Chronic Muscle Tension: Causes, Symptoms, and Natural Relief Strategies
What is Chronic Muscle Tension?
Understanding Chronic Muscle Tension
Chronic muscle tension refers to the persistent tightness and stiffness experienced in muscle groups over an extended period. Unlike acute muscle tension, which can arise from temporary physical stress or injury, chronic muscle tension often lingers for weeks, months, or even years. This condition can significantly impair mobility, decrease quality of life, and contribute to a range of health issues. It is essential to identify the underlying causes to effectively address and manage this uncomfortable phenomenon.
This type of muscle tension often affects common areas of the body, including the neck, shoulders, back, and jaw. The continuous contraction of these muscles leads not only to discomfort but also to a decrease in blood flow, which can hinder recovery and contribute to further tension. Understanding the mechanics of chronic muscle tension can assist individuals in recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
Chronic muscle tension can often be a manifestation of stress, anxiety, or poor posture. Prolonged hours spent at desks or in front of screens can distort natural body alignment, contributing to muscle tightness. Additionally, emotional stress can lead to subconscious muscle tightening, further exacerbating the issue. By learning about how chronic muscle tension develops, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate discomfort.
Common Causes of Chronic Muscle Tension
Several factors can contribute to the development of chronic muscle tension, with stress being one of the primary culprits. As individuals navigate through daily stresses, both physical and emotional, their bodies may respond by tightening muscles. This tension can create a cyclical pattern, as heightened tension leads to more stress, resulting in chronic discomfort. Understanding this relationship is crucial for developing effective relief strategies.
Poor ergonomics during work or leisure activities is another significant cause of chronic muscle tension. Individuals often overlook their posture while sitting at a desk or using mobile devices, which can lead to imbalances and strain in certain muscle groups. Over time, these habits create an environment conducive to chronic tension. By making conscious adjustments to ergonomics, such as using supportive chairs or adjusting screen heights, individuals can reduce the risk of developing muscle tension.
Physical inactivity can also be a contributing factor to sustained muscle tension. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to weakened muscles, which are more susceptible to tightness and strain from everyday activities. Engaging in regular exercise, including stretching and strengthening routines, can serve to both prevent and alleviate tension in the muscles. Simple changes like incorporating movement into daily routines can help mitigate the symptoms of chronic muscle tension.
Effectively Alleviating Chronic Muscle Tension
Addressing chronic muscle tension requires a multifaceted approach that combines physical and mental health strategies. One effective method is to integrate regular stretching and flexibility exercises into daily routines. These practices help to release tight muscles and improve overall mobility. Engaging in activities like yoga and pilates can provide additional benefits, promoting both flexibility and relaxation.
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and meditation, can also play a crucial role in alleviating chronic muscle tension. These practices help to reduce overall stress levels, allowing the body to release physical tightness. By fostering a mindful awareness of one’s body and stress triggers, individuals can learn to manage tension more effectively over time.
Additionally, seeking professional treatment, such as massage therapy or physical therapy, can provide targeted relief where it is needed most. Skilled therapists can identify areas of tightness and employ techniques to break the cycle of tension. Regular sessions can significantly enhance the effectiveness of self-care strategies while promoting long-term relief from chronic muscle tension.
Common Causes of Muscle Tension

Physical Factors Contributing to Muscle Tension
Muscle tension is often a byproduct of physical overexertion and repetitive strain injuries. When muscles are subjected to consistent stress or are forced to contract for extended periods, they can become tight and fatigued. Such conditions can arise from a variety of activities, including sports, manual labor, or even poor posture during daily tasks.
A common scenario leading to muscle tension is poor ergonomics, particularly in work environments where individuals sit for long hours. This can lead to tightness in the neck, shoulders, and back. Implementing proper ergonomic adjustments in the workplace can significantly alleviate these issues and improve overall comfort and productivity.
In addition to repetitive movements, sudden injuries such as sprains or strains can also contribute to muscle tension. The body responds to injury with inflammation, which can lead to increased muscle tightness in the affected area as a protective mechanism. Therefore, understanding the link between physical injuries and muscle tension is crucial for effective management.
Other physical factors include dehydration and nutritional deficiencies, which can impact muscle function and recovery. When the body lacks essential nutrients or hydration, it can lead to cramping and spasms, further exacerbating muscle tension. Maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated are important for muscle health and overall well-being.
