The Correlation Between OCD and Chronic Headaches: A Deep Dive
How OCD Contributes to Headache Development
Understanding the Link Between OCD Symptoms and Headaches
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is characterized by unwanted, intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors aimed at reducing anxiety. These symptoms can contribute to physical manifestations, such as chronic headaches.
Anxiety and stress are often prevalent in individuals with OCD, which can lead to muscle tension. This muscle tension, particularly in the neck and shoulders, is a common precursor to tension-type headaches, making the link between OCD and headaches more apparent.
Additionally, the cognitive patterns associated with OCD, such as hyper-focusing on distressing thoughts, can heighten stress levels. As stress levels rise, so does the likelihood of experiencing tension headaches, creating a cycle of discomfort.
Furthermore, individuals with OCD may struggle with sleep due to their intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. Poor sleep can exacerbate headaches, resulting in a chronic issue that intertwines with the ongoing symptoms of OCD.
By recognizing how the obsessive and compulsive nature of OCD affects both mental and physical health, we can better understand the complex relationship between this disorder and chronic headaches.
The Impact of Treatment Approaches on Headache Relief
Effective treatment for OCD often involves therapy, medication, or a combination of both. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), particularly exposure and response prevention (ERP), can help decrease anxiety levels and potentially mitigate headache occurrences.
Moreover, establishing a regular routine as part of treatment can improve sleep patterns, subsequently leading to fewer headaches. Ensuring quality sleep is critical for individuals with OCD, as it significantly influences overall health and well-being.
Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed for OCD treatment. While these medications have been shown to help manage OCD symptoms, they may also result in changes in headache frequency and severity in some patients.
Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as mindfulness and deep breathing exercises, can also provide benefits, as they help to reduce anxiety and lower muscle tension. This can consequently decrease the incidence of tension headaches.
Ultimately, a multifaceted treatment approach that addresses both OCD symptoms and headache management can lead to better outcomes for individuals experiencing these interconnected conditions.
The Role of Stress in Headache Severity
The Impact of Chronic Stress on Headache Frequency
Chronic stress has been identified as a significant contributor to the frequency of headaches, particularly tension-type headaches. When the body is under continuous stress, it enters a state of heightened alertness, leading to muscle tension, especially in the neck and shoulders.
This tension can trigger headaches, resulting in a painful cycle where stress causes headaches, which in turn leads to more stress. Identifying and managing sources of chronic stress can be key to reducing the frequency of headaches.
Moreover, chronic stress can alter pain perception, making individuals more susceptible to headaches. This change means that what may have been a minor annoyance can escalate into something more debilitating under prolonged stress conditions.
Effective stress management strategies, such as mindfulness, exercise, and therapy, can help alleviate the physical and emotional responses that contribute to headache onset. Regular practice of these strategies can lead to a notable decrease in headache frequency over time.
In summary, chronic stress is not just a background issue; it plays a crucial role in the emergence and persistence of headaches, suggesting that interventions targeting stress could have a direct impact on headache management.
The Biochemical Link Between Stress and Headache Pathways
The biochemical response to stress involves the release of various hormones, including cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare the body for a 'fight or flight' response. These hormonal fluctuations can lead to increased muscle tension and blood vessel changes that contribute to headaches.
Research shows that this stress-induced hormonal release can sensitize pain pathways in the nervous system. When these pathways become more sensitive, even mild stressors can trigger headache episodes.
Additionally, chronic exposure to stress hormones may lead to inflammation, which is another pathway associated with headache development. This inflammation can cause changes in the brain and blood vessels, further increasing headache susceptibility.
Understanding these biochemical links can help researchers develop targeted treatments to mitigate headache episodes by focusing on regulating stress responses in the body. This could involve pharmacological interventions as well as lifestyle changes to lower stress levels.
Overall, the connection between stress and headache pathways highlights the need for a multifaceted approach to headache management that includes both psychological and pharmacological strategies.
Identifying Stress Triggers for Better Headache Management
One of the first steps in managing headaches exacerbated by stress is identifying the specific stressors in an individual's life. Stress triggers can vary widely among individuals and may include work demands, personal relationships, health concerns, and financial difficulties.
Keeping a headache diary can be an effective method for identifying patterns and pinpointing stress-related triggers. By documenting headache occurrence alongside daily stressors, individuals can begin to recognize which events or situations correlate with increased headache frequency.
