Exploring the Essence of Existence: A Deep Dive into Nature's Intricacies
The Fundamental Elements of Nature
The Building Blocks of Matter
The universe is composed of various fundamental particles, which serve as the building blocks of matter. These particles include quarks, leptons, and bosons, all playing distinct roles in the formation of atoms and molecules. Quarks combine to form protons and neutrons, which are the nuclei of atoms, while leptons include electrons that orbit around these nuclei.
This intricate arrangement is governed by the four fundamental forces: gravity, electromagnetism, the weak nuclear force, and the strong nuclear force. Each of these forces operates at different scales and affects the interactions between particles. For instance, the strong nuclear force is what holds protons and neutrons together in the atomic nucleus, while electromagnetism governs the attraction and repulsion between charged particles.
Understanding these building blocks also leads to insights into the formation of elements on the periodic table. As stars evolve, they fuse lighter elements into heavier ones through nuclear fusion, enriching the universe with a diversity of materials essential for life. The study of these processes is fundamental in astrophysics and chemistry, bridging cosmic phenomena with earthly experiences.
Current research continues to unravel the mysteries of these particles, delving deeper into realms such as quantum mechanics and the Higgs boson. Discoveries at particle accelerators challenge and expand our understanding of the universe’s inception, potentially leading to revolutionary advancements in technology and a deeper comprehension of reality itself.
Biological Systems: The Complexity of Life
Life, as we know it, is an intricate network of biological systems that work together to sustain living organisms. At the core of these systems are cells, regarded as the basic unit of life. Cells are categorized into prokaryotic and eukaryotic types, each with unique structures and functions that contribute to the organism's overall health and survivability.
Within multicellular organisms, cells differentiate to perform specialized functions, forming tissues, organs, and systems. This specialization allows for greater efficiency and adaptability, enabling organisms to thrive in various environments. For instance, plant cells have chloroplasts that facilitate photosynthesis, while animal cells are equipped to manage energy through cellular respiration.
Additionally, the interplay between various ecological systems further illustrates the complexity of life. Ecosystems—from forests to oceans—are dynamic and interdependent, wherein organisms coexist and interact with their environment and each other. This balance is essential not only for individual species but for the overall health of the planet.
Research in biological sciences continues to evolve, with primary focus on genetics, ecology, and evolutionary biology. Understanding these biological intricacies not only enriches our knowledge but also informs conservation efforts that aim to protect biodiversity essential for the planet's future.
The Interconnectedness of Ecosystems
At the heart of nature lies the interconnectedness of diverse ecosystems that accommodate an array of organisms. Each ecosystem, whether it be a tropical rainforest, coral reef, or desert, has its own unique environmental conditions and organisms adapted to thrive within them. The transfer of energy and nutrients between these organisms facilitates a delicate balance that sustains life.
Food webs illustrate this complex network, showcasing how energy flows through multiple trophic levels, from producers to consumers and decomposers. The removal or extinction of one species can trigger a cascade of effects throughout the ecosystem, highlighting the importance of each organism in maintaining ecological balance.
This interconnectedness extends beyond flora and fauna; it encompasses the physical environment itself. Changes in climate, pollution, and human intervention create ripples that impact ecosystems globally. Studying these effects is critical for predicting changes in biodiversity and developing strategies to mitigate adverse impacts on our planet.
Conservation biology emerges as a crucial field in addressing these challenges, focusing on preserving biodiversity and promoting sustainable practices. By fostering awareness of these intricate connections, we can better advocate for policies that support the health and resilience of our ecosystems.
The Role of Natural Cycles
Natural cycles are fundamental phenomena that regulate life on Earth, including the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle. Each cycle consists of a series of processes that recycle essential elements and compounds, ensuring that they are available to support various life forms. Understanding these cycles sheds light on the intricate balance necessary for maintaining life.
The water cycle, for example, encompasses evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and infiltration. This continuous movement between liquid, vapor, and solid states not only supports drinking water needs but also nurtures ecosystems—feeding plants, animals, and microorganisms that depend on fresh water for survival.
Similarly, the carbon cycle highlights the transfer of carbon through different reservoirs, such as the atmosphere, oceans, and living organisms. Plants absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, returning it to the atmosphere via respiration and decomposition. This balance is crucial in regulating climate and sustaining ecosystems.