Finally, the role of physical activity cannot be overlooked. Regular exercise can help prevent and relieve muscle tension by promoting flexibility and muscle strength. However, it is vital to engage in balanced training routines that incorporate rest and recovery to avoid overuse injuries.
Emotional and Psychological Influences on Muscle Tension
The relationship between stress and muscle tension is well-documented in both scientific literature and anecdotal evidence. When individuals experience high levels of stress or anxiety, the body often responds by tightening muscles as a form of defense. This physiological reaction can create a cycle where stress leads to muscle tension, which in turn can increase feelings of stress and anxiety.
In many cases, individuals may go through life without recognizing the emotional baggage they carry, which can manifest as chronic muscle tension. Situations such as work pressure, relationship difficulties, or traumatic experiences can all contribute. Identifying and addressing these emotional issues is essential in breaking the cycle of chronic tension and finding relief.
Moreover, techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and breathing exercises can be powerful tools in managing emotional stress. By fostering a greater awareness of emotional states, individuals can learn to recognize when stress levels are rising and take proactive steps to mitigate its impact on their physical health.
Additionally, cognitive behavioral strategies can provide insight into the subconscious patterns that contribute to muscle tension. Counseling or therapy can assist individuals in uncovering the root causes of their emotional stress and developing coping mechanisms to address those issues directly, further alleviating physical symptoms.
Finally, engaging in leisure activities, hobbies, or social interactions can serve as an effective counterbalance to the stresses of everyday life. These activities promote relaxation and provide a necessary outlet for emotions, ultimately helping to reduce the manifestation of muscle tension. In sum, acknowledging and addressing the emotional factors at play is imperative for achieving long-term relief from chronic muscle tension.
Symptoms of Chronic Muscle Tension
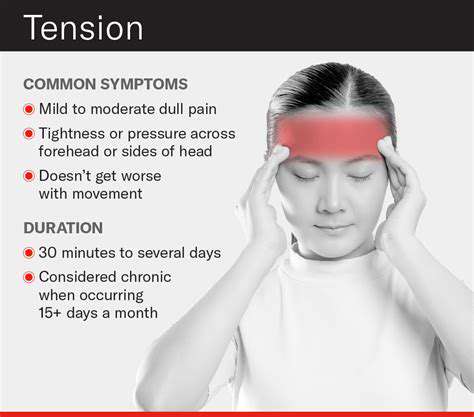
Chronic muscle tension often reveals itself through a constellation of physical symptoms, varying in intensity and location depending on the individual and the specific muscles affected. These symptoms can range from a mild, nagging ache to debilitating pain that significantly impacts daily activities and overall quality of life. One of the most frequently reported complaints is persistent headaches, frequently of the tension-type, characterized by a tight band-like pressure around the head, often accompanied by pain in the neck and shoulders. These headaches are often exacerbated by stress, poor posture, and lack of physical activity, making them a significant source of discomfort for many individuals experiencing chronic muscle tension.
Furthermore, individuals with chronic muscle tension frequently report stiffness and reduced range of motion in the affected areas, making everyday movements feel challenging and restricted. This stiffness can be particularly pronounced in the morning or after periods of inactivity, such as prolonged sitting or sleeping in an awkward position, and it can contribute to a cycle of pain and immobility. The chronic contraction of muscles can also lead to the development of trigger points, which are localized areas of extreme tenderness within the muscle that can refer pain to other areas of the body, intensifying the overall experience of discomfort and creating further complications for sufferers.
Another prominent symptom associated with chronic muscle tension is pain, which may vary in character from a dull ache to sharp, shooting pains, depending on the severity and nature of the underlying muscle tension. This pain can be localized to a specific area or can radiate to other parts of the body, further complicating diagnosis and management. This muscle discomfort is frequently accompanied by fatigue, as the body expends considerable energy trying to maintain muscle contraction, which may then lead to feeling exhausted and worn out, impairing physical and mental performance and making it difficult to cope with daily stressors.
