Breathing Techniques for Anxiety Relief: Effective Practices
Concentrating on breath control helps quiet mental chatter and brings order to internal chaos. The technique's adaptability makes it useful in diverse situations, establishing it as an essential stress management resource.
The Physiological Benefits of Controlled Breathing
Structured breathing like box breathing significantly influences bodily responses. It helps balance the autonomic nervous system, shifting from fight-or-flight mode to relaxation mode. This transition reduces stress hormones effectively.
Deliberately slowing your breathing rate directly affects heart rate and blood pressure, creating calmness and decreasing panic sensations. Regular practice contributes to better cardiovascular health and general wellness.
Practical Application and Steps
For proper box breathing practice, assume a comfortable seated or reclined position. Optionally close your eyes to enhance focus. Inhale deeply through your nose while counting slowly to four.
Hold that breath for another four-count. Exhale completely through your mouth for four counts. Maintain empty lungs for a final four-count. Repeat this sequence for several minutes, keeping counts consistent and even.
Box Breathing and Stress Management
Modern life's constant stress often causes physical and emotional strain. Box breathing provides a practical method to interrupt stress cycles when they begin.
Conscious breath control creates space between stressful events and your reactions, enabling more thoughtful responses to challenges. This improves overall stress coping abilities substantially.
Integrating Box Breathing into Daily Routine
Regular practice maximizes box breathing's benefits. Begin with brief five-minute sessions daily, gradually increasing duration as comfort grows.
Using this technique before anticipated stressors like presentations proves particularly helpful. It also serves as an effective quick-calming method during sudden anxiety episodes.
Box Breathing for Athletes and Performance Enhancement
Beyond stress relief, box breathing aids athletic performance. The calm, focused state it produces helps manage pre-competition nerves and optimizes concentration.
Deep, controlled breathing enhances oxygenation while reducing muscular tension, potentially boosting performance and lowering injury risks. Consistent practice maintains focus during demanding workouts.
Box Breathing and Mindfulness
Box breathing naturally complements mindfulness practices. It cultivates present-moment awareness by anchoring attention to breath sensations.
This mindfulness connection develops mental clarity and emotional control, essential for managing stress and anxiety. The technique provides a tangible focus point, helping disengage from past regrets or future worries.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation with Breathwork Integration
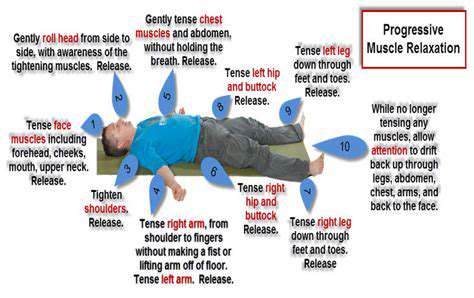
Understanding Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) reduces stress by systematically tensing and relaxing body muscle groups. This process identifies and releases physical tension accompanying stress. Focused attention on tension and relaxation sensations teaches better physical response management, leading to enhanced calmness. This method particularly benefits those with chronic stress or anxiety conditions.
The practice involves briefly tensing specific muscles, holding briefly, then fully releasing. This conscious tension-release cycle creates mental distance from stressors, enabling deeper relaxation. Repeating across muscle groups produces comprehensive physical and mental calmness, making it valuable for stress management and wellbeing improvement.
Steps and Techniques in Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Effective PMR involves several key steps. First, select a quiet, comfortable space to sit or lie down undisturbed. This environment enhances relaxation effectiveness. Second, systematically tense and release muscle groups individually. This methodical approach ensures thorough relaxation and helps identify specific tension areas. Typically starting with feet and progressing upward allows complete coverage.
Successful PMR requires focused attention on physical sensations. Carefully noticing tension and release differences develops deeper body awareness and control over stress responses. Maintaining a steady pace without rushing ensures maximum benefit. This practice builds valuable understanding of bodily stress manifestations.
Benefits and Applications of Progressive Muscle Relaxation
PMR offers benefits extending beyond stress reduction. It can improve sleep quality, reduce chronic pain, and enhance athletic performance. Effective tension management decreases stress-related symptoms like headaches and digestive issues. The technique complements various therapeutic approaches for mental health conditions.
PMR serves as a practical self-care tool for wellbeing enhancement. Regular practice cultivates greater calmness and physical/emotional response control. Its adaptability allows customization for individual needs and preferences.
Breathwork and Anxiety Management: Long-Term Strategies

Understanding the Connection
Breathwork provides powerful anxiety management tools, given the direct link between breathing patterns and nervous system function. Altered breathing directly affects stress responses and hormone release. Controlled deep breathing calms the nervous system, creating relaxation crucial for anxiety reduction.
Anxiety often triggers shallow, rapid breathing that worsens panic feelings. Learning to regulate this pattern forms a key anxiety management component, highlighting breathwork's therapeutic value.
Diaphragmatic Breathing
Diaphragmatic or abdominal breathing represents a foundational breathwork technique. It engages the diaphragm fully to maximize lung capacity. This approach creates balanced breathing that naturally slows heart rate and lowers blood pressure - common anxiety symptoms.
Regular diaphragmatic breathing practice significantly decreases anxiety sensations while promoting calmness. Its accessibility makes it ideal for on-the-spot anxiety management.
Box Breathing
Box breathing's structured pattern involves equal duration inhales, holds, exhales, and holds. This rhythm establishes control and focus particularly helpful for anxiety triggers.
Breath focus redirects attention from anxious thoughts. The technique's controlled nature provides a present-moment anchor, reducing anxiety intensity.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
PMR combined with breathwork targets anxiety-related physical tension. Systematic muscle group tensing and releasing identifies and relieves tension. Combined with breathwork, it creates powerful relaxation synergy.
This combined approach simultaneously calms body and mind, addressing anxiety's physical-emotional interconnection holistically.
Mindfulness and Breathwork
Mindfulness practices often incorporate breathwork to enhance present-moment awareness. Focusing on breath sensations cultivates presence while disengaging from anxious thoughts.
Mindfulness-based breathwork develops emotional regulation skills, fostering compassionate self-observation that reduces anxiety's impact.
Breathwork and Emotional Regulation
Beyond immediate anxiety relief, breathwork builds long-term emotional regulation capacity. Regular practice strengthens composed, resilient responses to stressors.
Consistent breathwork develops emotional resilience, enabling easier navigation of challenges and reduced daily anxiety interference.
Safety and Considerations
While generally safe, consult healthcare providers with pre-existing conditions. Some advanced techniques involving breath retention may require caution or modification.
Professional guidance ensures safe, effective breathwork integration into anxiety management plans. Always listen to your body's signals during practice.