Natural cycles are not isolated; they often interact with and influence one another, creating a dynamic web of processes essential for life. Recognizing the impact of human activities on these cycles is vital for developing approaches that promote environmental sustainability and biodiversity preservation.
Human Impact and Environmental Stewardship
As stewards of the planet, humans have a profound impact on the environment, often exacerbating issues such as pollution, deforestation, and climate change. Industrialization, urbanization, and agricultural practices significantly alter natural landscapes and disrupt ecological balance, posing threats to both biodiversity and human health.
However, awareness of these challenges has spurred a global movement toward sustainability and conservation. Individuals and organizations now strive to implement practices that minimize harm to the environment, from promoting renewable energy sources to advocating for sustainable agriculture and forestry practices.
Education plays a crucial role in fostering environmental stewardship. By informing communities about ecological interrelationships and sustainability practices, we empower individuals to make informed choices that positively impact the planet. Initiatives range from community clean-ups to wildlife conservation projects, aiming to restore and protect natural habitats.
Collaboration between governments, businesses, and individuals is essential in addressing environmental challenges. Policymaking that prioritizes conservation, along with corporate responsibility in environmental practices, can lead to meaningful change. By taking collective action, we can work towards a more sustainable future, safeguarding our planet for generations to come.
The Interconnectedness of Life
The Web of Life
The concept of the web of life illustrates the intricate relationships that bind all forms of existence. Each species plays a unique role, contributing to the overall health of ecosystems. Predators, prey, plants, and microorganisms are all part of a delicate balance. Disruption in one area can have cascading effects on others, highlighting the significance of biodiversity.
Ecologists have shown that the richness of life in an ecosystem translates to greater resilience. Diverse connections allow systems to adapt to changes, whether they stem from climate shifts or human intervention. This adaptability ensures that life can continue even in the face of adversity.
Plant life, often considered the backbone of ecosystems, provides essential services like oxygen production and carbon sequestration. Animals, in turn, facilitate pollination and seed dispersal, further enriching their environments. The interplay between autotrophs and heterotrophs underpins the sustenance of life.
Microbial life, though often overlooked, plays a foundational role in nutrient cycling. The decomposition of organic materials by bacteria and fungi helps to return nutrients to the soil, making them available for plants. This highlights the interconnectedness—even the smallest life forms are crucial to the greater system.
Understanding the web of life urges us to appreciate the complexity around us. It promotes a sense of stewardship towards nature, reminding us that every action has a reaction, and every species has its place in the grand tapestry of existence.
Ecological Balance and Harmony
Ecological balance refers to the state where biological communities exist in a stable condition, maintaining a dynamic equilibrium among all living organisms. This balance is vital for the continued survival of diverse species and the sustainability of environmental processes.
Predator and prey relationships exemplify this concept; they regulate each other's populations, preventing overpopulation and resource depletion. When one species is removed, the entire ecosystem can be thrown out of balance, leading to the decline of various organisms.
Human activities often challenge ecological balance. Urbanization, pollution, and deforestation disrupt habitats, causing many species to adapt, migrate, or face extinction. The consequences of these changes can lead to a decrease in biodiversity, further destabilizing ecosystems.
Conservation efforts aim to restore balance by protecting natural habitats and fostering biodiversity. Programs that focus on rewilding and the reintroduction of keystone species can help restore lost connections and improve ecological resilience.
A commitment to understanding and maintaining ecological balance encourages responsible interactions with our environment. It reinforces the importance of sustainable practices that protect the delicate links between all forms of life.
The Role of Humans in Nature
Humans have a profound impact on the natural world—both positive and negative. Our technological advancements have enabled us to manipulate environments, often leading to significant ecological changes. However, our ability to innovate also offers solutions to environmental challenges.
As stewards of the planet, we hold the responsibility to protect nature for future generations. This role entails recognizing our interconnectedness with all life forms and understanding that we are not separate from nature, but part of it.
Education plays a crucial part in fostering a sense of environmental responsibility. By raising awareness about ecosystems and the consequences of human actions, we can inspire individuals to engage in conservation efforts. This understanding empowers communities to act towards sustainable living.
Technology also offers tools for conservation, from renewable energy sources to sustainable agriculture practices. These advancements can help mitigate our impact, fostering a balance where human and ecological needs coexist harmoniously.
