Identifying Anxiety Related Dehydration: Symptoms and Solutions
The Subtle Connection Between Anxiety and Dehydration
Understanding the Link
Anxiety, a common mental health concern, often manifests with a range of physical symptoms. While many factors contribute to anxiety, a surprising and often overlooked aspect is dehydration. The body's intricate systems rely heavily on water for optimal function, and when levels dip below optimal, various physiological processes can be disrupted, potentially leading to heightened feelings of anxiety and nervousness. This subtle connection highlights the importance of proper hydration in managing overall well-being and anxiety.
The human brain, composed of roughly 73% water, is particularly sensitive to changes in hydration. Even mild dehydration can impact cognitive function, leading to difficulties with concentration, memory, and emotional regulation. These cognitive impairments can inadvertently amplify feelings of anxiety, creating a vicious cycle where dehydration fuels anxiety, and anxiety exacerbates the body's need for more water.
The Role of Electrolytes
Beyond water itself, electrolytes play a crucial role in maintaining optimal hydration and preventing anxiety. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium are essential for nerve and muscle function. Imbalances in these crucial minerals can lead to muscle cramps, fatigue, and irritability, all symptoms that can exacerbate existing anxiety or even trigger it in susceptible individuals.
Maintaining a balanced electrolyte intake through a healthy diet, including fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can significantly contribute to better hydration and emotional stability. Proper hydration helps maintain the delicate balance of electrolytes, which in turn, supports healthy nerve and muscle function, promoting a calmer state of mind.
Physical Symptoms and Dehydration
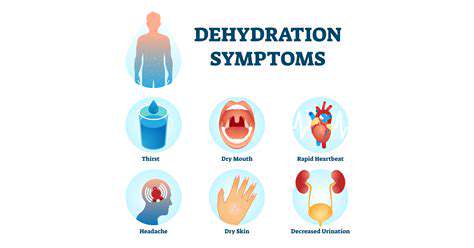
Dehydration can manifest in a variety of physical symptoms that are often confused with anxiety symptoms. Headaches, dizziness, and fatigue are common signs of dehydration. These symptoms can mimic or worsen feelings of anxiety, creating a confusing and potentially concerning experience for individuals. Recognizing these physical cues as potential signs of dehydration can lead to effective interventions, improving both physical and mental well-being.
Furthermore, dry mouth, a common symptom of dehydration, can further contribute to anxiety. The sensation of a dry mouth can be unsettling and trigger feelings of nervousness or discomfort, potentially amplifying pre-existing anxiety or causing anxiety in those who are susceptible.
Hydration Strategies for Anxiety Management
Implementing simple hydration strategies can significantly improve overall well-being and potentially alleviate anxiety symptoms. Carrying a reusable water bottle and setting reminders to drink water throughout the day can be incredibly helpful. Consuming hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables can also contribute to overall hydration levels.
In addition to drinking water, incorporating electrolyte-rich foods into the diet can help replenish lost minerals and further support hydration. Understanding the subtle connection between anxiety and dehydration can empower individuals to adopt proactive measures to maintain optimal hydration and potentially manage anxiety symptoms more effectively.
The Importance of Consistent Hydration
Consistent hydration is not just a temporary fix but a long-term approach to better overall health. Regular intake of water and electrolyte-rich foods can have a profound impact on maintaining emotional equilibrium and reducing the risk of anxiety flare-ups. Making hydration a priority can help regulate the body's physiological processes, potentially leading to a more stable and less reactive emotional response to stress and anxiety.
By understanding the profound impact of hydration on the body's systems, individuals can actively participate in managing their overall well-being, and perhaps discover a new tool for addressing anxiety-related discomfort. It's crucial to emphasize that while hydration can play a role, professional medical advice should always be sought for managing anxiety.
