Best Ways to Calm Anxiety: Techniques and Tips
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, is a fundamental technique for calming anxiety. It focuses on engaging the diaphragm, the large muscle beneath the lungs, to create a more complete and efficient breathing pattern. When practicing diaphragmatic breathing, you'll notice your belly rising and falling with each breath, rather than your chest. This controlled movement allows for a greater volume of air to be inhaled and exhaled, promoting relaxation and reducing feelings of panic.
To practice, find a comfortable position, either sitting or lying down. Place one hand on your chest and the other on your belly. Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose, feeling your belly expand. Exhale slowly through your mouth, allowing your belly to return to its normal position. Repeat this process for several minutes, focusing on the smooth and rhythmic nature of your breath.
Box Breathing: A Structured Approach to Anxiety Relief
Box breathing, a structured breathing technique, can be incredibly effective in calming anxiety. This method involves inhaling for a count of four, holding the breath for a count of four, exhaling for a count of four, and holding the empty breath for a count of four. This rhythmic pattern helps to regulate the breath and create a sense of groundedness.
The structure of box breathing provides a tangible anchor in moments of anxiety. The deliberate counting and focus on the breath can help to distract from racing thoughts and anxieties, promoting a sense of calm and control.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation and Breathing
Combining progressive muscle relaxation with deep breathing can significantly enhance the calming effect. Progressive muscle relaxation involves systematically tensing and releasing different muscle groups in the body. This process helps to identify and release physical tension often associated with anxiety.
As you tense and release each muscle group, focus on your breath. Deep, slow inhalations and exhalations can further relax the muscles, creating a powerful synergy between physical and mental relaxation. The mindful awareness of both physical and mental tension, released through breathing, can lead to a more profound sense of calm and well-being.
Breathwork for Specific Anxiety Triggers
Certain triggers, such as social situations or public speaking, can cause heightened anxiety. Practicing specific breathwork techniques tailored to these triggers can be extremely helpful. For example, focusing on slow, deep breaths before a social interaction can help to manage anticipatory anxiety.
Developing personalized breathwork strategies for specific anxiety triggers can empower individuals to proactively manage their responses to those situations. By connecting the breath to specific anxieties, individuals can cultivate a tool to effectively calm their nervous system and navigate challenging situations with greater ease.
Mindfulness Breathing for Long-Term Well-being
Incorporating mindfulness into your breathing practice is key to cultivating long-term well-being and resilience to anxiety. Mindful breathing involves paying close attention to the sensation of the breath without judgment. This practice encourages a non-reactive awareness of the present moment, helping to detach from anxious thoughts.
Regular mindfulness breathing sessions can strengthen the mind's ability to observe and respond to anxiety triggers in a more balanced and controlled manner. This, over time, can lead to a greater sense of inner peace and a more effective coping mechanism for managing anxiety throughout daily life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Techniques for Anxiety Management
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
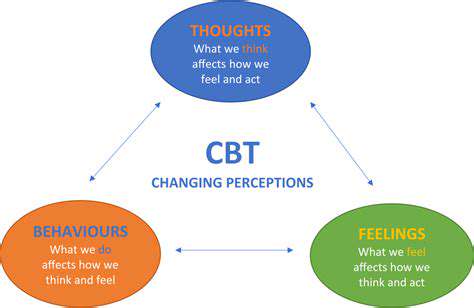
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely used and highly effective type of psychotherapy that focuses on the interconnectedness of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It's based on the principle that our thoughts and beliefs significantly influence our emotions and actions. By identifying and challenging negative or unhelpful patterns, CBT aims to promote positive change and improved well-being.
CBT operates on the premise that problematic behaviors and emotional responses often stem from maladaptive thought patterns. These patterns can become ingrained over time, leading to recurring difficulties. CBT provides a structured approach to help individuals recognize and modify these patterns, thereby fostering healthier coping mechanisms.
Identifying and Challenging Negative Thoughts
A core component of CBT involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns. These thoughts, often automatic and unconscious, can significantly impact mood and behavior. By becoming aware of these thoughts, individuals can start to question their validity and replace them with more realistic and balanced perspectives.
This process of challenging negative thoughts is crucial for breaking free from cycles of negativity and anxiety. It fosters a more adaptive and resilient mindset, allowing individuals to navigate challenges with greater ease and effectiveness.
