Anxiety Disorders: Shedding Light on Their Widespread Impact
The Rising Tide of Anxiety Disorders
Understanding Anxiety Disorders
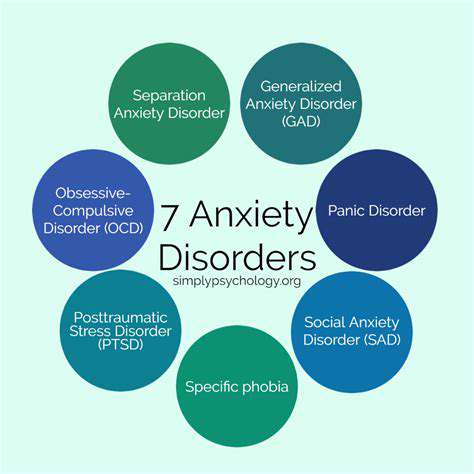
Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions that can affect individuals profoundly. A common misconception is that anxiety is merely a state of worry or fear; however, it can be a debilitating illness that interferes with daily life. Understanding the various types of anxiety disorders is crucial in dismantling the stigma surrounding mental health. Generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety are just a few examples that highlight the complexity of this group of disorders.
Each type of anxiety disorder has its own set of symptoms and impact on individuals. For example, those with generalized anxiety disorder may experience chronic worry about a multitude of issues, while those with panic disorder may face sudden and intense episodes of fear. This variability indicates that anxiety disorders require tailored approaches to treatment and management. Comprehensive awareness and education can lead to better coping mechanisms for those affected.
Moreover, environmental factors often play a significant role in the development of anxiety disorders. These can range from significant life changes, trauma, or chronic stress situations that can trigger or exacerbate symptoms. Understanding the relationship between these factors and anxiety can be key in preventative strategies and early interventions.
Additionally, it’s essential to acknowledge that anxiety disorders can co-occur with other mental health issues, such as depression and substance abuse, complicating diagnosis and treatment. Overall, fostering a widespread understanding of anxiety disorders can promote empathetic responses and enhance the social support systems for those who are struggling.
Symptoms and Signs of Anxiety Disorders
The symptoms of anxiety disorders can vary widely from person to person but generally encompass both physical and emotional responses. Common signs include heightened agitation, restlessness, and persistent feelings of fear or dread, which can make daily activities challenging. Recognizing these signs early can lead to timely intervention, improving outcomes for many individuals. Understanding these symptoms is essential for both individuals and their support systems.
Physical manifestations of anxiety often include rapid heart rate, sweating, and trembling. These acute stress responses can create a cycle wherein individuals experience anxiety about their anxiety, leading to greater psychological distress. Understanding the interplay between physical and psychological symptoms is vital in addressing anxiety disorders effectively.
Furthermore, social behaviors may change significantly in individuals dealing with anxiety disorders. Many may begin to withdraw from social situations or develop avoidance strategies that can isolate them from friends and family. Awareness of these behavioral changes can help loved ones provide support without judgment, recognizing the struggle that accompanies anxiety.
In settings such as workplaces or schools, anxiety disorders may interfere with performance and engagement, further exacerbating stress. Thus, it is vital for employers and educators to foster environments where open discussions about mental health can reduce stigma and encourage individuals to seek help.
Impact on Daily Life
Anxiety disorders can have profound effects on various aspects of daily life, including personal relationships and professional responsibilities. For individuals, these disorders can lead to difficulty concentrating, which may hinder productivity in the workplace or academic settings. The ripple effects of anxiety can extend to friends and family, impacting emotional connections and support systems. Individuals may struggle to maintain social relationships due to their withdrawal or avoidance behaviors.
In families, anxiety can compromise communication and emotional availability, leading to tension and misunderstandings. Parent-child dynamics may suffer, particularly if a parent struggles with anxiety, affecting the emotional development of children. Understanding these dynamics is crucial in providing adequate support not only for the individual but for the entire family unit.
Moreover, the financial burden of managing anxiety disorders should not be underestimated. Therapy, medication, and potential lost wages due to decreased work performance can create significant stressors that add to the cycle of anxiety. Recognizing the economic impact helps empower individuals and advocates to push for better mental health resources and insurance coverage.