The Role of Anxiety in Fluid Imbalance
Understanding the Physiological Basis of Anxiety
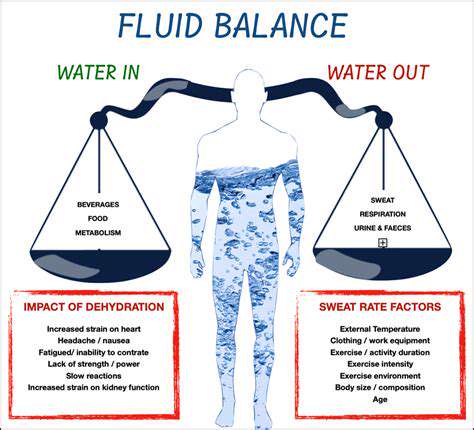
Anxiety, a pervasive human experience, is deeply intertwined with physiological processes, notably those related to fluid balance. This connection stems from the intricate interplay between the autonomic nervous system and the body's homeostatic mechanisms. Understanding this interplay is crucial for comprehending the potential impact of anxiety on fluid regulation. The body's response to perceived threat, a key component of anxiety, often involves a cascade of hormonal changes, including the release of adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones influence various bodily functions, including fluid distribution and electrolyte balance.
The sympathetic nervous system, activated during anxious states, can trigger vasoconstriction, impacting blood flow and potentially influencing the distribution of fluids throughout the body. This intricate physiological response highlights the need for further research into the specific mechanisms by which anxiety affects fluid balance. The body's attempt to maintain homeostasis during anxiety may lead to subtle but significant changes in fluid retention or excretion. These changes can manifest in various ways, potentially affecting overall health and well-being.
Anxiety's Impact on Thirst and Fluid Intake
Anxiety can significantly affect an individual's perception of thirst and subsequent fluid intake. The physiological stress response associated with anxiety can lead to a decreased awareness of thirst, potentially resulting in insufficient fluid intake. This can be compounded by anxious behaviors, such as avoidance of drinking or increased urination due to stress. Furthermore, the body's need for hydration might be overlooked during periods of heightened anxiety. This neglect can lead to dehydration, exacerbating the negative effects of anxiety on overall health.
Conversely, some individuals may experience an increased sense of thirst due to anxiety. This paradoxical effect underscores the complexity of the relationship between anxiety and fluid intake. The perceived need for hydration might be driven by the body's compensatory mechanisms to maintain equilibrium, or it could be a manifestation of the anxiety itself. Understanding these intricacies is essential to providing effective support for individuals experiencing anxiety-related fluid imbalance issues.
Anxiety-Induced Changes in Fluid Distribution
Anxiety can disrupt the normal distribution of fluids within the body. The body's attempt to cope with perceived threats during anxiety can lead to changes in capillary permeability, affecting the movement of fluids between blood vessels and tissues. These changes can potentially result in edema (swelling) in certain areas or reduced fluid volume in others. These alterations can have significant implications for overall health and well-being, potentially contributing to discomfort and other symptoms.
The impact of anxiety on fluid distribution is further complicated by the potential for electrolyte imbalances. These imbalances can arise from altered fluid movement and can exacerbate the effects of anxiety on the body. In essence, anxiety can play a critical role in disrupting the body's delicate balance of fluids and electrolytes.
Symptoms and Manifestations of Anxiety-Related Fluid Imbalance
The symptoms associated with anxiety-related fluid imbalance can range from subtle to severe. Individuals experiencing anxiety may notice changes in urination frequency or volume, along with feelings of excessive thirst or, conversely, a lack of thirst. These alterations in fluid regulation can be accompanied by headaches, fatigue, or other general discomfort. It is important to recognize these symptoms as potential indicators of an underlying anxiety-related fluid imbalance. Early detection and intervention can be critical in mitigating potential health risks.
Further investigation into the specific physiological mechanisms is necessary to fully understand the correlation between anxiety and these fluid-related symptoms. Detailed analysis of individual responses and potential contributing factors can provide a more comprehensive understanding of this complex interaction. This can be essential for developing effective strategies for managing anxiety-related fluid imbalance.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Addressing anxiety-related fluid imbalances requires a multifaceted approach that targets both the anxiety and the physiological disruptions it causes. Strategies for managing anxiety may include relaxation techniques, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and medication, as appropriate. These interventions can help to normalize the body's physiological responses, thereby reducing the impact on fluid balance. Simultaneously, ensuring adequate hydration and maintaining a healthy diet can support the body's natural ability to regulate fluid levels.
Regular monitoring of fluid intake and output, combined with professional medical advice, is vital. This allows for the identification of potential imbalances and the implementation of appropriate corrective measures. This proactive approach supports overall health and well-being, especially for individuals prone to anxiety-related fluid balance issues.