Behavioral Techniques in CBT
CBT incorporates various behavioral techniques designed to reinforce positive changes and reduce maladaptive behaviors. These techniques may include gradual exposure therapy, where individuals confront feared situations or stimuli in a controlled and progressive manner, ultimately reducing anxiety and phobias.
Another behavioral technique is relaxation training, which equips individuals with strategies for managing stress and anxiety through various relaxation exercises, fostering a sense of calm and control.
CBT's Focus on Present and Future
A key characteristic of CBT is its focus on the present and future. Rather than dwelling on past experiences, CBT emphasizes understanding and modifying current thought processes and behaviors to improve present-day functioning. This proactive approach is instrumental in empowering individuals to take control of their mental health and create a more positive future.
This forward-looking approach emphasizes the development of skills and strategies for managing future challenges, promoting long-term well-being.
CBT's Structure and Practical Application
CBT is typically structured, with a clear therapeutic process. Sessions often involve identifying specific problems, examining their underlying thought patterns, developing coping strategies, and practicing those strategies in real-life situations. This structured approach provides a practical framework for individuals to implement the tools learned in therapy.
By providing a practical and actionable framework, CBT empowers individuals to engage actively in their own healing process. This active participation is vital for achieving meaningful and lasting change.
Effectiveness and Versatility of CBT
CBT has been extensively researched and proven to be highly effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, phobias, and post-traumatic stress disorder. Its adaptability makes it a versatile approach that can be tailored to individual needs.
CBT's strength lies in its focus on practical skills development. Individuals learn concrete strategies for managing their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, empowering them to tackle challenges in a more effective way.
Ethical Considerations in CBT
As with any therapeutic approach, ethical considerations are paramount in CBT. Therapists must prioritize the well-being and safety of their clients, ensuring that the techniques employed are appropriate and aligned with ethical guidelines. Maintaining confidentiality and fostering a safe therapeutic environment are critical for successful treatment.
The establishment of a strong therapeutic alliance between client and therapist is essential for ethical practice, promoting trust and open communication.
Many parents grapple with the challenge of picky eating. It's a common experience, and understanding the root causes and implementing strategies for change can be a real game-changer. Often, picky eating isn't simply a phase; it can be a complex issue influenced by various factors. It's crucial to approach the situation with patience and understanding, recognizing that each child is unique.

Seeking Professional Help for Persistent Anxiety
Understanding the Signs of Persistent Anxiety
Persistent anxiety can manifest in various ways, impacting daily life significantly. Recognizing these signs is crucial for seeking appropriate help. Physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, excessive sweating, and trembling can be disruptive, often accompanied by feelings of overwhelming worry, fear, or dread. Individuals may experience difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, and irritability, making it challenging to engage in normal activities. These symptoms, when persistent and interfering with daily functioning, warrant professional attention.
Beyond the immediate physical and emotional distress, persistent anxiety can lead to more long-term problems. Social isolation, difficulty maintaining relationships, and decreased productivity at work or school are common consequences. Recognizing these patterns and understanding how anxiety is affecting your life is the first step towards seeking help and finding effective coping mechanisms. It's important to remember that you're not alone and professional support is available to help you navigate these challenges.
Effective Strategies for Managing Anxiety
While professional help is crucial for addressing persistent anxiety, incorporating effective coping strategies into your daily routine can significantly reduce its impact. Mindfulness techniques, like deep breathing exercises and meditation, can help you focus on the present moment and detach from overwhelming anxieties. Regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or swimming, can release endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while limiting processed foods and caffeine, can also contribute to better emotional regulation.
Developing healthy sleep habits is another vital aspect of managing anxiety. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a conducive sleep environment can significantly improve sleep quality. Furthermore, connecting with supportive friends, family, or joining a support group can provide a sense of belonging and shared understanding. Remember, these strategies are complementary to professional help and can augment your overall well-being.
Exploring relaxation techniques like progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery can offer tangible ways to manage physical tension associated with anxiety. Identifying and challenging negative thought patterns through cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques can also help reframe anxieties and promote more positive thinking. These strategies are valuable tools in your journey towards managing anxiety, but professional guidance remains essential for tailored support and long-term well-being.
Maintaining a balanced lifestyle that incorporates these strategies, along with ongoing professional support, can contribute to a more manageable and fulfilling life.