Understanding the Physical Symptoms of Anxiety and Stress
Contents
Anxiety activates our body's survival mechanisms, directly influencing cardiovascular functions.
Long-term stress creates persistent muscle stiffness that affects daily comfort.
Hormonal imbalances from chronic stress may trigger systemic health complications.
Early detection of anxiety signals enables timely intervention.
Dietary adjustments and movement patterns can reshape stress responses.
Specialized care becomes crucial when self-management reaches its limits.
Rhythmic daily patterns act as natural anxiety regulators.
Conscious relaxation methods strengthen psychological defenses against stressors.
How Anxiety and Stress Reshape Physical Health
Body's Emergency Response System
When anxiety strikes, it activates primal survival mechanisms that redirect blood flow to vital organs while increasing cardiac activity. This evolutionary adaptation explains why many report chest tightness during panic episodes. The National Institutes of Health reveals that 31% of Americans will experience anxiety disorders during their lifetime, making this physiological response a widespread phenomenon.
Stress hormones like cortisol create temporary hyper-alertness but prolonged exposure wears down adrenal reserves. Imagine your body constantly revving like an overworked engine - this sustained strain leads to system-wide fatigue. Recognizing this pattern helps explain why morning exhaustion often accompanies chronic anxiety.
Musculoskeletal Impact of Sustained Stress
Persistent tension transforms muscles into rigid bands, particularly affecting posture-critical areas. Office workers frequently develop stress shoulders - elevated trapezius muscles resembling permanent shrugs. Recent biomechanical studies demonstrate that stressed individuals exert 28% more muscular force during routine movements than relaxed counterparts.
Digestive disturbances reveal the gut-brain axis in action. Stress-induced gastric acidity doesn't just cause discomfort - it alters gut microbiota composition. This explains why probiotic interventions often accompany anxiety treatment plans. Functional medicine practitioners increasingly address both gastrointestinal and psychological symptoms concurrently.
Cumulative Health Risks of Unmanaged Anxiety
Cardiovascular strain from chronic anxiety operates like interest accrual - small daily impacts compound into significant risks. The European Heart Journal correlates untreated anxiety with 48% higher incidence of arrhythmias. Preventive cardiology now incorporates stress-reduction protocols alongside traditional risk factor management.
Immune suppression presents another hidden danger. Cortisol's anti-inflammatory effects sound beneficial until realizing they disable infection-fighting mechanisms. This paradox explains why stressed individuals often suffer prolonged recovery from minor illnesses. Seasonal flu shots become particularly crucial for anxiety-prone populations.
Intercepting Warning Signals
Early detection requires decoding the body's distress language. Subtle signs like micro-tremors during rest or taste perception changes often precede major episodes. Maintaining a symptom-tracking journal helps identify personal warning patterns - many discover their anxiety tells through consistent documentation.
Lifestyle as Medicine
Movement patterns directly influence anxiety biochemistry. Interval walking (alternating brisk and slow paces) proves particularly effective - the varied intensity stimulates different neurochemical pathways. Nutritionally, magnesium-rich foods like pumpkin seeds act as natural muscle relaxants while stabilizing neural activity.
Contrary to popular belief, mindfulness doesn't require silent meditation. Active techniques like sensory walks or cooking meditation provide accessible entry points. The key lies in full engagement with present-moment sensory experiences rather than specific activities.
When to Seek Specialized Support
Therapy becomes essential when stress patterns resist self-management. Modern approaches like biofeedback training equip patients with real-time physiological data, creating concrete improvement metrics. Group therapy offers unexpected benefits - hearing others describe similar physical symptoms often reduces health-related anxiety.
Architecting Resilience Through Routine
Consistent circadian rhythms regulate cortisol production. Implementing fixed wake-up times (even weekends) trains the body's stress hormone cycle. Strategic meal timing further stabilizes energy - protein-rich breakfasts within 90 minutes of waking prevent mid-morning anxiety spikes.