When awareness of anxiety disorders grows within society, it becomes easier for those afflicted to seek help and for communities to provide essential support. Creating inclusive environments can encourage open dialogue and ensure that individuals do not feel isolated in their struggles with anxiety. Collectively, society must prioritize mental health education to enhance understanding and compassion.
Treatment Options for Anxiety Disorders
Successfully treating anxiety disorders often requires a multi-faceted approach, combining therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stands out as an evidence-based treatment intervention for many anxiety disorders. This therapy focuses on addressing negative thought patterns, enabling individuals to develop healthier coping strategies. Through CBT, clients learn to reframe their thoughts and lessen the grip of anxiety on their daily lives.
Medications, such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications, can also play essential roles in alleviating symptoms. While not all individuals may require medication, those with more severe symptoms may find pharmacological treatments helpful when combined with therapy. It's important to approach medication under the guidance of a qualified medical professional to monitor its effectiveness and address any potential side effects.
In addition to these treatments, lifestyle adjustments can significantly alleviate anxiety symptoms. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep have all been shown to improve emotional well-being. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can also serve as valuable tools for managing anxiety. Cultivating a recreation habit can create a healthier balance in one’s life.
Support groups can provide a community environment where individuals facing similar challenges can gather. Engaging with others who understand their experiences can foster a sense of belonging and encourage open conversations about emotions. This sense of community can be incredibly powerful in helping individuals feel less alone in their struggles with anxiety disorders.
The Role of Society in Addressing Anxiety Disorders
Societal perceptions and attitudes towards mental health significantly impact how anxiety disorders are addressed and treated. In many cultures, mental health issues are still stigmatized, leading to reluctance in seeking help. Challenging these societal norms is essential in creating an environment where individuals feel safe to discuss their experiences without fear of judgment. Advocacy and educational campaigns can pave the way for changing perceptions about mental health.
Workplaces also play a critical role in addressing anxiety disorders, as they can implement policies that prioritize mental wellness. Organizations that promote flexible working conditions, such as remote options and mental health days, can ease the burden on employees dealing with anxiety. A supportive workplace culture can enhance employee morale and efficiency, thereby benefiting both individuals and organizations.
Schools and educational institutions are pivotal in placing mental health on the agenda, integrating it into curricula, and teaching students about emotional intelligence and coping strategies. Empowering young people with knowledge about anxiety disorders allows them to recognize symptoms in themselves and others, promoting compassion and understanding. By creating supportive environments, schools can encourage discussions that normalize mental health challenges.
Overall, society must insist on prioritizing mental health in policy-making discussions. Funding for mental health services must be increased, ensuring that adequate support is available for all community members. By acknowledging and addressing anxiety disorders, we can foster healthier communities where individuals can thrive without the burdens of stigma.
Types of Anxiety Disorders and Their Impact
Understanding Different Types of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders encompass a broad range of conditions that affect millions around the globe. Among the most common are generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and various phobias. GAD is characterized by persistent and excessive worry about numerous aspects of life, often leading to significant distress and impairment in daily functioning. In contrast, panic disorder involves recurrent, unexpected panic attacks accompanied by a fear of future episodes, which can significantly restrict an individual's activities.
Moreover, social anxiety disorder focuses on intense fear or anxiety regarding social situations and potential embarrassment. This can lead to avoidance behaviors that severely limit social interactions and relationships. Specific phobias, such as fear of heights or spiders, trigger disproportionate reactions that can incapacitate individuals when faced with the feared object or situation. Together, these disorders not only disrupt personal well-being but also hinder professional and academic pursuits.
The Emotional and Physical Toll of Anxiety Disorders
The emotional impact of anxiety disorders is profound, often causing individuals to experience feelings of helplessness, dread, and isolation. People suffering from these conditions might feel trapped in a cycle of anxiety that steals away joy and contentment in daily life. The emotional distress can be compounded by feelings of stigma or misunderstanding from others, leading to a potential deterioration in one’s support system.