Once these triggers are identified, individuals can develop strategies to manage or avoid them. For instance, if work-related stress is found to increase headache severity, seeking support from colleagues or adjusting work routines may be beneficial.
Moreover, addressing the identified stressors through lifestyle changes or professional support can significantly reduce the impact of stress on headache severity. Techniques such as time management, delegation, and conflict resolution skills can alleviate work-related stress.
Ultimately, recognizing and managing stress triggers is a crucial component of an effective headache management plan, allowing for more personalized and successful interventions.
Therapeutic Approaches to Reduce Stress and Improve Headache Outcomes
Various therapeutic approaches can help reduce stress and, consequently, the severity and frequency of headaches. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one such effective method that helps individuals restructure negative thought patterns and provide coping strategies for managing stress.
Mindfulness and meditation practices are also gaining recognition for their role in stress reduction. These techniques encourage individuals to focus on the present moment, helping to decrease anxiety and promote relaxation, which can lead to a reduction in headache occurrences.
Physical therapies, such as massage, acupuncture, and chiropractic care, can also play a significant role in headache management. These therapies can help relieve muscle tension and stress, leading to fewer tension headaches.
Additionally, lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, can bolster the body's resilience to stress. Exercise, in particular, releases endorphins, natural pain-relievers that can alleviate tension and improve mood.
In conjunction with these therapies, medication may be prescribed to manage severe headaches or alleviate underlying conditions. A comprehensive approach that includes various treatments can yield the best results in headache management and overall well-being.
Comorbid Conditions and Their Impact
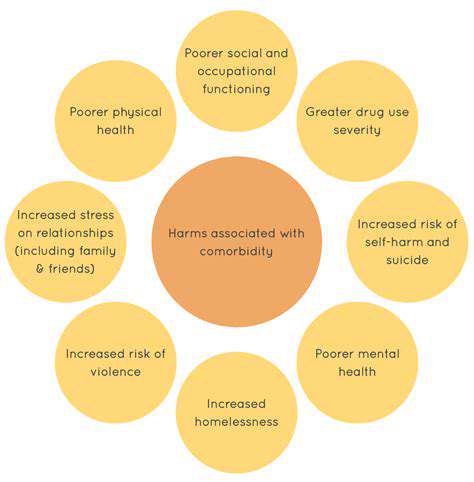
Understanding Comorbid Conditions
Comorbid conditions are health issues that occur alongside a primary condition, often complicating diagnosis and treatment. In the case of OCD, headaches can significantly impact a patient's quality of life, leading to increased anxiety and stress. This dual burden can make it difficult for individuals to manage their symptoms effectively.
Research indicates that individuals with OCD may experience a higher incidence of chronic headaches compared to the general population. The interplay between the two conditions can create a cycle where the anxiety from OCD exacerbates headache pain, and in turn, chronic headaches increase anxiety levels.
The Role of Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety are substantial contributors to both OCD and chronic headaches. For many individuals, the obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors associated with OCD can elevate their stress levels, leading to tension headaches or migraines. Finding effective strategies to manage these feelings is crucial for breaking the cycle.
Understanding how anxiety contributes to headache disorders opens up potential pathways for treatment. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and relaxation techniques may help reduce anxiety, which could, in turn, alleviate headache symptoms.
Treatment Approaches for Both Conditions
Effective management of both OCD and chronic headaches requires a comprehensive treatment plan. This typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments tailored to the individual’s needs. Addressing both conditions simultaneously can lead to improved outcomes and a clearer path toward recovery.
Additionally, alternative therapies such as biofeedback and mindfulness practices may offer relief for both OCD and chronic headaches by promoting relaxation and reducing stress. Integrating these approaches can enhance the overall treatment experience and foster resilience against future episodes.
Effective Treatment Approaches
Understanding the Link Between OCD and Headaches
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition characterized by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions). Research indicates a significant correlation between OCD and chronic headaches, as the stress and anxiety often associated with OCD can contribute to headache development.
Studies show that individuals with OCD may experience tension-type headaches more frequently than those without the disorder. The exact mechanism of this relationship is not fully understood; however, it is believed that the heightened state of anxiety can lead to muscle tension, particularly in the head and neck region.
