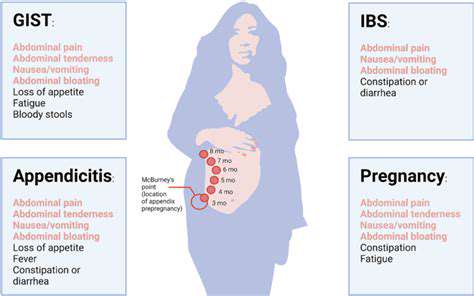
Potencjalne Przyczyny Nakładających się Objawów
Wiele schorzeń medycznych może charakteryzować się podobnymi objawami,
Disclaimer: All articles on this site are original, please do not reprint
Read more about Związek między niedoczynnością tarczycy a poziomem lęku
Zarządzanie lękiem poniedziałkowym: Porady na bezstresowy początek tygodnia
Zarządzanie lękiem poniedziałkowym: Porady na bezstresowy początek tygodnia
Objawy zespołu obsesyjno-kompulsyjnego według DSM-5: Wyczerpujący przewodnik
Objawy zespołu obsesyjno-kompulsyjnego według DSM-5: Wyczerpujący przewodnik
Związek między problemami tarczycy a atakami paniki
Związek między problemami tarczycy a atakami paniki
Badanie opcji leczenia lęku: Znalezienie odpowiedniego rozwiązania
Badanie opcji leczenia lęku: Znalezienie odpowiedniego rozwiązania
Rozumienie objawów lęku specificznego: szczegółowe badanie
Rozumienie objawów lęku specificznego: szczegółowe badanie
Zarządzanie nudnościami związanymi z lękiem: rozwiązania i wsparcie
Przyczyny, strategie i ulga. Czy doświadczasz częstych nudności w połączeniu z uczuciem lęku? Odkryj, jak te dwa stany są ze sobą powiązane i zbadaj skuteczne strategie zarządzania i łagodzenia objawów. Ten...
Identyfikacja drętwienia twarzy spowodowanego stresem: spostrzeżenia i wskazówki
Identyfikacja drętwienia twarzy spowodowanego stresem: spostrzeżenia i wskazówki
Przewlekła choroba depresyjna z lękiem: Kluczowe spostrzeżenia
Przewlekła choroba depresyjna z lękiem: Kluczowe spostrzeżenia
Sposoby radzenia sobie z ciężką lękiem w życiu codziennym
Sposoby radzenia sobie z ciężką lękiem w życiu codziennym
Badanie ciągłego niepokoju jako kluczowej cechy lęku
Badanie ciągłego niepokoju jako kluczowej cechy lęku