In addition to emotional challenges, anxiety disorders significantly affect physical health. Individuals may experience a range of symptoms, such as heart palpitations, muscle tension, fatigue, and gastrointestinal issues. These physical responses can further exacerbate anxiety, creating a vicious cycle of worry and panic. Consequently, it becomes essential to recognize the link between mental and physical health in managing anxiety disorders effectively.
Treatment Options and Their Effectiveness
Effective treatments for anxiety disorders exist, ranging from psychotherapy and medication to lifestyle changes. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has proven particularly effective, focusing on identifying and altering negative thought patterns and behaviors linked to anxiety. Through various techniques, individuals can develop coping strategies to manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Regular sessions with trained professionals help foster a support system that is critical for recovery.
Medications such as antidepressants and benzodiazepines may also play a role in treatment, decreasing anxiety symptoms and allowing individuals to engage more fully in therapeutic processes. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, proper nutrition, and mindfulness practices like yoga and meditation, can enhance overall well-being and resilience against anxiety. This holistic approach emphasizes that addressing anxiety disorders requires a multifaceted strategy for optimal recovery.
The Importance of Awareness and Education
Understanding Anxiety Disorders Through Education
Education plays a critical role in demystifying anxiety disorders, which affect millions of individuals across various demographics. By disseminating accurate information about these conditions, society can foster a supportive environment conducive to understanding and acceptance. Such initiatives are essential for combating the stigma associated with mental health issues, initiating crucial conversations, and breaking down barriers that people face when seeking help.
Comprehensive educational resources empower individuals to recognize the impending signs of anxiety disorders early on. Knowledge equips friends, family members, and community leaders with the tools necessary to identify symptoms and provide support to those struggling. This awareness is vital because early intervention can significantly improve the quality of life and lead to effective management strategies before these conditions escalate.
Schools and workplaces can implement educational programs about anxiety disorders, making these discussions more commonplace. Engagement in consistent training sessions or workshops helps sharpen the understanding of mental health in educational systems and workplaces, which is essential for creating an empathetic atmosphere. It fosters a culture of assistance where people feel secure in sharing their struggles without facing judgement.
Moreover, integrating education around anxiety disorders into the curricula provides young individuals with the language and resources to articulate their feelings. Adolescents often experience anxiety in heightened ways, and equipping them with knowledge can empower them to seek help sooner rather than later. This proactive approach can prevent intergenerational cycles of anxiety and mental health issues.
The critical discourse surrounding anxiety disorders extends beyond individual education, influencing policies and practices within healthcare as well. Increased awareness drives healthcare practitioners to prioritize mental health in their treatment protocols, ensuring a holistic approach to patient care that encompasses emotional and psychological wellbeing alongside physical health.
The Role of Awareness in Addressing Stigma
Awareness and education play pivotal roles in reshaping societal attitudes towards anxiety disorders, aiming to dismantle the entrenched stigma that often surrounds mental health issues. When communities engage in open discussions about anxiety, it helps to cultivate environments that are supportive, inclusive, and understanding. Normalizing conversations around mental health leads to enhanced empathy and reduces the fear of ostracism for those who are affected.
One significant challenge that anxiety sufferers face is the fear of being labeled or judged. This stigma often prevents individuals from coming forward, which exacerbates their anxiety. Public awareness campaigns can counteract these negative perceptions, spreading the message that anxiety disorders are legitimate medical conditions requiring care similar to that of physical illnesses. These campaigns can take various forms, including social media initiatives, community events, and informative literature.
Educational institutions play a crucial role in addressing stigma by incorporating discussions about mental health into their curricula. Initiating these topics in classrooms not only informs students but also encourages them to communicate with peers about their own mental health. This openness fosters a culture of support, where seeking help is viewed positively rather than as a sign of weakness.
Moreover, advocacy groups and mental health organizations can provide influential platforms for awareness campaigns. By sharing personal stories of those dealing with anxiety disorders, individuals can connect with broader audiences, creating a relatable narrative that resonates. The emotional weight of these stories often fosters a deeper understanding and compels others to reconsider their perceptions about mental health.
Ultimately, raising awareness and improving education about anxiety disorders can lead to more supportive communities, which are essential for recovery. When society collectively embraces the understanding that mental health is just as crucial as physical health, it paves the way for more compassionate treatment policies and nurtures an environment where individuals can flourish without the added burden of stigma.