Beyond the more obvious physical symptoms, some individuals with chronic muscle tension may experience other less obvious manifestations, such as muscle spasms, which are involuntary contractions that can be sudden and painful. These spasms can further exacerbate existing pain and discomfort, making movement even more difficult and contributing to a sense of frustration and helplessness. Digestive issues, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), can sometimes be linked to chronic muscle tension, adding a further dimension to the complexity of the condition and creating more discomfort.
Psychological and Emotional Effects of Chronic Muscle TensionThe persistent physical discomfort associated with chronic muscle tension can have significant psychological and emotional consequences, often contributing to a cycle of stress, anxiety, and frustration. The constant awareness of pain and physical limitations can erode an individual's sense of well-being, making it difficult to fully engage in daily activities and social interactions. This can lead to feelings of isolation, helplessness, and even depression, impacting a person's overall mental and emotional state and contributing to a reduced quality of life, compounding the existing physical concerns.
Furthermore, the chronic experience of pain and physical restrictions can make it difficult to cope with everyday stressors, and even minor challenges can feel overwhelming and debilitating. This increased sensitivity to stress can, in turn, exacerbate muscle tension, perpetuating a vicious cycle of pain, tension, and emotional distress. The constant anticipation of pain or discomfort can also contribute to anxiety, making it challenging to relax and enjoy life. This can lead to a heightened state of alertness and hypervigilance, further contributing to muscle tension and impacting sleep quality.
Sleep disturbances are also a common consequence of chronic muscle tension, as the physical discomfort and emotional distress can make it difficult to fall asleep, stay asleep, or achieve restful sleep. This sleep deprivation can then amplify the effects of muscle tension, further contributing to fatigue, pain, and cognitive difficulties, creating a very difficult situation for many individuals. The lack of restorative sleep can also exacerbate existing mental health issues, such as anxiety and depression, creating a downward spiral of physical and emotional distress.
The emotional and psychological toll of chronic muscle tension can also manifest in behavioral changes, such as social withdrawal, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Individuals may find themselves avoiding activities they once enjoyed, isolating themselves from friends and family, and struggling to maintain focus and productivity at work or school. These changes can further impact their relationships, career, and overall sense of self, leading to a sense of loss and diminished life satisfaction, further contributing to a sense of isolation and despair.
Diagnostic Approaches and ConsiderationsDiagnosing chronic muscle tension typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, additional diagnostic tests to rule out other potential underlying conditions. The healthcare provider will begin by asking detailed questions about the patient's symptoms, including the location, intensity, and duration of the pain, as well as any factors that seem to trigger or worsen the symptoms. Information about the patient's lifestyle, stress levels, and any previous injuries or medical conditions is also relevant, and can greatly contribute to a better understanding of the condition as a whole, as well as its root causes.
During the physical examination, the healthcare provider will assess the patient's posture, range of motion, and muscle tenderness, paying particular attention to the areas where the patient reports pain or discomfort. Palpation, the process of examining the body by touch, will be used to identify any areas of muscle spasm, tightness, or trigger points. The healthcare provider may also assess the patient's reflexes and neurological function to rule out any underlying neurological conditions that may be contributing to the symptoms. Additional imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRIs, may be ordered if the healthcare provider suspects underlying structural problems, however these tests are not often used to diagnose chronic muscle tension itself but to rule out other causes.
In addition to physical examinations and imaging studies, the healthcare provider may also assess the patient's psychological and emotional state, as these factors can significantly impact the experience of chronic muscle tension. This may involve asking questions about the patient's stress levels, mood, and coping mechanisms, as well as referring the patient to a mental health professional for further evaluation and treatment if necessary. This holistic approach acknowledges the interconnectedness of the mind and body and recognizes that effective treatment often requires addressing both physical and psychological aspects of the condition.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the differential diagnosis, which involves ruling out other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as fibromyalgia, arthritis, or other musculoskeletal disorders. This requires a careful evaluation of the patient's symptoms, physical examination findings, and any relevant diagnostic test results. Ruling out other possible causes of the symptoms ensures that the patient receives the most appropriate and effective treatment for their specific condition. This careful diagnostic process helps to provide a detailed picture of the patient's unique circumstances.