In addition to tension-type headaches, individuals with OCD may also be more susceptible to migraines. Migraines can be triggered by various factors, including stress and anxiety, which are prevalent in those with OCD. Understanding this connection is crucial for effective management of both conditions.
Furthermore, the compulsive behaviors associated with OCD may lead to lifestyle choices that exacerbate headache symptoms. Poor sleep, inadequate hydration, and a lack of regular exercise are common among individuals with OCD, all of which can contribute to the development or worsening of headaches.
Therefore, recognizing the signs of chronic headaches in individuals with OCD is essential for developing a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both mental health needs and headache relief.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD and Headache Management
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective treatment approaches for OCD, and it can also provide benefits for headache management. CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to their symptoms.
For those experiencing both OCD and chronic headaches, CBT can teach coping mechanisms to manage anxiety that often leads to headache symptoms. Techniques such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises can be incorporated into the therapy, which can help reduce muscle tension and stress levels.
Additionally, CBT can assist in creating healthier lifestyle habits. By working with a therapist, individuals can develop strategies to improve their sleep hygiene, exercise routines, and hydration habits, which can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches.
Moreover, CBT is a structured approach that allows for gradual exposure to one’s obsessions in a controlled environment, reducing the compulsive reactions that can create stress and tension, further alleviating headache symptoms.
Engaging in CBT not only targets the core symptoms of OCD but also addresses the related headaches, resulting in a more holistic treatment approach and improved quality of life for the individuals.
Medication Options for Managing OCD and Associated Headaches
In addition to psychotherapy, various medications can be effective for treating OCD, and some may also alleviate headache symptoms. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed for OCD and may have a beneficial effect on headache frequency.
SSRIs work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain, which can improve mood and reduce anxiety. By managing the anxiety linked with OCD, patients may notice a reduction in the incidence of tension headaches as well.
Other medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants, have also shown promise in treating both OCD and migraines. These medications affect neurotransmitter activity, potentially providing relief from both conditions.
It's essential for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate medication regimen. Adjustments may be necessary to find the right balance that effectively reduces OCD symptoms while managing headache occurrences.
Additionally, the potential side effects of these medications need to be closely monitored, as some may lead to increased headache symptoms in certain individuals. Open communication with healthcare providers will allow for timely adjustments and personalized treatment plans.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Symptoms
Incorporating lifestyle modifications can greatly assist individuals in managing both OCD and chronic headaches. Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being, making it an effective strategy for alleviating both conditions.
Practicing stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help lower tension and anxiety, which are common triggers for headaches. These activities not only promote relaxation but also provide an outlet for individuals to cope with their OCD symptoms.
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is essential for overall health and can help to prevent headaches. Lack of sleep can exacerbate OCD symptoms and lead to increased headache frequency, making it crucial for individuals to prioritize their sleep hygiene.
Additionally, staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can have significant effects on headache prevention. Certain foods and dehydration have been linked to trigger headaches, so individuals should be mindful of their dietary choices and water intake.
By combining these lifestyle changes with professional treatment approaches, individuals can create a comprehensive strategy to manage their OCD and chronic headaches, enhancing their overall quality of life.
Living with OCD: Strategies for Managing Headache Symptoms

Understanding the Link Between OCD and Headaches
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is often linked to various physical symptoms, one of the most prevalent being chronic headaches. Studies have shown that individuals with OCD may experience a higher frequency of headaches compared to the general population.
This correlation can often be attributed to the heightened levels of anxiety and stress that accompany OCD. Managing these emotional factors is crucial for alleviating headache symptoms.
Effective Coping Strategies for Headache Relief
Several strategies can help manage headache symptoms that coincide with OCD. Maintaining a regular schedule, including sleep patterns, can significantly reduce the occurrence of headaches.
Additionally, integrating relaxation techniques such as mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial. These practices not only help in reducing anxiety but also promote overall well-being.
Seeking Professional Help and Support
For those suffering from both OCD and chronic headaches, consulting healthcare professionals can be a vital step towards relief. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is often recommended for treating OCD and can also address headache symptoms effectively.
Furthermore, medication may be prescribed to manage OCD symptoms, which in turn could help reduce headache frequency. Establishing a comprehensive treatment plan is essential to enhancing quality of life for those affected.