Creating Supportive Environments
Understanding the Role of Physical Spaces
Creating supportive environments starts with recognizing the impact of physical surroundings on mental well-being. Research indicates that well-lit, organized, and comfortable spaces can significantly reduce anxiety levels. For individuals struggling with anxiety disorders, an environment that promotes calmness and order can serve as a sanctuary, providing them with the much-needed respite from daily stressors.
Ambient elements such as color schemes, noise levels, and even the arrangement of furniture can alter one's mood and sense of security. For instance, soft colors like blues and greens are often associated with tranquility, while cluttered spaces can evoke feelings of chaos. Therefore, ensuring that environments, whether at home, work, or educational settings, promote comfort and relaxation is essential for those dealing with anxiety disorders.
Fostering Emotional Support Networks
Supportive environments also encompass the social dimensions of mental health. Establishing strong emotional support networks is vital in providing individuals with anxiety disorders a platform to share their experiences. Family members, friends, and peers can play a crucial role in offering understanding and encouragement, which has proven beneficial in alleviating feelings of isolation that often accompany anxiety.
Furthermore, fostering communities where open discussions about mental health are normalized can help in reducing stigma. Creating spaces—both physical and virtual—where individuals can connect, share resources, and participate in group therapy sessions can empower them and provide numerous coping strategies. These connections can reinforce resilience and promote long-lasting healing through shared experiences.
Implementing Inclusive Policies and Practices
An essential aspect of creating supportive environments lies in the implementation of inclusive policies and practices that cater to the needs of individuals with anxiety disorders. Organizations and institutions should strive to develop frameworks that prioritize mental health awareness, accessibility, and responsive support systems. This includes providing mental health training for staff and establishing clear protocols for when someone is in distress.
Additionally, integrating flexibility in work or academic settings can greatly alleviate anxiety symptoms. For example, offering remote work options, accommodating breaks when needed, and allowing personalized support can create an adaptive environment that respects individual challenges. By prioritizing mental health in policy-making, we can pave the way for environments that not only support those with anxiety disorders but also foster overall well-being for everyone.
Resources for Help and Recovery
Support Groups for Anxiety Disorders
Support groups provide an essential platform for individuals grappling with anxiety disorders. These groups allow participants to share their experiences, fostering a sense of belonging and understanding among peers. Connection with others facing similar challenges can alleviate feelings of isolation, often a significant aspect of anxiety disorders.
Facilitated by trained mental health professionals or peer leaders, these gatherings instill hope and reinforce positive coping strategies. The discussions often center around techniques for managing anxiety, overcoming negative thoughts, and dealing with daily stressors, providing invaluable insights to members.
Furthermore, support groups cater to different demographics, including groups specifically for adolescents, women, or those dealing with acute anxiety. This segmentation helps address unique circumstances and allows participants to speak freely about issues pertinent to their experiences, leading to richer conversations.
Many support groups operate both in-person and virtually, ensuring accessibility for individuals who may find it challenging to attend physically due to anxiety. Online platforms augment convenience, making it easier for individuals to connect from the comfort of their homes while still benefiting from communal support.
Ultimately, these support systems play a critical role in the recovery journey. By sharing struggles and triumphs, individuals can find solace in their shared experiences and empower each other to take actionable steps towards managing their anxiety disorders confidently.
Professional Therapy Options
One of the most effective ways to address anxiety disorders is through professional therapy. Trained therapists use various therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which has proven highly effective. This method helps individuals identify and alter negative thought patterns contributing to their anxiety.
Therapy sessions provide a safe and confidential space to explore thoughts and feelings. The opportunity to discuss personal experiences openly with a professional can lead to breakthroughs and a deeper understanding of the disorder. Therapeutic relationships often develop into a cornerstone of recovery, providing ongoing support and guidance.
In addition to traditional talk therapy, other therapeutic modalities, such as mindfulness and exposure therapy, can also be adapted to help manage anxiety symptoms. These therapies aim to immerse individuals in the present moment or gradually expose them to anxiety-inducing situations, thereby reducing the impact of their anxieties over time.