Technology boundaries require creative solutions. Many find success with analog hours - designated screen-free periods using old-fashioned alarm clocks and paper books. This digital detoxification period allows nervous system recalibration.
Key Physical Indicators Requiring Attention
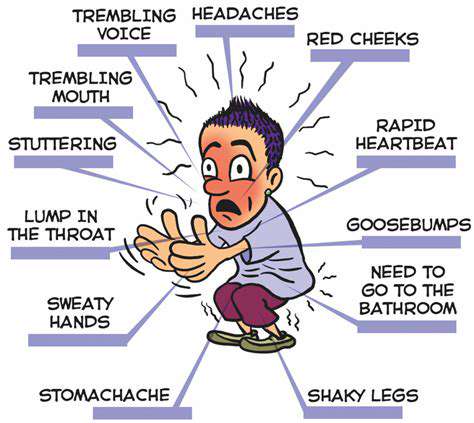
Stress-Induced Sensory Changes
Heightened startle responses and altered pain perception frequently accompany chronic stress. Some develop hypersensitivity to sounds or textures, while others experience muted sensory feedback. These neurological shifts explain why stressed individuals might misinterpret normal stimuli as threatening.
Respiratory System Responses
- Diaphragmatic constriction causing air hunger sensations
- Involuntary breath-holding during concentration
- Exercise-induced dyspnea disproportionate to effort
Controlled exhale exercises (prolonged exhalation through pursed lips) effectively counter stress breathing patterns. Many pulmonary rehabilitation techniques now incorporate anxiety management components for comprehensive care.
Gut-Brain Communication Breakdowns
Stress-induced digestive changes often follow specific sequences: appetite suppression → rebound overeating → bowel irregularity. Tracking these cycles helps identify intervention points. Fermented foods and soluble fiber particularly benefit stress-compromised guts by supporting microbial diversity.
The Critical Importance of Symptom Literacy
Decoding Body-Mind Signals
Physical symptoms act as the body's dashboard warning lights. Persistent dry mouth might indicate chronic hyperventilation, while cold extremities often reflect vasoconstriction from adrenaline surges. Developing this symptom literacy enables proactive health management rather than reactive crisis response.
Preventive Health Monitoring
Baseline metric tracking (resting heart rate, sleep quality scores) creates personalized health references. Wearable technology now makes this accessible - many smartwatches detect subtle stress indicators like heart rate variability changes. This data empowers individuals to intervene before symptoms escalate.
Cultivating Body Awareness
Proprioceptive exercises (body scanning, balance training) enhance interoceptive awareness - the ability to perceive internal states. This skill proves crucial for early anxiety detection. Yoga practitioners demonstrate 40% better interoceptive accuracy than non-practitioners according to recent neuroscience studies.
Practical Approaches for Symptom Management
Environmental Modifications
Simple spatial adjustments yield significant benefits. Blue-enriched lighting during daytime hours regulates cortisol rhythms, while warm-toned evening lighting supports melatonin production. Acoustic environments matter too - introducing low-level nature sounds can lower stress hormones by 17% according to environmental psychology research.
Movement as Neurological Reset
Non-linear movement patterns (dance, martial arts drills) particularly benefit anxious minds by disrupting rumination cycles. These activities demand full present-moment focus, creating natural mindfulness states. Recent studies show capoeira practitioners exhibit superior stress resilience compared to traditional gym users.
Nutritional Timing Strategies
Strategic caffeine management illustrates practical intervention. Delaying morning coffee by 90 minutes prevents cortisol-conflict crashes. Similarly, pairing carbohydrates with protein snacks maintains stable glucose levels - crucial for preventing anxiety-induced brain fog.
Community-Based Support Systems
Participation in skill-sharing groups (cooking classes, repair workshops) provides dual benefits - practical education and organic social connection. This format often feels less intimidating than traditional support groups while achieving similar stress-reduction outcomes.