The Role of Beta Blockers in Social Anxiety Management
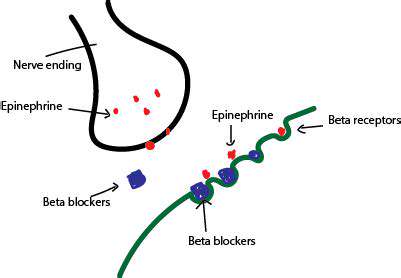
Beta-blockers achieve their effects by competing with adrenaline for binding sites on beta-adrenergic receptors. When adrenaline binds to these receptors, it triggers a cascade of biochemical events that ultimately lead to increased heart rate, blood pressure, and other physiological changes associated with the stress response. Beta-blockers effectively occupy these binding sites, preventing adrenaline from exerting its effects. This competitive binding results in a reduction of these physiological responses.
Beta-Blockers and Cardiovascular Health
One of the primary applications of beta-blockers is in the management of cardiovascular conditions. By reducing heart rate and blood pressure, they can help to lessen the strain on the heart, potentially preventing further damage and reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. This protective effect is particularly relevant in individuals with conditions like hypertension, angina, and certain types of arrhythmias.
Beta-Blockers and Social Anxiety
Interestingly, beta-blockers are sometimes prescribed to individuals experiencing social anxiety. The physiological effects of anxiety, such as increased heart rate and trembling, can be effectively mitigated by beta-blockers. By reducing these physical symptoms, beta-blockers can help individuals feel more calm and composed in social situations, ultimately improving their ability to interact with others. This application highlights the multifaceted role of beta-blockers in managing various aspects of human health.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While beta-blockers can be beneficial, they can also have side effects, such as fatigue, dizziness, and breathing difficulties, particularly in individuals with pre-existing respiratory issues. It's crucial to discuss any potential side effects with a healthcare professional before starting treatment. Furthermore, beta-blockers can interact with other medications, so complete disclosure of all medications being taken is essential to avoid adverse drug interactions. Careful monitoring and adjustment of dosage are often necessary to ensure optimal efficacy and minimize the risk of side effects.
Dosage and Administration
The appropriate dosage and administration of beta-blockers vary significantly based on individual needs and the specific condition being treated. A healthcare professional will carefully assess the patient's medical history, current health status, and other factors to determine the most suitable dosage regimen. Adherence to the prescribed dosage and administration schedule is essential for achieving the desired therapeutic effects. Failure to follow instructions can lead to reduced efficacy or the emergence of adverse effects.
Cognitive Development is crucial for lifelong learning and critical thinking.
Dosage and Side Effects

Dosage Considerations
Determining the appropriate dosage for any medication is crucial for achieving therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential adverse effects. This process often involves a careful evaluation of several factors, including the patient's age, weight, overall health, and the specific condition being treated. Individualized dosage adjustments are frequently necessary to optimize treatment outcomes and ensure patient safety. For example, a patient with liver or kidney impairment may require a lower dosage than a healthy individual to prevent drug accumulation and toxicity.
Furthermore, the route of administration can significantly impact the dosage required. Oral medications, for instance, may have different absorption rates and bioavailability compared to intravenous or intramuscular injections. Consequently, the dosage regimen must be tailored to the specific route of administration to ensure effective delivery of the medication to its target site. Understanding these factors is essential for healthcare professionals to prescribe the correct dosage and prevent potential complications.
Potential Side Effects
While medications are designed to treat various ailments, they can sometimes produce unwanted side effects. These side effects can range from mild discomfort to more serious complications, and their severity can vary considerably from person to person. Understanding the potential side effects associated with a particular medication is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients.
Some common side effects include nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, and fatigue. These are often mild and temporary, resolving on their own as the body adjusts to the medication. However, some side effects can be more severe and require immediate medical attention. For example, severe allergic reactions, such as hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing, necessitate immediate intervention. It is important for patients to report any unusual or concerning side effects to their healthcare provider promptly.