Finding the right therapist is crucial in this process. Factors such as specialization, therapeutic approach, and personal comfort level can greatly influence the effectiveness of therapy. It's important for individuals to interview potential therapists to ensure a good fit before commencing treatment.
Lastly, therapy is not just a temporary fix. Many individuals find that ongoing sessions, even after learning to manage symptoms, provide valuable tools for navigating life’s challenges, empowering them long after their initial treatment ends.
Medication Management for Anxiety
For some individuals, medication can be an essential part of managing anxiety disorders. Prescribed by healthcare professionals, these medications often aim to balance brain chemicals that influence mood and stress response. Options are varied, including antidepressants, benzodiazepines, and beta-blockers, tailored to individual needs and circumstances.
Medication management requires careful consideration and regular monitoring by a healthcare provider to ensure effectiveness and minimize side effects. Communication between patient and provider is key to fine-tuning dosages and switching medications if necessary, particularly when finding the right treatment regime can take time.
Patients should be informed of potential side effects and the importance of adherence to their prescribed regimen. An informed approach strengthens the relationship between the patient and the psychiatrist, creating a collaborative atmosphere for effective management of anxiety disorders.
It's essential to remember that medication is most effective when combined with therapy and lifestyle changes. Relying solely on pharmaceutical solutions without addressing underlying issues or engaging in self-help strategies may yield limited results long-term.
Ultimately, medication can provide significant relief for those struggling with anxiety, helping to facilitate the ability to participate more fully in therapeutic practices, social activities, and daily living. Open discussions about medication with professionals are crucial elements in enhancing recovery strategies.
Holistic Approaches for Anxiety Recovery
Many individuals opting for a comprehensive recovery strategy often turn to holistic approaches. These methods include practices such as yoga, meditation, acupuncture, and nutritional counseling, all aimed at promoting overall well-being and alleviating anxiety symptoms. Adopting these strategies can lead to a more balanced lifestyle, which is beneficial for mental health.
Yoga, for instance, combines physical movement with breath work, which can significantly influence stress reduction and emotional balance. Many practitioners find that incorporating yoga into their daily routine enhances emotional regulation and creates a greater connection with their body.
Meditation, particularly mindfulness meditation, has gained popularity as a powerful tool for managing anxiety. Regular practice encourages individuals to focus on the present moment, creating space to observe stressful thoughts without judgment and promoting a sense of calm.
Moreover, the role of nutrition in mental health cannot be understated. A balanced diet rich in nutrients can support brain function and mood regulation. Consulting with a nutritionist may help individuals identify foods that can improve their mental well-being and energy levels.
Lastly, embracing alternative therapies like acupuncture may offer additional benefits for anxiety reduction. Many individuals report experiencing significant reductions in anxiety symptoms after sessions, citing the relaxing effects of this therapeutic practice. By exploring various holistic methods, individuals can find personalized paths to recovery that align with their values and preferences.
Educational Resources and Literature
Educating oneself about anxiety disorders is vital in fostering understanding and establishing effective coping mechanisms. Numerous books, articles, documentaries, and online resources delve into the complexities of anxiety, offering essential insights and strategies for managing symptoms. Reading about others’ experiences can provide validation and hope for recovery.
Accessibility to information from reputable sources, such as mental health organizations and universities, can augment a person's understanding of anxiety disorders. This knowledge ultimately empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their treatment and recovery journey.
Online platforms also provide webinars and workshops, connecting individuals with expert opinions and practical advice. These educational opportunities can help demystify anxiety disorders, reducing stigma and encouraging open discussions within families and communities.
Furthermore, podcasts focusing on mental health topics have surged in popularity, providing easily digestible content for those seeking to learn about anxiety on-the-go. Listening to conversations featuring experts and individuals who have experienced anxiety disorders can nurture a sense of community and shared experience.
Lastly, local libraries and mental health clinics often have resource lists featuring recommended literature and guides, offering a multitude of avenues to widen one’s knowledge base. This wealth of information can serve as an anchor in navigating the recovery process and instilling a sense of confidence in managing anxiety and its effects on daily life.