Exploring Anxiety NOS: Navigating Unspecified Anxiety Disorders
Defining Anxiety NOS: A Comprehensive Overview
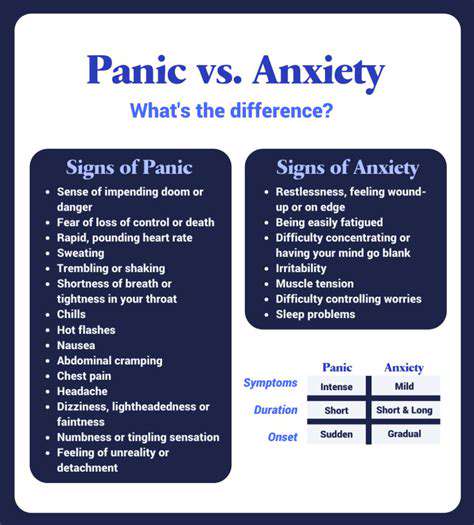
Anxiety NOS, or Anxiety Not Otherwise Specified, is a diagnostic category used in mental health to describe anxiety symptoms that don't meet the full criteria for any specific anxiety disorder, such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Panic Disorder, or Social Anxiety Disorder. Clinicians use this diagnosis when anxiety symptoms are significant but don't align perfectly with established categories.
Accurate diagnosis of anxiety requires careful consideration of each individual's unique experiences and symptoms. This flexible diagnostic approach allows mental health professionals to acknowledge the complexity of anxiety presentations that fall outside traditional classifications.
Diagnostic Criteria and Considerations
Unlike specific anxiety disorders with clearly defined criteria, Anxiety NOS requires clinicians to exercise professional judgment. The diagnostic process involves comprehensive evaluation of symptom patterns, their impact on daily functioning, and potential contributing factors.
Mental health professionals must carefully assess symptom duration, intensity, and fluctuation patterns when considering this diagnosis. They also evaluate how symptoms affect relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
Symptoms and Manifestations
People experiencing Anxiety NOS may present with diverse symptoms that vary in frequency and severity. Common manifestations include persistent nervousness, sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating, and physical symptoms like muscle tension or gastrointestinal discomfort.
These symptoms often appear less predictable than in specific anxiety disorders, sometimes emerging in response to multiple triggers or without obvious cause. This variability can make diagnosis and treatment particularly challenging.
Underlying Causes and Contributing Factors
Anxiety NOS typically results from complex interactions between biological, psychological, and environmental factors. Research suggests genetic predisposition combined with life stressors often plays a significant role in symptom development.
Neurochemical imbalances, particularly involving serotonin and norepinephrine, frequently contribute to these anxiety symptoms. Additionally, learned behavioral patterns and cognitive distortions can maintain and exacerbate anxious responses.
Differentiating Anxiety NOS from Other Conditions
Clinicians must carefully distinguish Anxiety NOS from other mental health conditions with overlapping symptoms. This includes ruling out mood disorders, trauma-related conditions, and medical issues that might mimic anxiety.
Thorough differential diagnosis is essential to avoid misclassification and ensure appropriate treatment planning. Comprehensive assessment often requires multiple sessions and sometimes collaboration with medical professionals.
Treatment Approaches for Anxiety NOS
Effective treatment typically combines psychotherapy and, when appropriate, medication management. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has shown particular effectiveness in helping individuals identify and modify maladaptive thought patterns.
Treatment plans should be personalized, considering the individual's specific symptom profile, lifestyle factors, and treatment preferences. Regular progress monitoring allows for necessary adjustments to optimize outcomes.
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
With appropriate intervention, many individuals with Anxiety NOS achieve significant symptom reduction and improved functioning. However, maintenance strategies are often necessary to prevent recurrence.
Developing sustainable coping skills and maintaining therapeutic gains requires ongoing commitment and sometimes periodic professional support. Lifestyle modifications and stress management techniques often play crucial roles in long-term success.
Treatment Options: Tailoring Approaches to Individual Needs
Pharmacological Interventions
Medication can be an important component of comprehensive anxiety treatment, particularly when symptoms significantly impair daily functioning. Various medication classes, including SSRIs, SNRIs, and occasionally short-term benzodiazepines, may be considered based on individual needs.