Managing Side Effects
Many medications can cause side effects, but there are often ways to manage them effectively. Healthcare providers can often prescribe medication to mitigate the symptoms or suggest lifestyle changes that can help. For instance, certain medications can be taken with food to reduce gastrointestinal upset. This can also be an important consideration when determining the best time of day to take a medication.
In some cases, non-pharmacological approaches can be helpful, such as increasing fluid intake, applying compresses, or engaging in relaxation techniques. Patient education on recognizing and managing common side effects is vital for promoting patient well-being and adherence to treatment plans. This includes providing clear instructions on when and how to report side effects to healthcare providers. This proactive approach can help ensure that any potential problems are addressed promptly and effectively.
Combining Beta-Blockers with Other Therapies
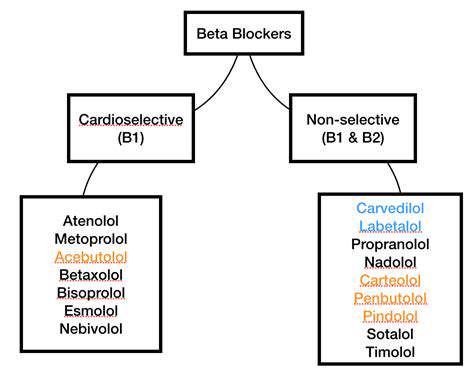
Combining Beta-Blockers with Other Medications
Beta-blockers, a class of medications commonly prescribed for various conditions like hypertension and angina, can interact with other drugs, potentially leading to adverse effects. Understanding these interactions is crucial for ensuring patient safety and achieving optimal treatment outcomes. Careful monitoring and adjustments to dosages may be necessary when combining beta-blockers with other medications.
The interaction between beta-blockers and other medications can range from mild to severe. Some drugs can enhance the effects of beta-blockers, while others can reduce their effectiveness. It's vital that patients inform their healthcare providers about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, to assess potential interactions.
Potential Interactions with Antihypertensives
Combining beta-blockers with other antihypertensive medications, such as ACE inhibitors or diuretics, can have a synergistic effect on blood pressure reduction. This can be beneficial in managing hypertension, but it also increases the risk of hypotension, a dangerously low blood pressure. Close monitoring of blood pressure is essential in such cases.
The combined effect of these medications can be unpredictable, and it's essential to have a clear understanding of the specific mechanisms involved. Patients should discuss dosage adjustments with their doctor to achieve the desired therapeutic effect without compromising safety. Careful titration of medications is often necessary to avoid adverse events.
Interactions with Medications Affecting the Cardiovascular System
Beta-blockers can interact with medications affecting the cardiovascular system, such as calcium channel blockers or digoxin. These interactions can lead to changes in heart rate and rhythm, potentially triggering arrhythmias or other complications. Understanding these potential interactions is critical for healthcare professionals to ensure optimal patient care.
Careful consideration of the patient's individual medical history and current medications is imperative when prescribing beta-blockers in conjunction with other cardiovascular medications. Monitoring for any signs of adverse effects is crucial during the initial stages of combined therapy.
Combining Beta-Blockers with Central Nervous System Agents
Beta-blockers can interact with central nervous system agents, such as antidepressants or sedatives. These interactions can lead to an increased risk of drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired cognitive function. Patients should be aware of these potential side effects and report any unusual symptoms to their doctor.
Additionally, the combined effect of these medications may affect the patient's ability to perform tasks that require mental alertness and coordination. Driving or operating machinery may need to be approached with caution, especially in the initial stages of combined therapy or if dosage adjustments are made.
Interactions with Other Drug Classes
Beta-blockers can also interact with other drug classes, including those used to treat asthma, allergies, and diabetes. These interactions can lead to unpredictable and potentially harmful outcomes. Thorough assessment of all medications is essential before initiating combined therapy.
Healthcare professionals should consult comprehensive drug interaction databases and guidelines to ensure they are aware of the potential risks involved in combining beta-blockers with other medications. Patient education regarding potential side effects is also crucial for proactive management of any adverse reactions.