Komorbiditäten: Erforschung von Depression und Angststörung
Schlüsselmerkmale>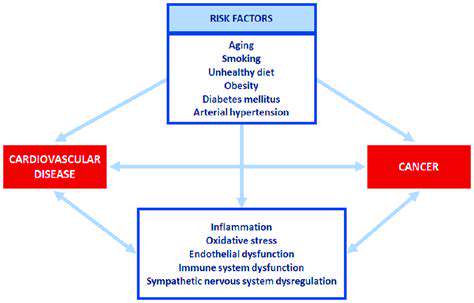
Die Prävalenz und Auswirkungen von Komorbidität
Komorbidität verstehen
Wenn mehrere medizinische Erkrankungen gleichzeitig auftreten, beobachten wir ein Phänomen, das als Komorbidität bezeichnet wird. Dies schafft diagnostische Herausforderungen, da sich überlappende Symptome möglicherweise
Potenzielle zugrundeliegende Mechanismen: Ein Blick auf gemeinsame Risikofaktoren

Genetische Vulnerabilitätsfaktoren
Zwingende Belege zeigen eine starke genetische Beteiligung
Disclaimer: All articles on this site are original, please do not reprint
Read more about Komorbiditäten: Erforschung von Depression und Angststörung
Anzeichen und Symptome von Angstzuständen: Was Sie wissen müssen
Anzeichen und Symptome von Angstzuständen: Was Sie wissen müssen
Antizipationsangst bewältigen: Techniken zur Beruhigung der Nerven
Antizipationsangst bewältigen: Techniken zur Beruhigung der Nerven
Angst- und Panikattacken bewältigen: Entspannungstrategien
Angst- und Panikattacken bewältigen: Entspannungstrategien
Wie man einen Angstzustand stoppt: Effektive Techniken
Wie man einen Angstzustand stoppt: Effektive Techniken
Was tun, wenn Sie einen Panikattacke haben: Bewältigungsstrategien
Ein umfassender Leitfaden Suchen Sie nach schnellen und effektiven Möglichkeiten, Stress, Angstzustände oder emotionale Überlastung zu bewältigen? Entdecken Sie bewährte Erdungstechniken, die sofortige Linderung bieten und Ihnen helfen, die emotionale Stabilität wiederzuerlangen.
Das Verständnis von Luftverschluckungsangst: Symptome und Lösungen
Das Verständnis von Luftverschluckungsangst: Symptome und Lösungen
Trennungsangst bei 4-jährigen Kindern: Symptome und Lösungen
Trennungsangst bei 4-jährigen Kindern: Symptome und Lösungen
Symptome von hochfunktionierender Angst erkennen: Was Sie wissen müssen
Symptome von hochfunktionierender Angst erkennen: Was Sie wissen müssen
Management von schwerer Angst und Depression: Strategien zur Verbesserung
Management von schwerer Angst und Depression: Strategien zur Verbesserung
Chronische Angst verstehen: Ursachen und Bewältigungsstrategien
Chronische Angst verstehen: Ursachen und Bewältigungsstrategien
Analyse von Mundtrockenheit als häufige Angstsymptom
Analyse von Mundtrockenheit als häufige Angstsymptom