Ultimately, embracing our role in nature requires a shift in mindset—a recognition that our wellbeing is inextricably linked to the health of our environment. By cultivating a spirit of cooperation with the natural world, we can create a more sustainable future.
The Beauty of Natural Diversity
Natural diversity encompasses the vast array of life forms found on Earth, each contributing unique characteristics to their ecosystems. This diversity not only enhances ecological resilience but also enriches human culture and experience.
From the majestic variety of trees in a tropical rainforest to the vibrant colors of coral reefs, nature’s beauty is a testament to the intricate processes that have evolved over billions of years. Each species, no matter how small, plays a role in the larger ecosystem, reminding us of the importance of every form of life.
Appreciating biodiversity involves understanding the myriad benefits that different species provide. For instance, rich ecosystems contribute to agriculture, medicine, and recreation. They offer resources that humans rely on for survival, proving that diversity is essential to our way of life.
Moreover, experiencing natural diversity fosters a sense of wonder and connection. It encourages mindfulness and appreciation for what the Earth offers, promoting an intrinsic motivation to protect our planet’s habitats and inhabitants.
As we face environmental crises, celebrating and preserving biodiversity becomes increasingly vital. Protecting diverse habitats strengthens ecosystem services, ensuring that both nature and humanity can thrive together into the future.
Human Impact on Natural Systems
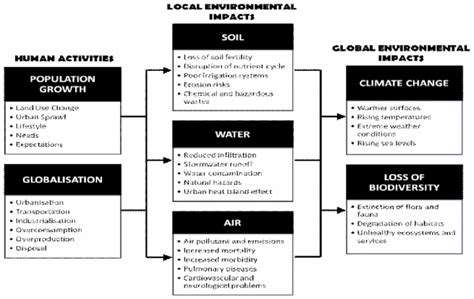
Understanding Ecosystem Dynamics
Ecosystems are intricate networks that embody the interactions among living organisms and their physical environment. These connections are vital for maintaining balance and ensuring the survival of various species within their habitats.
Human activity has a profound effect on these dynamics, often leading to disruptions that can ripple through the entire ecosystem. Recognizing the delicate balance within ecosystems is crucial for conservation efforts.
Deforestation and Its Consequences
Deforestation is one of the most significant threats to natural systems, resulting in the loss of biodiversity and the disruption of water cycles. When trees are removed, not only is habitat for countless species destroyed, but carbon sequestration capabilities are also diminished.
Furthermore, the long-term consequences of deforestation can include soil erosion and increased greenhouse gas emissions. These changes can lead to a cascade of negative effects impacting both wildlife and human populations.
Pollution: A Global Challenge
Pollution, in its various forms, poses a serious threat to natural systems worldwide. From air pollution that affects climate patterns to water pollution disrupting aquatic ecosystems, human activity releases substances that can wreak havoc on our environment.
Addressing pollution requires collective efforts to reduce emissions and contaminants and to promote sustainable practices. The health of our planet relies on our ability to mitigate these challenges and restore affected areas.
Climate Change and Biodiversity Loss
Climate change represents one of the most pressing issues that directly impacts natural systems and biodiversity. Altered weather patterns, rising temperatures, and unpredictable climate events have the potential to displace many species.
As habitats change or disappear, the interconnectedness of life can be highly disturbed, resulting in a loss of biodiversity that may take centuries to recover. Understanding and addressing climate change are imperative for the protection of our natural systems and the future of our planet.
The Role of Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are essential in mitigating the adverse effects of human impact on natural systems. These initiatives can range from protected areas meant to preserve biodiversity to community-driven projects aimed at restoring habitats.
By encouraging sustainable practices and raising awareness, conservation programs strive to ensure that future generations can enjoy and benefit from the richness of our natural world. With collective commitment, it is possible to achieve a harmonious balance between humanity and the environment.
Embracing Nature Through Conservation Efforts

Understanding the Importance of Conservation
The concept of conservation goes beyond merely preserving nature; it is about maintaining the balance of ecosystems and safeguarding biodiversity. Conservation activities not only protect endangered species but also preserve the habitats that are crucial for their survival. By focusing on conservation efforts, we ensure that future generations can experience the beauty and complexity of the natural world.