Natural Strategies for Relieving Muscle Tension
Chronic muscle tension is often a multifaceted issue, stemming from a complex interplay of physical, psychological, and environmental factors. Prolonged periods of stress, whether from work deadlines, relationship problems, or financial anxieties, can trigger the body's fight-or-flight response, leading to sustained muscle contractions throughout the body. These constant contractions, even if subtle, can eventually result in stiffness, pain, and a decreased range of motion, perpetuating a cycle of discomfort that impacts daily life and overall well-being. Understanding these underlying causes is the first step towards implementing effective relief strategies and promoting lasting relaxation.
Furthermore, poor posture, improper ergonomics, and repetitive motions, particularly common in office settings and physically demanding jobs, contribute significantly to muscle tension. Sitting hunched over a computer for hours, lifting heavy objects incorrectly, or performing the same movement repeatedly can place excessive strain on specific muscle groups, leading to imbalances and chronic pain. Lifestyle choices, such as insufficient physical activity and a lack of regular stretching, also exacerbate the problem, limiting blood flow and hindering the muscles' natural ability to release tension. Recognizing these everyday habits that impact your body's mechanics allows you to begin making proactive changes to better care for your muscles.
The Importance of Mind-Body PracticesIntegrating mind-body practices into your daily routine can be incredibly beneficial in mitigating chronic muscle tension and fostering a sense of overall relaxation and well-being. Techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, and deep breathing exercises help to calm the nervous system, reducing the production of stress hormones that contribute to muscle contraction. Regular practice allows individuals to become more aware of their body's signals, enabling them to identify and consciously release tension before it becomes chronic. This heightened awareness equips individuals with the ability to manage stress effectively and promote a state of mental and physical calmness which has lasting benefits.
Yoga and Tai Chi are particularly effective mind-body practices that combine gentle movements, controlled breathing, and mindful awareness to improve flexibility, strength, and body awareness. These practices help to stretch and lengthen muscles, releasing built-up tension and improving circulation. The focus on the present moment, the controlled movements, and the integration of breath with movement can help to calm the mind, reduce stress levels, and cultivate a sense of inner peace. Consistent participation in these types of activities can lead to significant improvements in muscle health and overall physical and mental resilience. Furthermore, these practices can be adapted to fit all fitness levels, making them accessible to most individuals.
Dietary and Lifestyle Adjustments for Muscle HealthBeyond specific practices, making conscious dietary and lifestyle adjustments can significantly support muscle health and reduce tension. Consuming a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help to reduce inflammation throughout the body, lessening the potential for muscle pain and stiffness. Adequate hydration is also crucial, as water helps to transport nutrients to muscles, flush out toxins, and maintain optimal muscle function. Prioritizing sleep is non-negotiable, as the body repairs and regenerates muscles during sleep, so ensuring enough restful sleep is vital for muscle recovery and overall health.
Additionally, incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is essential for maintaining muscle health and preventing chronic tension. Engaging in regular exercise, even moderate activities like walking or swimming, helps to improve blood flow, strengthen muscles, and release endorphins, which have mood-boosting and pain-relieving effects. Regularly changing positions to avoid staying in static postures for too long is also crucial to break up periods of tension. Finding activities you enjoy makes it easier to stay consistent with these practices, which are key for long-term success. This focus on proactive steps, combined with consistent effort, will yield excellent results for long term relaxation and well-being.
The Role of Therapeutic ApproachesIn addition to lifestyle changes, therapeutic approaches can provide significant relief from chronic muscle tension. Massage therapy, for instance, is an effective method for releasing knots and adhesions in the muscles, improving circulation, and promoting relaxation. Different massage modalities, such as Swedish massage, deep tissue massage, and myofascial release, can be tailored to address specific needs and preferences. The skilled hands of a trained massage therapist can identify and address areas of tension that may be difficult to reach or release through self-care practices alone, thereby promoting a significant improvement in the individual's overall physical state and comfort.
Furthermore, other therapies, such as acupuncture, trigger point therapy, and physical therapy, can be beneficial in addressing chronic muscle tension. Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the nervous system and promote the release of endorphins, which have pain-relieving effects. Trigger point therapy focuses on releasing knots and tender points in the muscles, while physical therapy involves exercises and stretches to improve flexibility, strength, and posture. Consulting with healthcare professionals to identify the most appropriate therapeutic approaches for your specific condition is highly recommended for achieving optimal outcomes and long-term relief. This holistic approach helps to address both the physical and emotional aspects of muscle tension.