Medication decisions should involve careful discussion of potential benefits, side effects, and treatment duration. Regular follow-up allows for monitoring effectiveness and making necessary adjustments to dosage or medication type.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps individuals recognize and modify thought patterns that contribute to anxiety. Through structured exercises, patients learn to challenge irrational fears and develop more balanced perspectives.
This evidence-based approach typically includes homework assignments to practice skills between sessions. Many patients experience noticeable improvement within 12-20 weeks of consistent therapy.
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
ERP gradually exposes individuals to anxiety-provoking situations while preventing avoidance behaviors. This technique helps break the cycle of fear and avoidance that maintains anxiety.
Therapists carefully design exposure hierarchies, starting with moderately challenging situations and progressing to more difficult ones as confidence builds. This method proves particularly effective for specific anxiety patterns.
Mindfulness-Based Interventions
Mindfulness techniques teach individuals to observe anxious thoughts and physical sensations without judgment. Regular practice can decrease emotional reactivity and increase distress tolerance.
These approaches often incorporate meditation, body scans, and breathing exercises. Many patients find mindfulness helps them respond to anxiety triggers with greater calm and clarity.
Lifestyle Modifications
Simple lifestyle changes can significantly impact anxiety levels. Regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and consistent sleep patterns all contribute to emotional regulation.
Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake often helps minimize anxiety symptoms. Establishing predictable routines and incorporating relaxation practices can also enhance overall well-being.
Support Groups and Social Connections
Peer support provides valuable opportunities to share experiences and coping strategies. Many individuals find comfort in connecting with others facing similar challenges.
Strong social networks serve as protective factors against anxiety escalation. Maintaining meaningful relationships helps combat the isolation that often accompanies anxiety disorders.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find complementary approaches helpful when used alongside conventional treatments. Options like acupuncture or herbal supplements may provide additional support for some patients.
It's essential to discuss any alternative therapies with healthcare providers to ensure safety and avoid potential interactions. Evidence-based approaches should remain the foundation of treatment.
Living with Anxiety NOS: Building Resilience and Support Systems
Understanding Anxiety NOS
Anxiety NOS represents genuine distress that deserves attention and care, even if symptoms don't match textbook descriptions. This diagnosis validates experiences that might otherwise go unaddressed.
Recognizing that your anxiety is real and worthy of treatment represents an important first step toward recovery. Professional evaluation can provide clarity and direction for effective management.
Identifying Your Symptoms
Keeping a symptom journal helps track patterns and identify potential triggers. Note specific situations, physical sensations, thought patterns, and behavioral responses associated with anxiety episodes.
This documentation provides valuable information for treatment planning and helps measure progress over time. Many people discover previously unnoticed connections between events and anxiety responses.
Exploring Potential Triggers
Common triggers include stressful life events, health concerns, relationship conflicts, or work pressures. Internal triggers like perfectionistic tendencies or negative self-talk also frequently contribute.
Identifying your personal triggers enables more targeted and effective coping strategies. This awareness helps anticipate challenging situations and prepare appropriate responses.
Developing Coping Mechanisms
Effective coping strategies combine immediate relief techniques with long-term skill building. Breathing exercises and grounding techniques can provide quick relief during acute anxiety.
Consistent practice of relaxation techniques builds resilience against future anxiety episodes. Developing a toolkit of varied strategies ensures flexibility in different situations.
Seeking Professional Support
Therapists specializing in anxiety disorders offer evidence-based interventions tailored to individual needs. They provide structured guidance for understanding and managing symptoms.
Professional support creates a safe space to explore anxiety's roots and develop personalized management plans. Regular sessions help maintain progress and address new challenges as they arise.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Well-being
Prioritizing self-care strengthens the foundation for anxiety management. Establishing consistent sleep schedules supports emotional regulation and stress resilience.
Nutritional choices that stabilize blood sugar and support gut health may positively influence anxiety levels. Regular physical activity remains one of the most effective natural anxiety reducers.
Building a Support System
Educating trusted friends and family about anxiety helps them provide appropriate support. Clear communication about needs and boundaries fosters understanding.
Developing mutual support relationships creates reciprocal benefits for all involved. Online communities can supplement in-person connections, especially for those in areas with limited resources.