One of the primary goals of conservation is to mitigate human impact on the environment. This involves implementing sustainable practices that minimize resource depletion and restore damaged ecosystems. By engaging in conservation, we acknowledge our responsibility towards the Earth and strive to create a healthier planet.
Conservation initiatives can take many forms, from local community clean-ups to international treaties aimed at protecting wildlife. These efforts often require collaboration among various stakeholders, including governments, non-profit organizations, and individuals. Through education and outreach, we can motivate more people to participate in these vital conservation programs.
Moreover, conservation has significant social and economic benefits. Healthy ecosystems contribute to clean air and water, which are essential for human life. Additionally, thriving natural areas can bolster local economies through eco-tourism and sustainable practices. This demonstrates that conservation is not only an ethical imperative but also a sound investment in our future.
Steps Individuals Can Take Towards Conservation
Every person has the power to contribute to conservation efforts, starting with small, everyday actions. For instance, reducing waste by practicing the principles of recycling can significantly decrease the strain on natural resources. By choosing reusable products over single-use items, individuals can make a positive impact on the environment.
Supporting local conservation organizations is another effective way to get involved. Volunteering time or donating resources to these groups helps them carry out their essential work. Being part of community-driven conservation efforts creates a sense of connection with both nature and fellow enthusiasts.
Advocacy plays a crucial role in conservation as well. By raising awareness about environmental issues and policy changes, individuals can influence decision-makers to prioritize conservation in legislation. Engaging in discussions and social media campaigns allows people to share their passion and extend the reach of their voices.
Lastly, fostering a personal relationship with nature enhances our appreciation and commitment to conservation. Spending time outdoors, whether through hiking, birdwatching, or simply enjoying parks, allows individuals to connect with the beauty of the world around them. This connection ultimately inspires a desire to protect the very ecosystems that enrich our lives.
The Philosophical Perspective on Nature
The Interconnection of All Living Things
Nature operates as an intricate web, where every organism, from the smallest microorganism to the largest mammal, plays a vital role. This interconnectedness illustrates how damage to one part of the ecosystem can ripple throughout, affecting countless species and their environments.
Humans benefit immensely from this complex network, often taking for granted the air they breathe, the water they drink, and the food they consume. The health of our planet directly influences our own well-being, emphasizing the importance of preserving biodiversity.
Understanding these connections is crucial in fostering respect and responsibility towards our natural surroundings. By acknowledging our place within this web, we cultivate a sense of stewardship, encouraging sustainable practices that help preserve our environment for future generations.
Ultimately, the interconnection of all living things reminds us that we are part of a greater whole. Every action we take has the potential to impact the entire ecosystem, thus highlighting the importance of mindfulness in our daily lives.
Cultural Significance of Nature
Throughout history, various cultures have intricately woven their beliefs and practices around the natural world. From indigenous tribes that see nature as a sacred entity to modern societies discussing environmental ethics, nature continuously shapes human culture and spirituality.
Art, literature, and music have long drawn inspiration from nature, reflecting its beauty and complexity. These expressions serve not only as a means of appreciation but also as a medium to convey deeper truths about human existence and our relationship with the Earth.
Rituals and traditions often center around seasonal changes, agricultural cycles, and natural phenomena. Such practices are not merely reflections of societal norms but are also profound acknowledgments of nature's influence on human life.
In exploring the cultural significance of nature, we gain insights into how different societies perceive their environment and reinforce the importance of preserving these cultural connections to the natural world.
Scientific Insights into Natural Processes
The study of nature through science has revealed remarkable insights into the processes that sustain life on Earth. From the intricate workings of photosynthesis to the complex behaviors of animal migrations, scientific inquiry sheds light on the mechanisms that govern our environment.
Research into ecosystems and their dynamics helps us understand how various components interact and the significance of each species within their habitats. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies that aim to protect endangered species and restore damaged ecosystems.
Moreover, scientific advancements have led to an increased understanding of climate change and its impacts on natural systems. By investigating these changes, scientists can predict potential outcomes and help inform policy decisions geared toward environmental protection.
Ultimately, science acts as a bridge between human curiosity and the depths of nature's intricacies, enabling us to appreciate not only the beauty of the natural world but also the urgent need to safeguard it for generations to come.